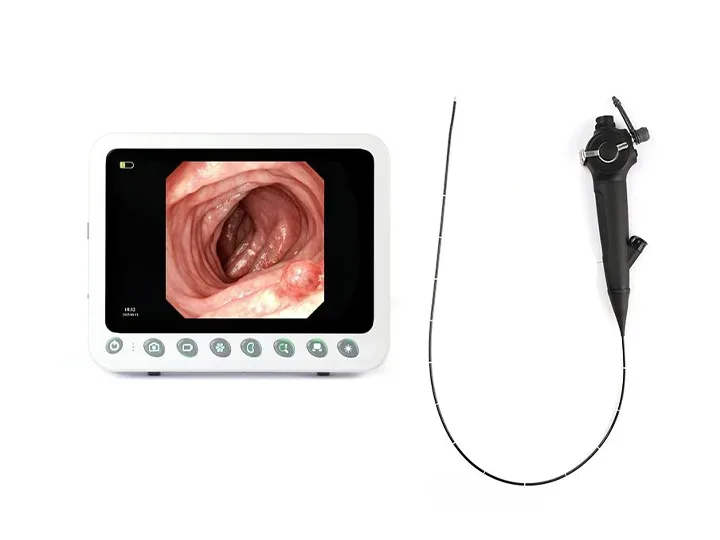
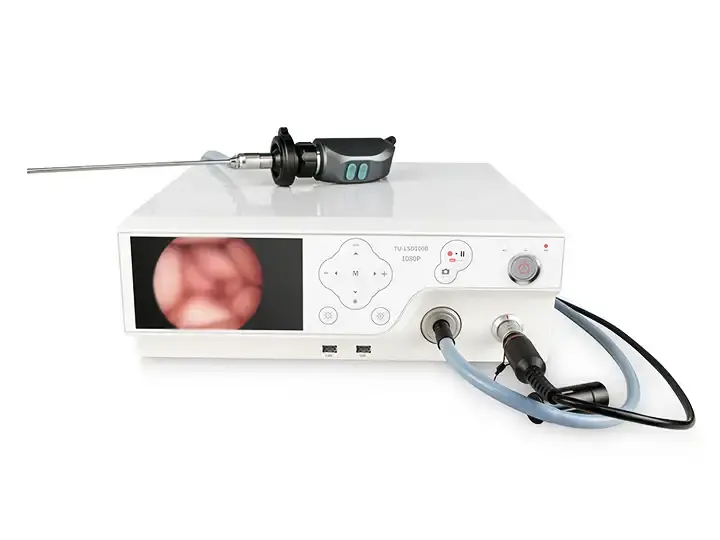
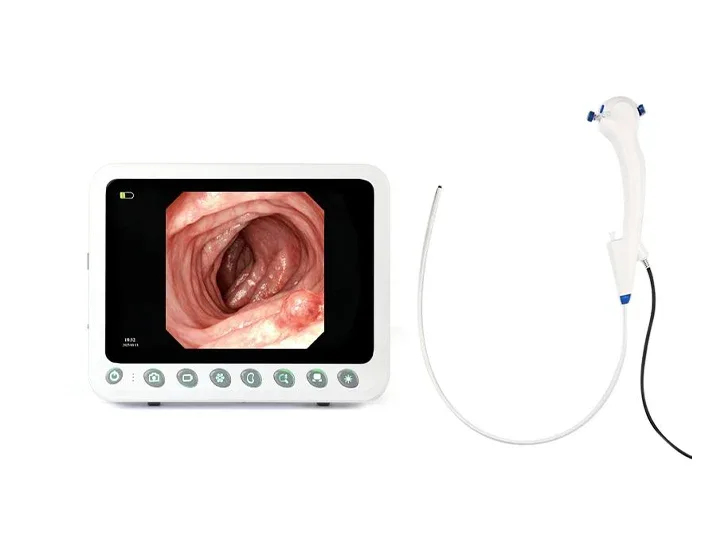
Gastrointestinal Endoscope Host
This host delivers 4K UHD imaging for gastrointestinal medical endoscopes, enhancing visualization during diagnostic procedures. Its compact design supports efficient clinical workflows for endoscope medical examinations.
Core Specifications
4K Ultra-HD imaging (3840×2160 resolution)
Physical control knobs for sterile operation
Integrated carrying handle for mobility
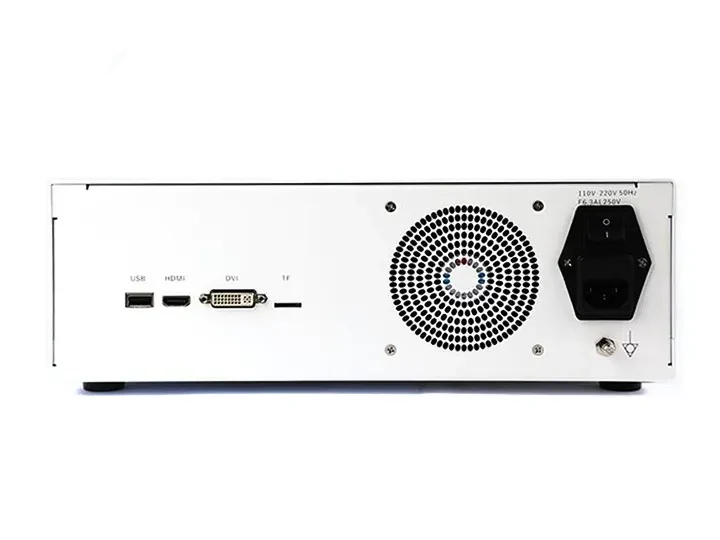
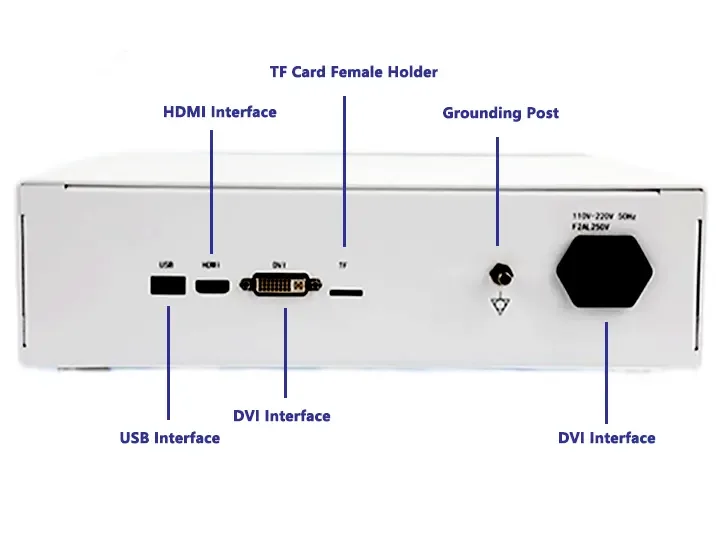
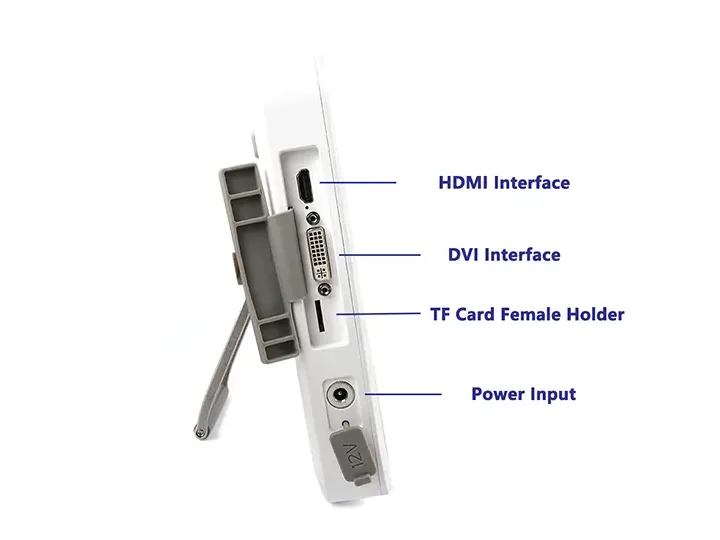
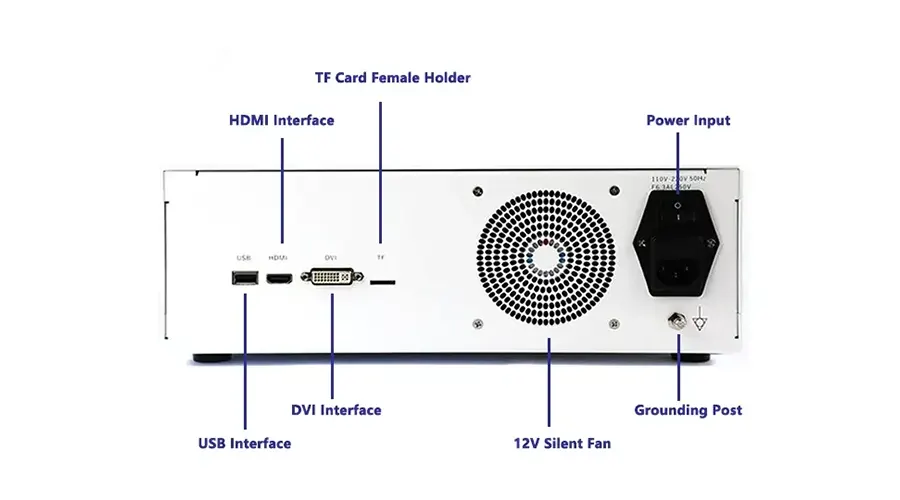
HDMI/USB 3.0 video output interfaces
4+ hours continuous operation
Clinical Applications
Tissue examination: Clear visualization of mucosal surfaces
Diagnostic procedures: Enhanced detection of abnormalities
Operational efficiency: Streamlined setup for examinations
Key Advantages
Reliable imaging performance for gastrointestinal medical endoscopes
User-friendly interface for clinical environments
Stable operation in endoscopy settings
Designed specifically for gastrointestinal endoscopy practice, this host prioritizes essential imaging functions with clinical workflow efficiency.

Strong Compatibility
Compatible with Gastrointestinal Endoscopes, Urological Endoscopes, Bronchoscopes, Hysteroscopes,Arthroscopes, Cystoscopes, Laryngoscopes, Choledochoscopes, Strong Compatibility.
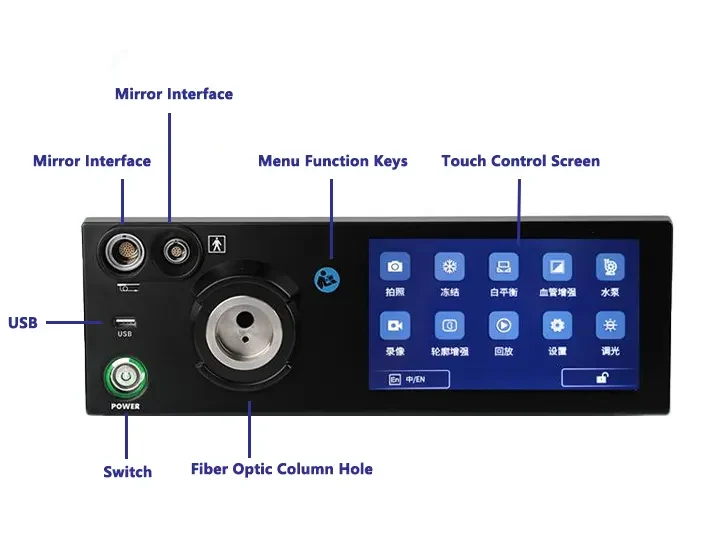
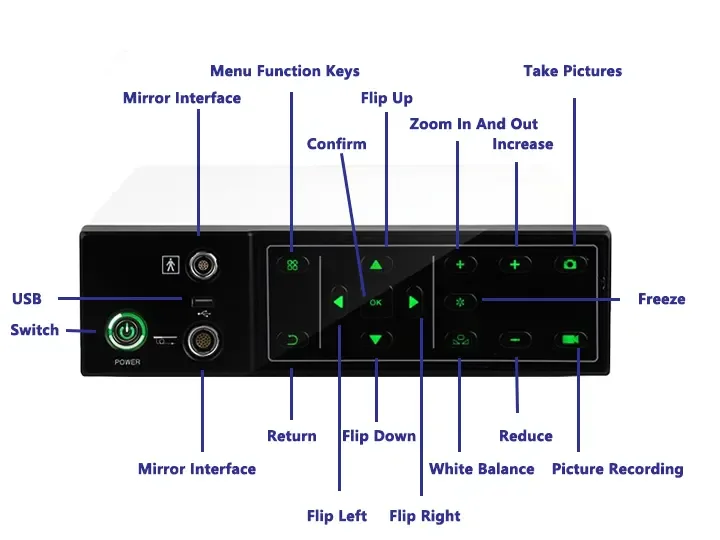
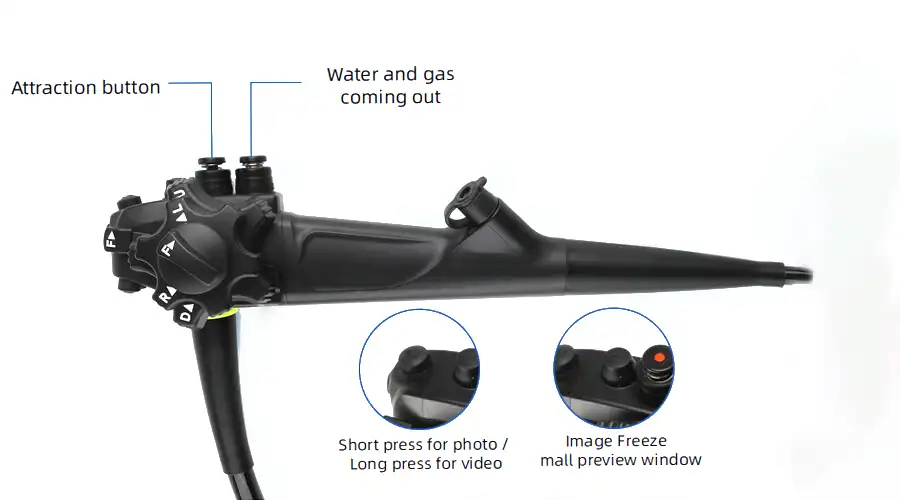
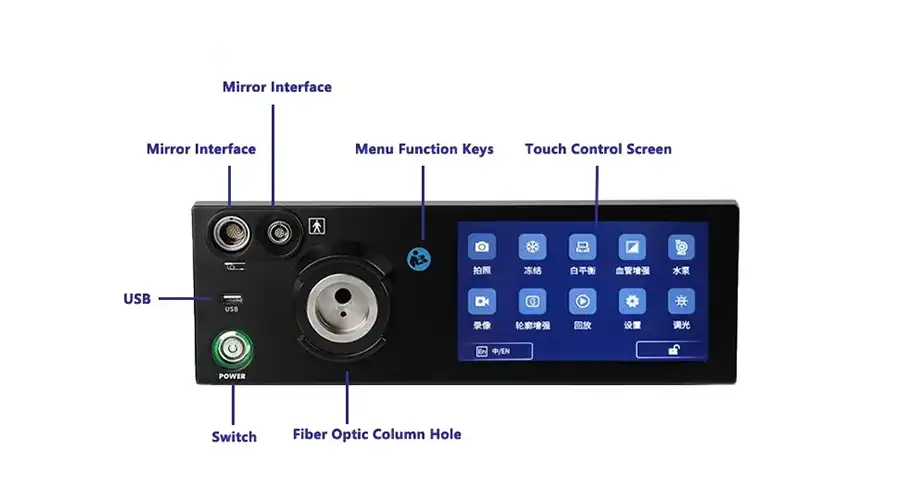
Capture
Freeze
Zoom In/Out
Image Settings
REC
Brightness: 5 levels
WB
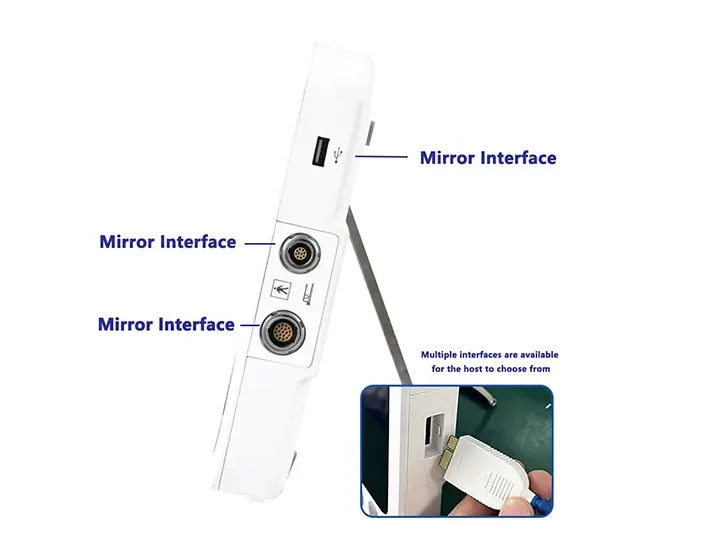
Multi-Interface
1920 1200 Pixel Resolution Image Clarity
With Detailed Vascular Visualization
for Real-Time Diagnosis
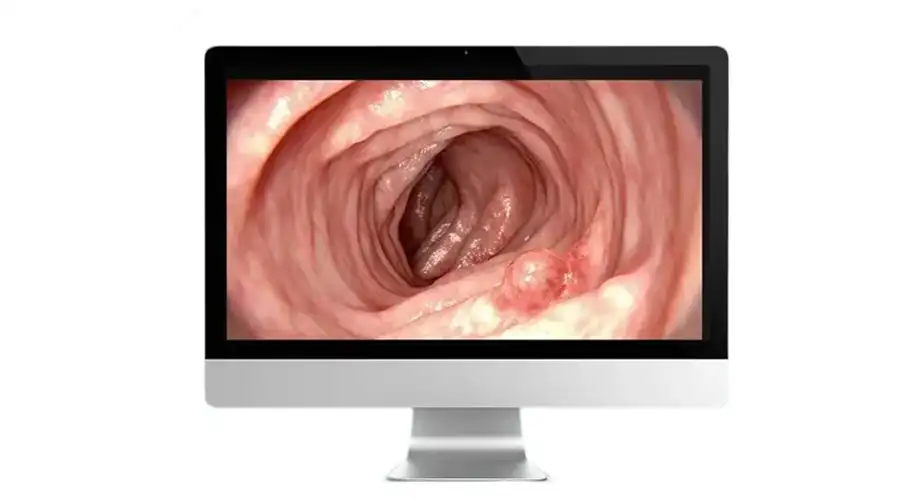

High Sensitivity High-Definition Touchscreen
Instant Touch Response
Eye-comfort HD display
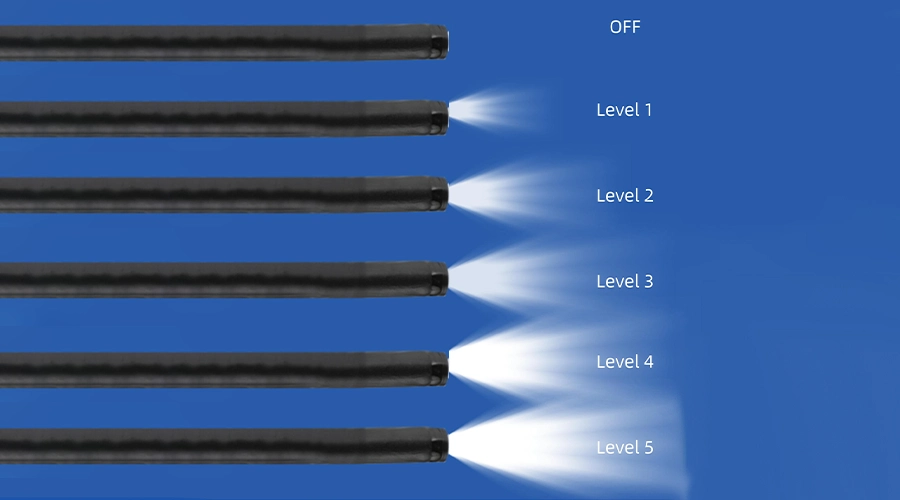
Dual LED Lighting
5 adjustable brightness levels, Brightest at Level 5
gradually dimming to OFF


Brightest at Level 5
Brightness: 5 levels
OFF
Level 1
Level 2
Level 6
Level 4
Level 5
Lightweight handpiece
Superior handling for effortless operation
Newly upgraded for exceptional stability
Intuitive button layout enables
precise and convenient control
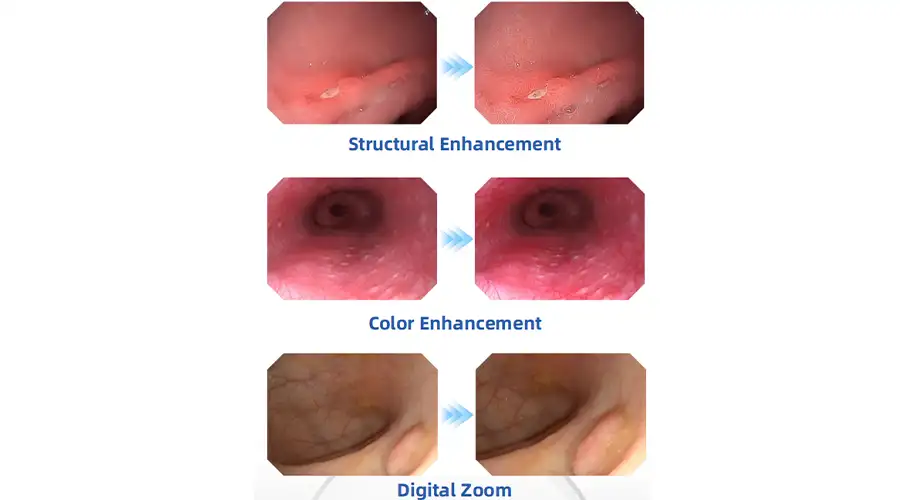
Vision Clarity for Confident Diagnosis
High-definition digital signals combined
with structural enhancement and color
enhancement technologies ensure
every image is crystal clear
The gastrointestinal endoscope host is the core equipment for digestive endoscopy diagnosis and treatment. It integrates image processing, light source control, data management and other functions, and supports the inspection and treatment of soft endoscopes such as gastroscopes and colonoscopes. The following is a comprehensive analysis from five dimensions: working principle, core function, clinical application, technical advantages and development trend.
1. Working principle
Optical imaging system
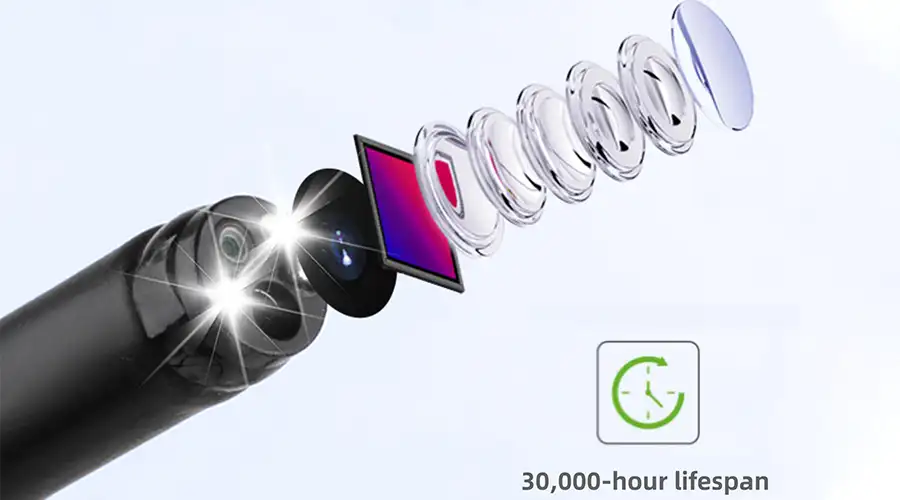
Electronic endoscope imaging: The end CMOS sensor (such as Sony IMX586) collects images with a resolution of 4K (3840×2160), a pixel size as low as 1.0μm, and supports a wide-angle field of view of 90°~120°.
Spectroscopic technology:
Narrow band imaging (NBI): 415nm (mucosal surface blood vessels) and 540nm (deep blood vessels) dual-band enhanced contrast, early gastric cancer detection rate increased by 25%.
Confocal laser (CLE): 488nm laser scanning achieves 1000 times magnification, in vivo pathology-level imaging (resolution 1μm).
Light source and illumination
Xenon/LED hybrid light source: color temperature 5500K (simulating natural light), automatic brightness adjustment (10,000~150,000 lux), support white light/NBI/AFI (autofluorescence) mode switching.
Infrared imaging: with ICG fluorescence angiography, real-time display of lymphatic drainage and tumor boundaries (sensitivity up to 95%).
Image processing engine
Using dedicated ISP chips (such as Fuji RELI+), real-time noise reduction (signal-to-noise ratio>40dB), HDR enhancement (dynamic range 80dB) and AI-assisted annotation (polyp recognition accuracy 98%).
2. Core functions
High-definition diagnostic function
4K/8K ultra-high-definition imaging: can identify type IIc early gastric cancer with a diameter of <5mm.
Magnifying endoscopy (ME-NBI): optical magnification 80 times + electronic magnification 150 times, combined with JNET classification to evaluate the nature of lesions.
Intelligent auxiliary system
AI real-time analysis:
Automatically identify Barrett's esophagus (CADx system, AUC 0.92), early colorectal cancer (ENDOANGEL system).
Bleeding risk assessment (Forrest classification) and automatic screenshot recording.
Three-dimensional reconstruction: Synthesize 3D model of submucosal tumor based on multi-frame images (accuracy 0.1mm).
Treatment integration
Multi-channel control: Supports simultaneous operation of high-frequency electrosurgical knife (EndoCut mode), argon gas knife (APC), and mucosal injection (such as glycerol fructose).
Pressure feedback: Intelligent gas/water injection system (pressure range 20~80mmHg) to avoid intestinal perforation.
III. Clinical application value
Diagnostic field
Early cancer screening: ESD preoperative boundary marking error <1mm (NBI+magnifying endoscopy).
Inflammation assessment: Use CE (chromoendoscopy) to improve the consistency of ulcerative colitis activity interpretation (κ value increased from 0.6 to 0.85).
Treatment areas
Minimally invasive surgery:
EMR/ESD operation time is shortened by 30% (integrated electrocoagulation and water injection functions).
POEM for achalasia, postoperative recurrence rate <10%.
Hemostasis treatment: combined with Hemospray (hemostatic powder) and titanium clips, the immediate hemostasis success rate is >95%.
Research and teaching
Case database (supporting DICOM format) and VR training system (such as GI Mentor), shorten the physician learning curve by 50%.
4. Comparison of technical advantages
Brand/model Core technology Clinical features Price range
Olympus EVIS X1 Dual focus optics (switching between near and far view) 8K+AI polyp classification $120,000+
Fuji ELUXEO 7000 LASEREO laser light source 4K+ blue laser imaging (BLI) $90,000~150k
Pentax i7000 Ultra-thin lens body (Φ9.2mm) Magnetically controlled capsule endoscopy collaboration $70,000~100k
Domestic Kaili HD-550 Domestic 4K CMOS 5G remote consultation module $40,000~60k
V. Development Trends and Challenges
Frontier Technologies
Molecular imaging endoscopy: targeted fluorescent probes (such as anti-CEA antibody-IRDye800) to achieve specific tumor markers.
Magnetic-controlled capsule robot: host linkage to achieve full gastrointestinal painless examination (such as Ankon MiroCam).
Existing Challenges
Cleaning and disinfection: complex mirror body design increases the difficulty of disinfection (must comply with WS 507-2016 standard).
Cost control: maintenance costs of high-end models account for 20% of the purchase cost per year.
Future Direction
Cloud intelligence: edge computing + 5G to achieve real-time AI quality control (such as blind spot reminders, operation scoring).
Miniaturization: host size is reduced by 50% (such as Storz modular design).
Summary
The host of gastrointestinal endoscopy is evolving from a single diagnostic tool to an intelligent diagnosis and treatment platform, and its technological breakthroughs have significantly improved the detection rate of early cancer (the 5-year survival rate of gastric cancer in Japan has reached 80% after popularization). Things to pay attention to when choosing:
Clinical needs: Primary hospitals can focus on cost-effectiveness (such as opening HD-550), while tertiary hospitals prefer AI functions (such as EVIS X1).
Scalability: Whether it supports future upgrades (such as adding a fluorescent module).

Faq
-
What examinations is the gastrointestinal endoscopy host suitable for?
The gastrointestinal endoscopy host is mainly used for gastroscopy and colonoscopy examinations, which can assist in the diagnosis of diseases such as gastric cancer, ulcers, polyps, etc. It also supports endoscopic treatment, such as hemostasis, polypectomy, ESD/EMR and other minimally invasive surgeries.
-
How to choose a gastrointestinal endoscopy host?
Attention should be paid to resolution (such as 4K/HD), light source type (LED/xenon lamp), image enhancement function (NBI/FECE), and ensure compatibility with existing mirror and workstation systems in the hospital.
-
How to maintain the gastrointestinal endoscope host?
Clean the surface daily, calibrate the white balance and light source regularly, avoid humid and high-temperature environments, strictly disinfect the mirror body after use, and prevent cross infection and equipment aging.
-
How to maintain the gastrointestinal endoscope host?
First, check the power supply and connecting wires, replace the spare mirror body for testing, and confirm whether the light source is normal. If the problem persists, contact the manufacturer's technical support or undergo professional repairs.
Latest articles
-
How XBX Cystoscope Supplier Ensures Quality and Precision for Hospital Procurement
Discover how the XBX Cystoscope Supplier provides hospitals with high-precision, OEM-ready endoscopy systems built for reliability, safety, and consistent imagi...
-
How XBX Bronchoscope Factory Delivers Reliable OEM Systems
Discover how the XBX Bronchoscope Factory ensures quality and reliability through advanced OEM manufacturing, optical precision, and strict quality control.
-
How XBX Laparoscope Minimizes Surgical Trauma in Abdominal Surgery
Discover how the XBX Laparoscope reduces surgical trauma through precision imaging, minimal incisions, and faster recovery in modern abdominal procedures.
-
How XBX Hysteroscope Detects and Removes Uterine Polyps
Discover how the XBX Hysteroscope enables precise detection and removal of uterine polyps, improving accuracy, safety, and comfort in women’s health care.
-
What Is an XBX Flexible Ureteroscope for Stone Removal?
Learn how the XBX flexible ureteroscope improves access, visibility, and efficiency in ureteral stone management with 4K imaging and ergonomic control.
Recommended products
-
Desktop medical endoscope host
Desktop medical endoscope host delivers HD imaging for endoscopy medical endoscopes, enhancing diagn
-
multifunctional medical endoscope desktop host
Multifunctional medical endoscope desktop host delivers HD imaging for endoscopy medical endoscopes,
-
Medical Bronchoscope machine
Bronchoscopy is a core tool for the diagnosis and treatment of modern respiratory diseases. It provi