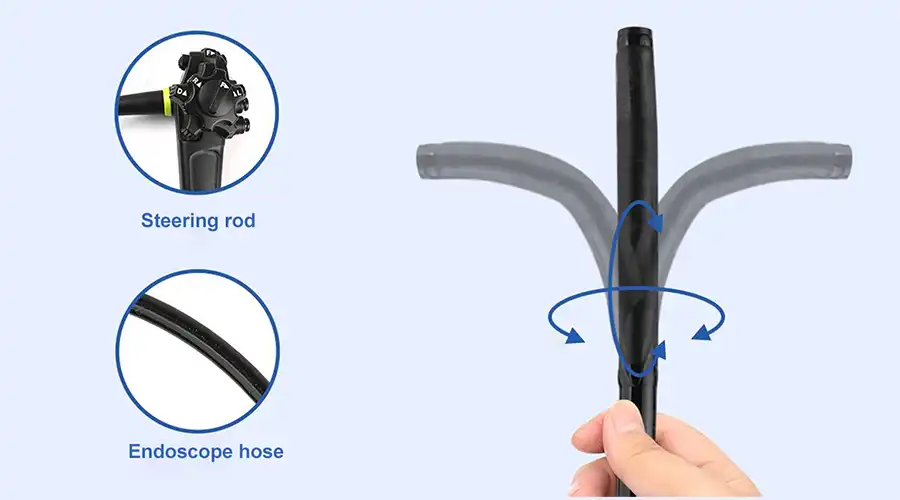
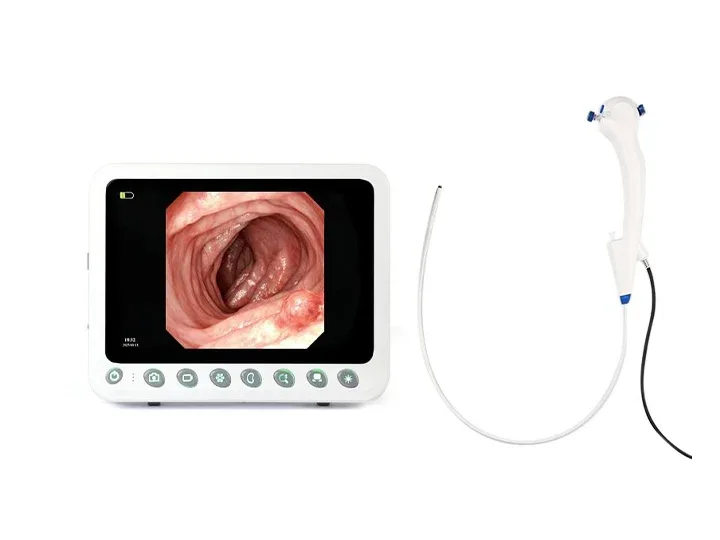
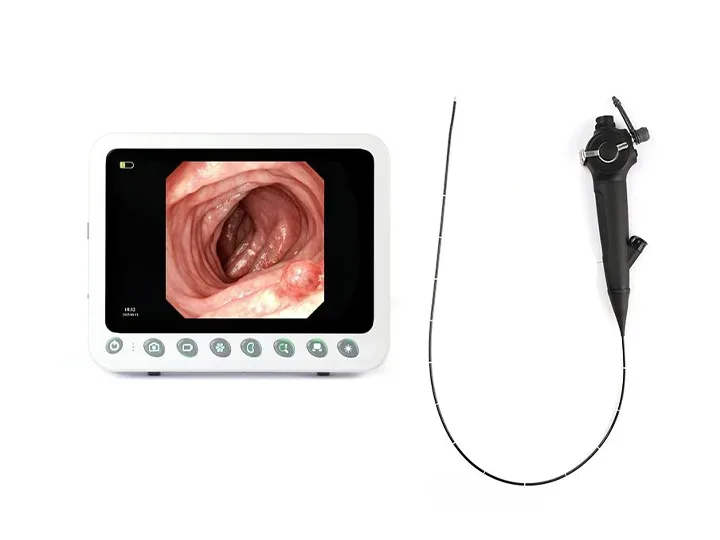
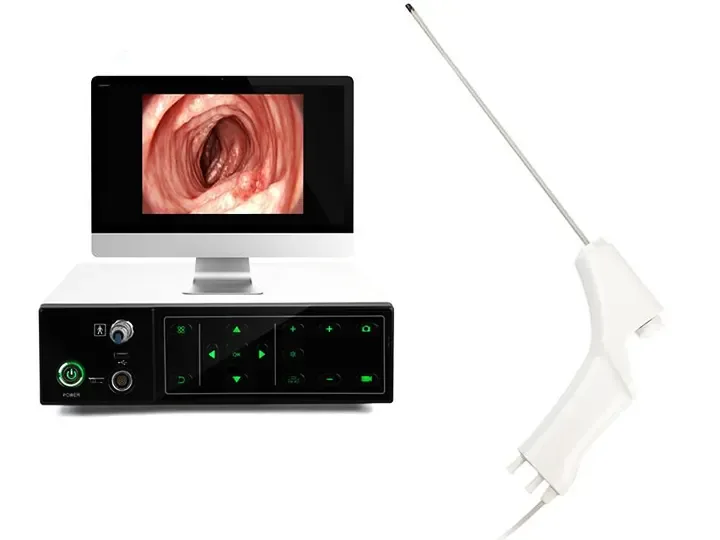
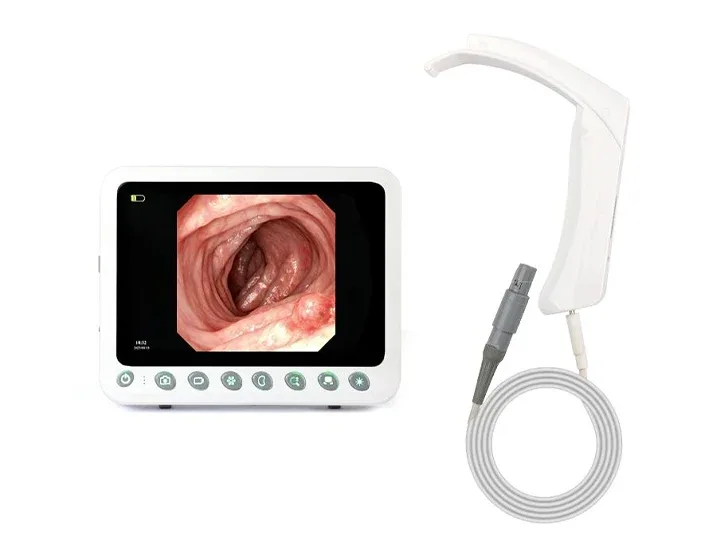
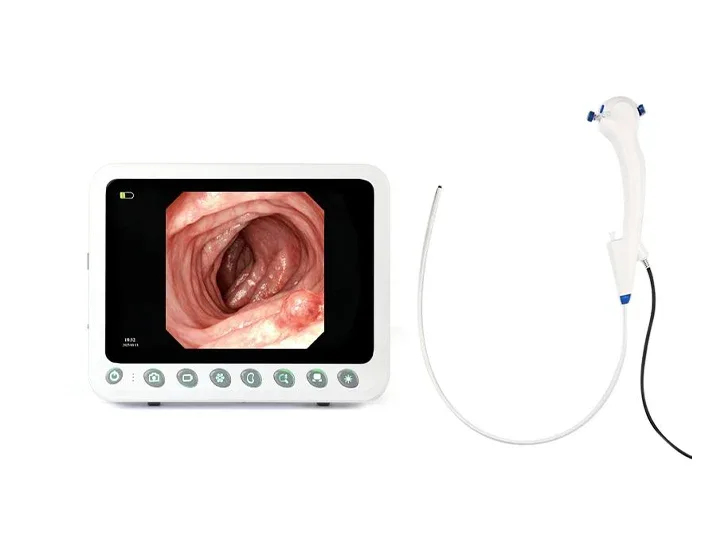
360° no-blind-angle steering
360° rotation left and right, effectively eliminating blind spots;
Upper angle ≥ 210°
Lower angle ≥ 90°
Left angle ≥ 100°
Right angle ≥ 100°
Wide Compatibility
Wide compatibility:Ureteroscope, Bronchoscope, Hysteroscope, Arthroscope, Cystoscope, Laryngoscope, Choledochoscope
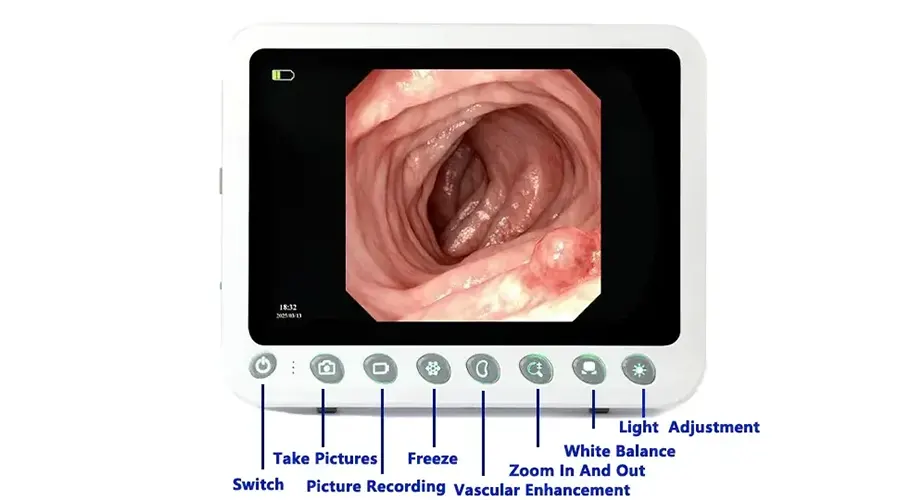
Capture
Freeze
Zoom In/Out
Image Settings
REC
Brightness: 5 levels
WB
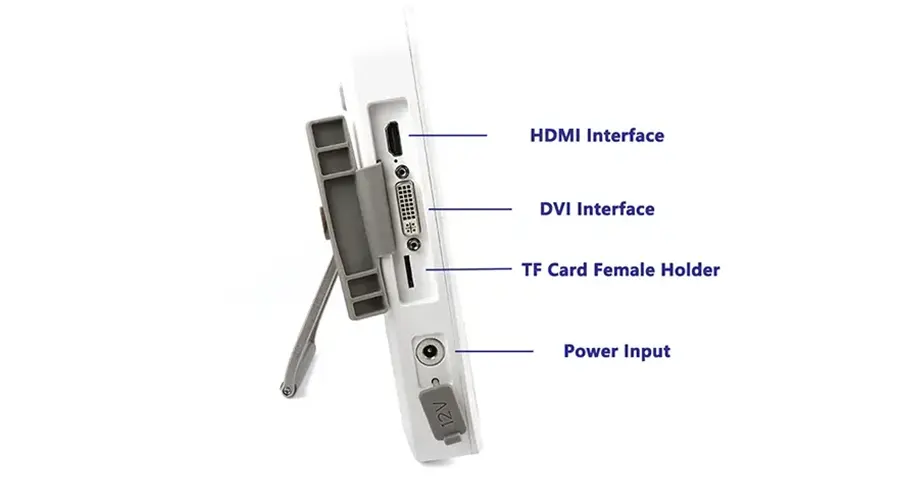
Multi-Interface

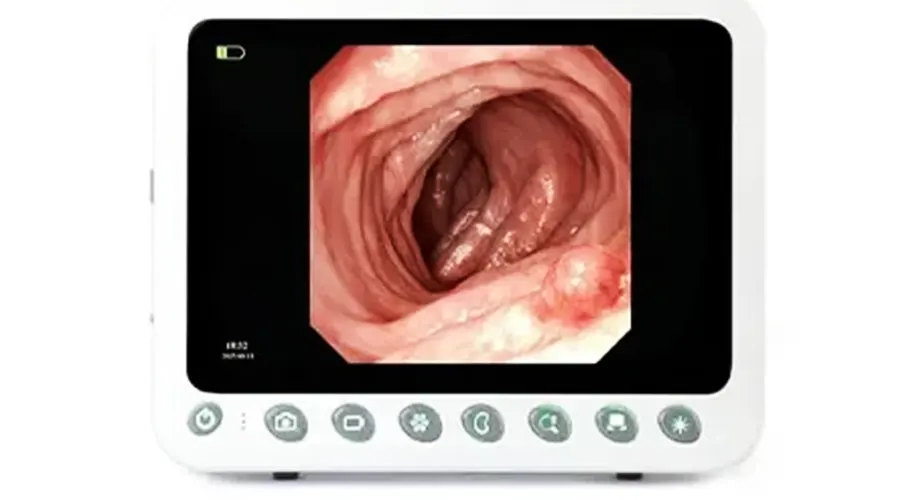
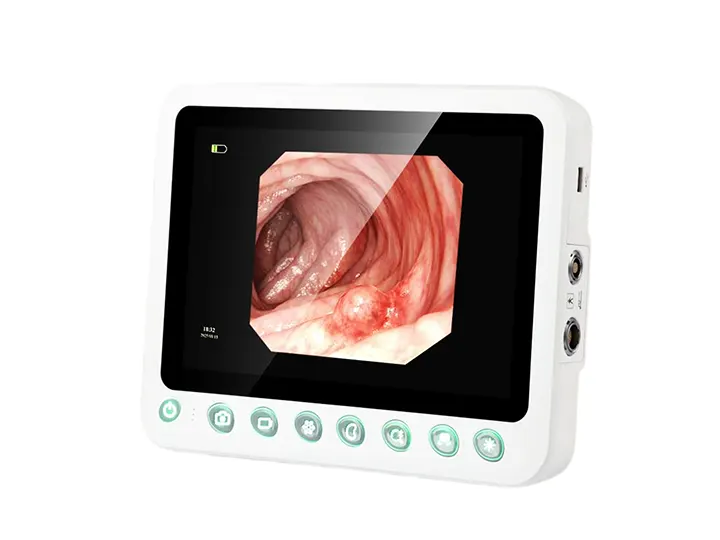
1280×800 Resolution Image Clarity
10.1" Medical Display,Resolution 1280×800,
Brightness 400+,High-definition
High-definition Touchscreen Physical Buttons
Ultra-responsive touch control
Comfortable viewing experience
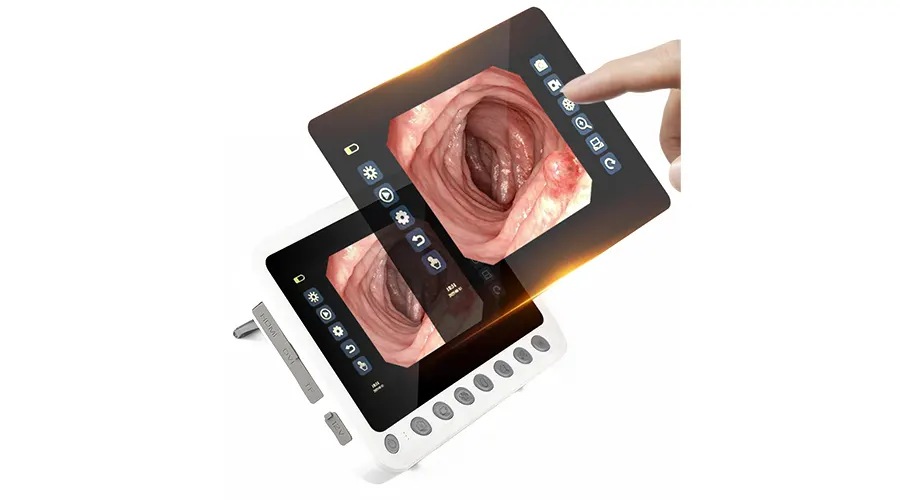

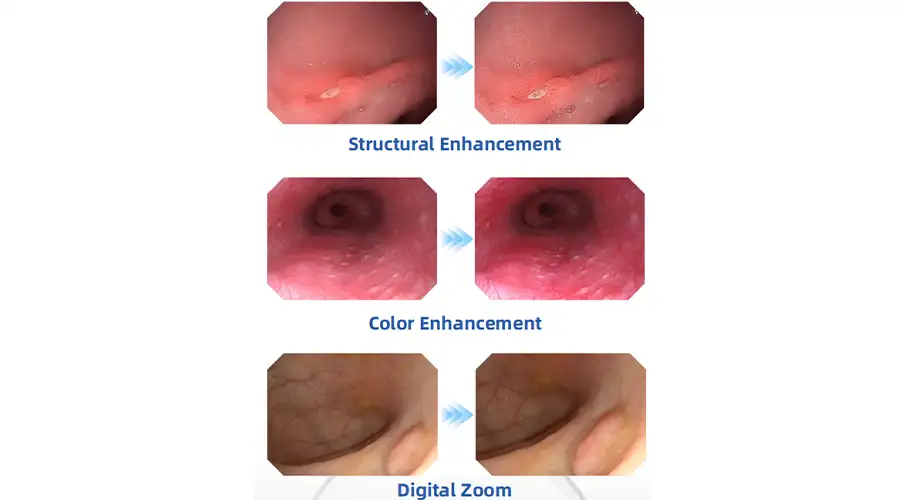
Clear Visualization For Confident Diagnosis
HD digital signal with structural enhancement
and color enhancement
Multi-layer image processing ensures every detail is visible
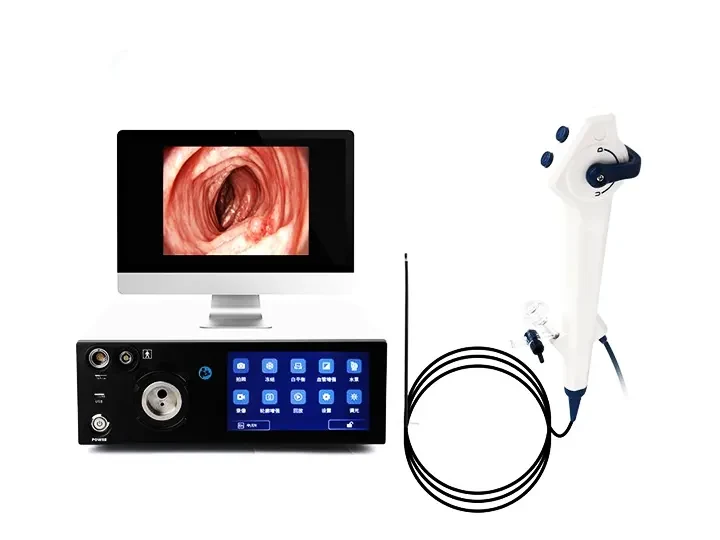
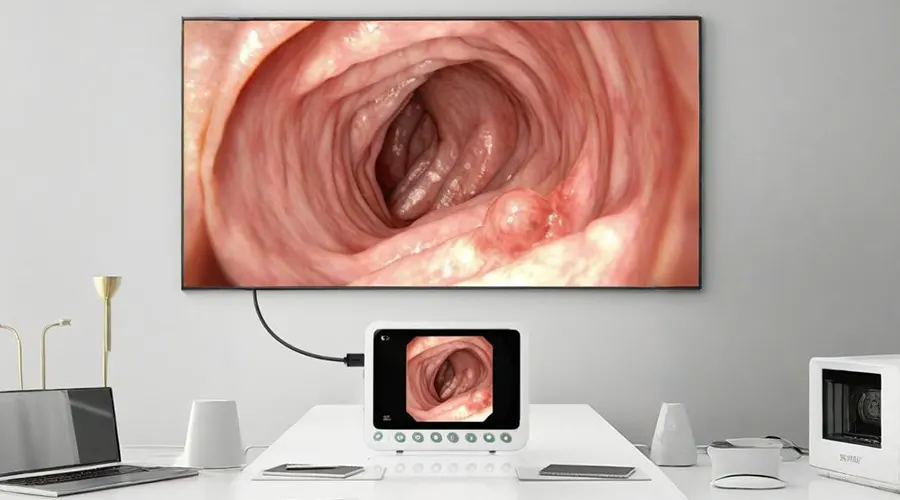
Dual-screen Display For Clearer Details
Connect via DVI/HDMI to external monitors - Synchronized
display between 10.1" screen and large monitor
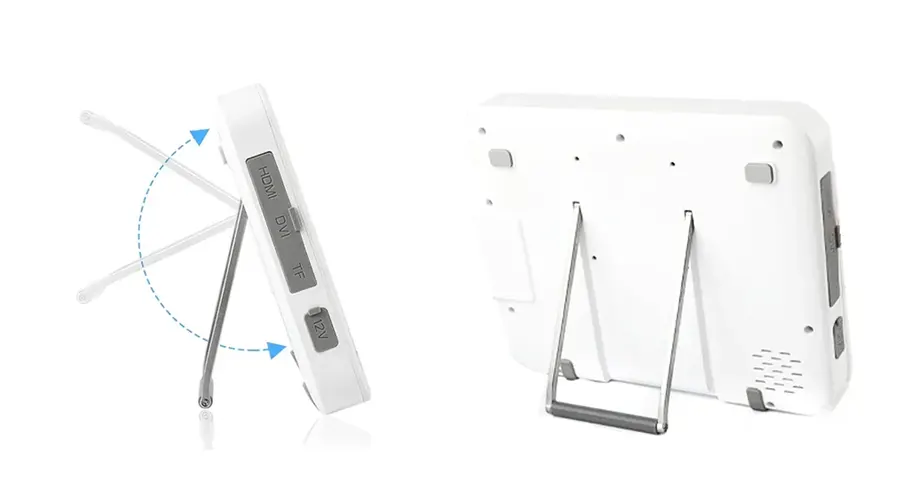

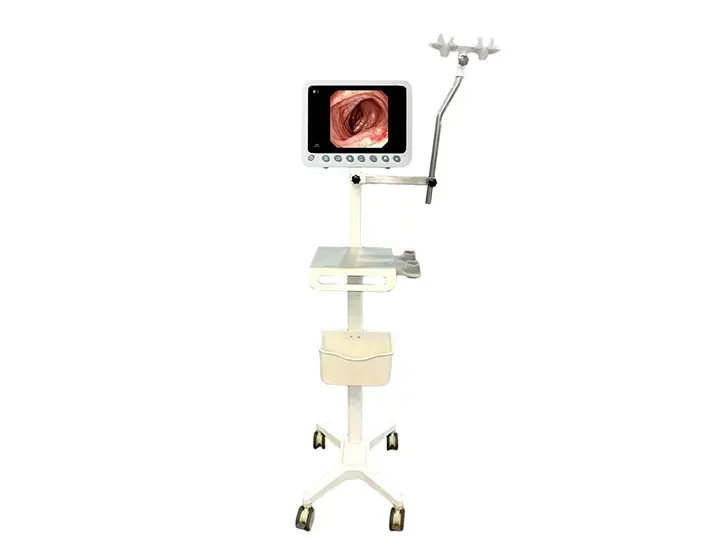
Adjustable Tilt Mechanism
Slim and lightweight for flexible angle adjustment,
Adapts to various working postures (standing/sitting).
Extended Operation Time
Ideal for POC and ICU examinations - Provides
doctors with convenient and clear visualization
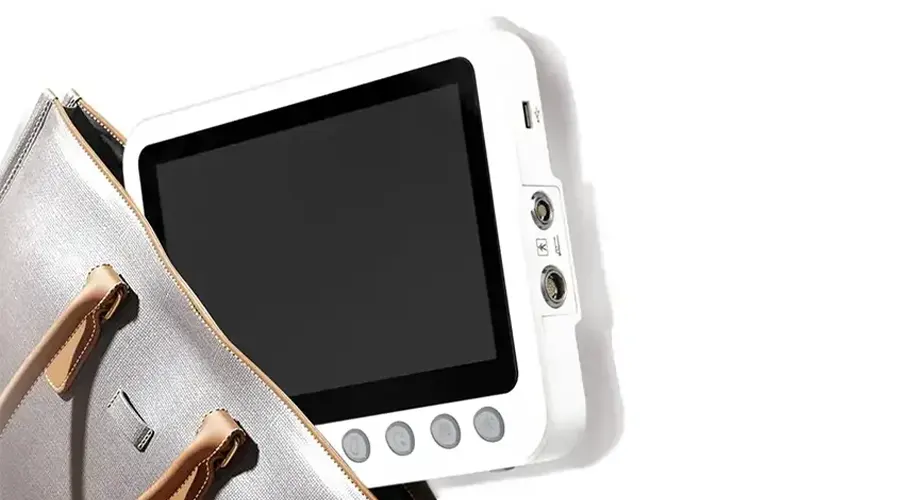

Portable Solution
Ideal for POC and ICU examinations - Provides
doctors with convenient and clear visualization
Bronchoscope is a core tool for the diagnosis and treatment of modern respiratory diseases. It realizes a full-process solution from diagnosis to treatment through minimally invasive, visual and precise technical means. The following is an introduction from five dimensions: technical principle, clinical application, equipment type, operation process and development trend.
1. Technical principle and equipment composition
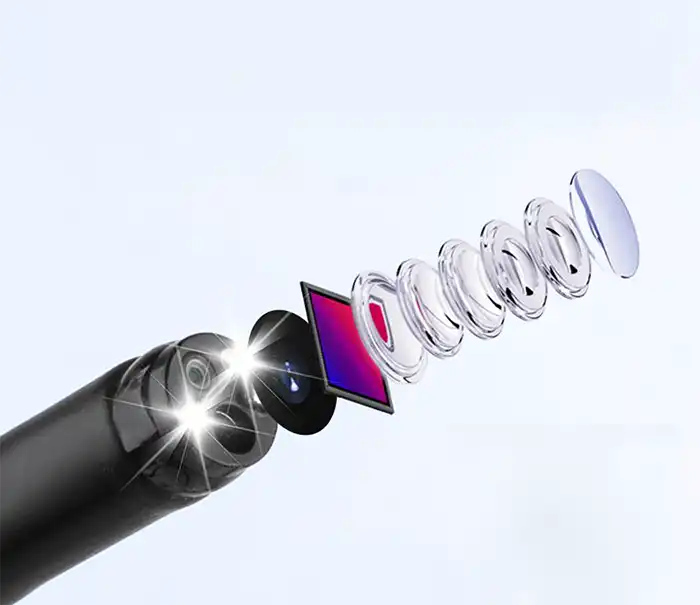
Bronchoscopy is a flexible or rigid endoscope that enters the trachea, bronchi and more distal airways through the mouth/nose. The main components include:
Mirror body: ultra-fine diameter (2.8~6mm), bendable design, adaptable to complex airway anatomical structure.
Imaging system: high-definition CMOS/fiber optic image transmission, supporting white light, NBI (narrow band imaging), fluorescence and other modes.
Working channel: can insert biopsy forceps, brushes, cryoprobes, laser optical fibers and other treatment tools.
Auxiliary system: suction device, irrigation equipment, navigation positioning (such as electromagnetic navigation EBUS).
2. Clinical application scenarios
1. Diagnostic field
Lung cancer screening: Detect early central lung cancer and guide biopsy (TBLB/EBUS-TBNA).
Infectious diseases: Obtain sputum/bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) for pathogen detection.
Airway assessment: Diagnosis of stenosis, fistula, foreign body, tuberculosis and other lesions.
2. Treatment field
Foreign body removal: Emergency treatment of children/adults who accidentally aspirate foreign bodies.
Stent placement: Relieve airway stenosis caused by malignant tumors or scars.
Ablation therapy: Laser/cryosurgery/argon gas knife to remove tumors or granulomas.
Hemostasis treatment: Electrocoagulation or drug spraying to control severe hemoptysis.
3. Equipment type and selection
Type Features Applicable scenarios
Fiber bronchoscope Flexible mirror body, thin diameter (2.8~4mm) Children, peripheral airway exploration
Electronic bronchoscope High-definition imaging, support NBI/magnification function Early cancer screening, precise biopsy
Hard bronchoscope Large channel (6~9mm), support complex surgery Massive hemoptysis, stent placement, laser ablation
Ultrasound bronchoscope (EBUS) Combined with ultrasound scanning, evaluate mediastinal lymph nodes Lung cancer staging (N1/N2 lymph node biopsy)
4. Operation process (taking diagnostic bronchoscope as an example)
Preoperative preparation
The patient fasts for 6 hours, local anesthesia (lidocaine spray) or general anesthesia.
ECG monitoring (SpO₂, blood pressure, heart rate).
Path of entry
Nasal (more comfortable) or oral (wider channel).
Examination steps
Observe the glottis, trachea, carina, left and right main bronchi and subsegmental branches in turn.
After the lesion is found, biopsy, brushing or lavage is performed.
Postoperative treatment
Monitor for complications such as pneumothorax and bleeding, and do not eat or drink for 2 hours.
V. Technology Frontiers and Development Trends
AI-assisted
AI marks suspicious lesions (such as carcinoma in situ) in real time to reduce the rate of missed diagnosis.
Electromagnetic navigation bronchoscope (ENB)
Reach peripheral lung nodules (<1cm) as accurately as "GPS".
Disposable bronchoscope
Avoid cross infection, suitable for infectious diseases such as tuberculosis and COVID-19.
Robotic bronchoscope
The robot arm operates stably to improve the success rate of distal biopsy (such as Monarch platform).

Summary
Bronchoscopic technology is developing in a more accurate, intelligent and minimally invasive direction, and its core value lies in:
✅ Early diagnosis - discover hidden lesions of diseases such as lung cancer and tuberculosis.
✅ Precision treatment - replace thoracotomy and directly treat airway lesions.
✅ Rapid recovery - most examinations can be completed as outpatients and activities can be resumed on the same day.
In the future, with the integration of molecular imaging and robotic technology, bronchoscopy will become the core platform for the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory diseases.
Faq
-
What are the risks of incomplete disinfection of endoscopic equipment?
It may cause cross infection and spread pathogens (such as hepatitis B, HIV, Helicobacter pylori, etc.). Strictly following the disinfection process (such as pre-cleaning, enzyme washing, disinfectant immersion or high-temperature sterilization) is the key. Some endoscopes need to be sterilized using ethylene oxide or hydrogen peroxide low-temperature plasma.
-
What are the common faults of endoscopes? How to maintain them?
Faults: Blurred image (lens contamination/sensor damage), water leakage (seal aging), lighting failure (fiber breakage). Maintenance: Clean immediately after use to prevent secretions from drying and clogging the pipes. Check the seal regularly to prevent liquid from penetrating and damaging the circuit. Avoid excessive bending (soft mirror) or impact (hard mirror).
-
What are the advantages of endoscopic surgery (such as laparoscopy) over open surgery?
It has small trauma, less bleeding, quick recovery and small scars, but it depends on the doctor's operating skills and equipment performance.
-
What are the advantages and disadvantages of disposable endoscopes compared to traditional reusable endoscopes?
Advantages: No cross infection, no need for disinfection, suitable for emergency or high-risk patients. Disadvantages: High cost, environmental issues (increased medical waste), image quality may be slightly lower.
Latest articles
-
How XBX Cystoscope Supplier Ensures Quality and Precision for Hospital Procurement
Discover how the XBX Cystoscope Supplier provides hospitals with high-precision, OEM-ready endoscopy systems built for reliability, safety, and consistent imagi...
-
How XBX Bronchoscope Factory Delivers Reliable OEM Systems
Discover how the XBX Bronchoscope Factory ensures quality and reliability through advanced OEM manufacturing, optical precision, and strict quality control.
-
How XBX Laparoscope Minimizes Surgical Trauma in Abdominal Surgery
Discover how the XBX Laparoscope reduces surgical trauma through precision imaging, minimal incisions, and faster recovery in modern abdominal procedures.
-
How XBX Hysteroscope Detects and Removes Uterine Polyps
Discover how the XBX Hysteroscope enables precise detection and removal of uterine polyps, improving accuracy, safety, and comfort in women’s health care.
-
What Is an XBX Flexible Ureteroscope for Stone Removal?
Learn how the XBX flexible ureteroscope improves access, visibility, and efficiency in ureteral stone management with 4K imaging and ergonomic control.
Recommended products
-
Endoscope Equipment for ENT Specialists
Top-quality endoscope equipment for ENT specialists. High precision, durability, and advanced tech for accurate diagnosi...
-
Medical Hysteroscopy Equipment
Medical Hysteroscopy Equipment delivers HD imaging for uterine endoscopy medical endoscopes, enhanci
-
Medical laryngoscope equipment
Comprehensive introduction to laryngoscope equipmentAs the core tool for upper respiratory tract dia
-
Medical Bronchoscope machine
Bronchoscopy is a core tool for the diagnosis and treatment of modern respiratory diseases. It provi