Table of Contents
1、 Disruptive breakthroughs in the field of diagnosis
1. Wireless Capsule Endoscopy (WCE)
Disruptive: Completely solve the blind spot of small intestine examination and replace the painful traditional push type small intestine endoscope.
Technical upgrade:
AI assisted diagnosis: such as Given Imaging's PillCam SB3, equipped with adaptive frame rate technology, AI automatically marks bleeding points/ulcers (sensitivity>90%).
Magnetic controlled capsule gastroscopy (such as NaviCam from Anhan Technology): precise control of capsule rotation by external magnetic field enables comprehensive examination of the stomach, and the accuracy of early screening for gastric cancer is comparable to traditional gastroscopy (>92%).
Biopsy capsule (experimental stage): such as the micro clamp capsule developed by the South Korean research team, which can be remotely controlled for sampling.
2. Intelligent staining endoscopic technology
Narrowband Imaging (NBI):
Principle: 415nm/540nm narrow spectrum light enhances mucosal vascular contrast.
Disruptive effect: The detection rate of early gastric cancer has increased from 45% in conventional white light endoscopy to 89% (according to the Japanese JESDS standard).
Linkage Imaging (LCI):
Advantage: Fuji's patented algorithm has a 30% higher recognition rate for superficial gastritis and intestinal metaplasia compared to NBI.
3. Confocal Laser Endoscopy (pCLE)
Technical highlight: The probe diameter is only 1.4mm (such as the Cellvizio system), achieving real-time cell level observation at a magnification of 1000 times.
Clinical value:
Instant identification of Barrett's esophageal dysplasia to avoid repeated biopsies.
The negative predictive value for monitoring ulcerative colitis carcinogenesis is 98%.
2、 Revolutionary solutions in the field of treatment
1. Endoscopic mucosal dissection (ESD)
Technological breakthrough:
Bipolar electric knife (such as FlushKnife BT): saline infusion reduces the risk of perforation.
CO ₂ laser assisted: precise vaporization of submucosal layer, bleeding volume<5ml.
Clinical data:
The curative resection rate for early gastric cancer is over 95%, and the 5-year survival rate is comparable to traditional surgery (over 90%).
The DDW study in the United States shows that the overall resection rate of colon lateral developmental tumors (LST) larger than 3cm is 91%.
2. Endoscopic surgery via natural cavity (NOTES)
Representative surgical techniques:
Transgastric cholecystectomy: Olympus TriPort multi-channel endoscope is used, and food is consumed 24 hours after surgery.
Transrectal appendectomy: South Korean team reports the world's first successful case in 2023.
Core equipment: Full layer closed clamp (such as OTSC) ®) Resolve the biggest challenge of NOTES - cavity closure.
3. Endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR)
Indication breakthrough: Treatment of gastric stromal tumors (GIST) originating from the intrinsic muscle layer.
Technical key: Laparoscopic endoscopic combined surgery (LECS) ensures safety.
New suture instruments (such as OverStitch) ™) Realize full layer stitching.
3、 Integrated scheme for tumor diagnosis and treatment
1. Endoscopic guided radiofrequency ablation (EUS-RFA)
Treatment of pancreatic cancer: 19G puncture needle was introduced into the RF probe, and the local control rate was 73% (≤ 3cm tumor).
Compared to open surgery, the complication rate has decreased from 35% to 8%. Liver cancer application: Duodenal ablation of tumors in the caudate lobe of the liver.
2. Fluorescent navigation endoscopic surgery
ICG labeling technology: Preoperative intravenous injection, near-infrared endoscopy (such as Olympus OE-M) to display lymphatic drainage range. The completeness of lymph node dissection during gastric cancer surgery is improved by 27%.
Targeted fluorescent probes (experimental stage): such as MMP-2 enzyme responsive probes, specifically label small metastases.
4、 Innovation in Emergency and Critical Care Scenarios
1. Acute gastrointestinal bleeding
Hemospray hemostatic powder:
Under endoscopic spraying, a mechanical barrier is formed, with a hemostasis rate of 92% (Forrest Grade Ia bleeding).
Over The Scope Clip (OTSC):
O Bear Claw design, closing ulcer perforation with a diameter of up to 3cm.
2. Endoscopic decompression for intestinal obstruction
Self expanding metal bracket (SEMS):
Bridge therapy for malignant colon obstruction, with a relief rate of over 90% within 48 hours.
New laser cutting brackets (such as Niti-S) ™) Reduce the shift rate to 5%.
5、 Future technological directions
1. AI real-time decision-making system:
Like Cosmo AI ™ Automatically recognize the withdrawal speed during colonoscopy examination, reducing adenoma missed diagnosis (ADR increased by 12%).
2. Degradable capsule endoscope:
Magnesium alloy frame+polylactic acid shell, dissolved in the body within 72 hours after inspection.
3. Micro robot endoscope:
The origami robot from ETH Zurich can be developed into a surgical platform for sampling.
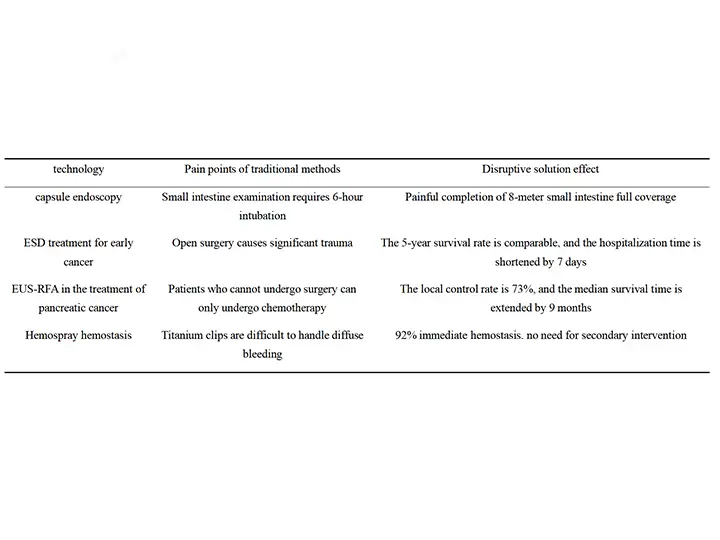
Clinical Effect Comparison Table
Implementation considerations
Grassroots hospitals: Priority should be given to equipping magnetic control capsule gastroscopy+OTSC hemostatic system.
Third class hospital: It is recommended to establish an ESD+EUS-RFA minimally invasive cancer treatment center.
Research direction: Focus on AI pathology real-time analysis+degradable robotic endoscopy.
These technologies are reconstructing the diagnosis and treatment paradigm of gastrointestinal diseases through three major paths: non-invasive, precise, and intelligent. Actual application needs to be combined with individual patient differences and accessibility of medical resources.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS