Table of Contents
An endoscope is a long, flexible tube with a built-in camera and light source used by medical professionals to examine the interior of the body without the need for invasive surgery. Endoscopes allow doctors to see inside the digestive tract, respiratory system, and other internal organs in real time. This revolutionary tool is essential in modern diagnostics and minimally invasive procedures. Whether inserted through the mouth, rectum, nose, or small surgical incision, endoscopes provide a clear visual of areas that would otherwise require open surgery to explore.
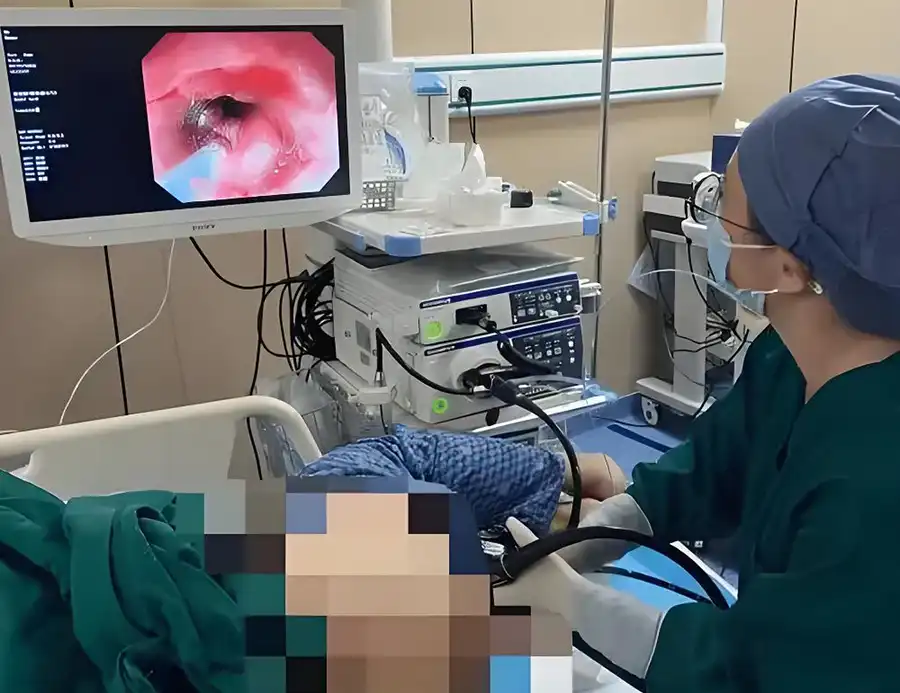
Endoscopy—the procedure performed using an endoscope—is commonly used to identify the cause of symptoms such as chronic pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, difficulty swallowing, or abnormal growths. Its non-invasive nature significantly reduces patient recovery time, risk of infection, and surgical complications.
The development and advancement of the endoscope have transformed modern diagnostics and treatment. From identifying early-stage cancers to treating gastrointestinal bleeding on the spot, endoscopes offer unparalleled access to the human body with minimal discomfort and downtime.
Endoscopy plays a critical role in early diagnosis, which is key to treating diseases like cancer, ulcers, and inflammatory conditions before they become severe. The ability to perform biopsies or interventions during the same procedure adds enormous value for both patients and clinicians.
Moreover, innovations like capsule endoscopy, narrow-band imaging, and robot-assisted endoscopy continue to enhance the precision, reach, and safety of this essential medical technology.
Modern endoscopy enables physicians to visually examine various internal structures of the human body using specially designed endoscopes. These instruments vary in size, flexibility, and functionality depending on the organ or system being inspected. Today, there are numerous types of endoscopic procedures tailored to specific body regions, making it a cornerstone of diagnostic and therapeutic medicine.
Below is a detailed breakdown of the most common types of endoscopic examinations and what areas they are used to assess:
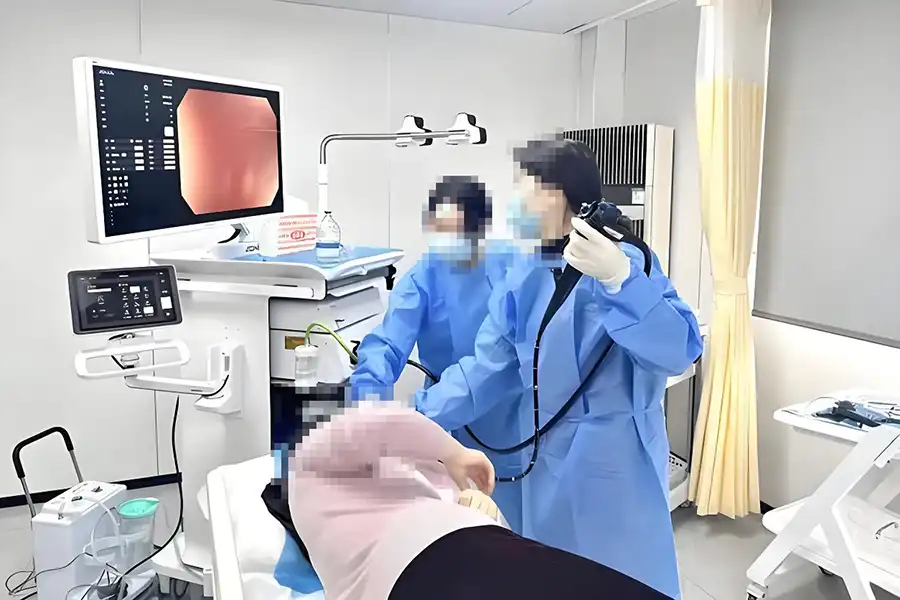
Also known as esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), this procedure allows doctors to examine the upper digestive tract, including the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). It can be used for both diagnosis and treatment.
Why is it done?
Doctors may recommend an EGD for issues such as:
Persistent heartburn or acid reflux
Difficulty swallowing
Chronic nausea or vomiting
Unexplained weight loss
Gastrointestinal bleeding
Suspected ulcers or tumors
What can be done during the procedure?
Biopsy collection
Polyp or foreign object removal
Bleeding control using clips or cauterization
Widening of narrowed areas (dilation)
What to expect:
Patients typically receive a sedative to minimize discomfort. A local anesthetic may be sprayed into the throat to reduce the gag reflex. The endoscope is gently inserted through the mouth and guided down into the stomach and duodenum. A camera transmits high-resolution images to a monitor for the doctor to review.
The procedure usually takes 15–30 minutes, followed by a short observation period until sedation wears off.
This procedure uses a flexible endoscope inserted through the rectum to examine the entire colon (large intestine) and rectum. It's commonly used for colon cancer screening and evaluating lower digestive tract symptoms.
Why is it done?
Colorectal cancer screening (especially for people over 50)
Blood in the stool, chronic diarrhea, or constipation
Unexplained anemia or weight loss
Suspected colon polyps or inflammatory bowel disease
What can be done during the procedure?
Removal of colon polyps
Tissue biopsies
Treatment of minor lesions or bleeding
What to expect:
After a bowel prep the day before, patients receive sedation for the procedure. The colonoscope is inserted through the rectum, and the doctor examines the full length of the colon. Any polyps found can often be removed on the spot. The exam usually takes 30–60 minutes. Due to sedation, patients should arrange a ride home afterward.
Bronchoscopy allows doctors to view the inside of the trachea and bronchi, making it useful for diagnosing lung or airway issues.
Why is it done?
Chronic cough or coughing up blood
Abnormal chest X-ray or CT scan findings (e.g., nodules, unexplained pneumonia)
Suspected tumors or foreign body inhalation
Sampling tissue or fluid for infection or cancer testing
What can be done during the procedure?
Collection of tissue or mucus samples
Removal of foreign bodies
Bleeding control
Bronchoalveolar lavage (lung wash)
What to expect:
Local anesthesia is typically applied through inhalation; some patients also receive sedation. The bronchoscope is inserted through the nose or mouth and guided into the airways. The procedure usually lasts 20–40 minutes. Some throat irritation or coughing may occur afterward.
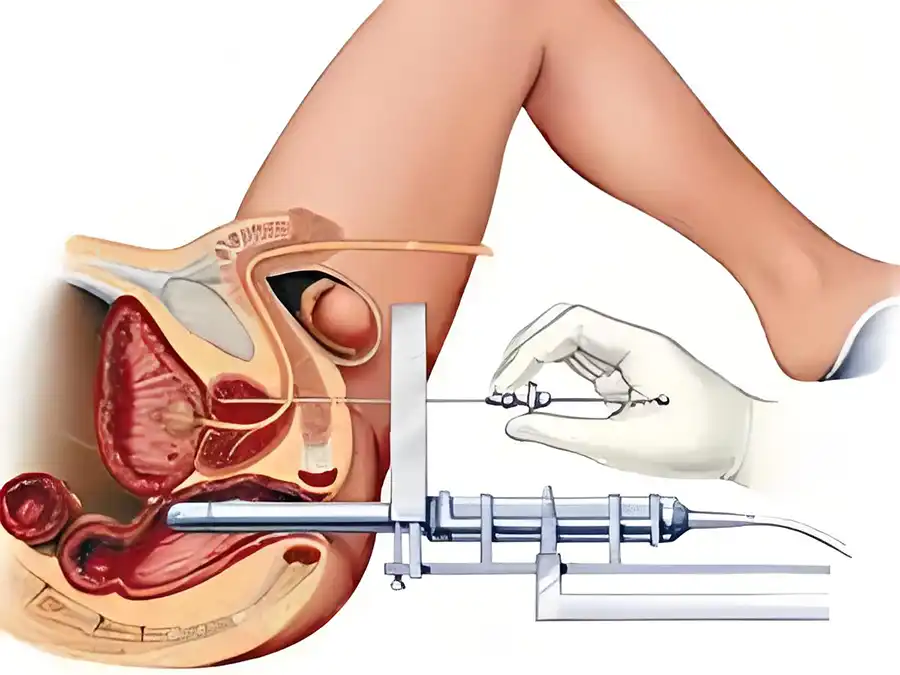
Cystoscopy involves inserting a thin scope through the urethra to inspect the bladder and urinary tract, primarily for diagnosing urological conditions.
Why is it done?
Blood in urine (hematuria)
Frequent or urgent urination, difficulty urinating
Incontinence
Suspected bladder tumors or stones
Urethral strictures or foreign objects
What can be done during the procedure?
Biopsies
Removal of small tumors or stones
Evaluation of bladder structure and capacity
Placement of catheters or stents
What to expect:
Performed under local anesthesia or mild sedation, the scope is inserted through the urethra. Male patients may feel more discomfort due to a longer urethra. The exam typically takes 15–30 minutes, with mild burning or frequent urination afterward being common.
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure where an endoscope is inserted into the abdomen through small incisions in the abdominal wall. It's a standard technique in modern surgical practices.
Why is it done?
Diagnosing unexplained abdominal or pelvic pain, or infertility
Treatment of ovarian cysts, fibroids, or ectopic pregnancy
Gallbladder, appendix, or hernia surgery
Biopsy or evaluation of abdominal tumors
What can be done during the procedure?
Biopsy or tumor removal
Gallbladder or appendix removal
Adhesion release
Endometriosis treatment
What to expect:
Performed under general anesthesia, one to three small incisions are made in the abdomen to insert the laparoscope and surgical tools. CO₂ gas is used to inflate the abdominal cavity for better visibility. Recovery is typically quick, with short hospital stays.
This procedure uses a thin, flexible or rigid scope inserted through the nose or mouth to examine the nasal cavity, throat, and larynx.
Why is it done?
Hoarseness, sore throat, or trouble swallowing
Nasal congestion, discharge, or bleeding
Suspected tumors, polyps, or vocal cord disorders
What can be done during the procedure?
Assess vocal cord function
Inspect the nasopharynx and Eustachian tube openings
Biopsy of suspicious areas
What to expect:
Usually done in a clinic setting with local anesthesia, no sedation is needed. The scope is inserted through the nose, and the exam is completed in a few minutes. Mild discomfort is common, but recovery time is not required.
Hysteroscopy involves inserting a thin scope through the vagina into the uterus to directly view the uterine cavity.
Why is it done?
Abnormal uterine bleeding
Evaluation of infertility
Suspected endometrial polyps or submucosal fibroids
Uterine adhesions
What can be done during the procedure?
Biopsy
Polyp or fibroid removal
Adhesion separation
IUD placement
What to expect:
Usually done under local anesthesia or mild sedation in an outpatient setting. The scope is inserted through the vagina, and fluid is used to expand the uterine cavity for clear viewing. The exam generally takes less than 30 minutes.
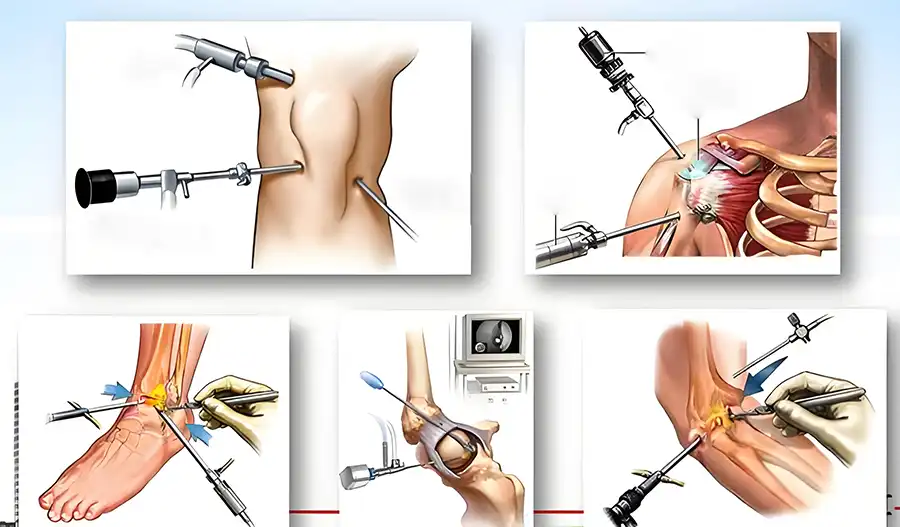
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat joint problems, commonly in the knee or shoulder.
Why is it done?
Joint pain or limited mobility
Suspected meniscus or ligament injuries
Joint swelling, infection, or inflammation
Unexplained chronic joint issues
What can be done during the procedure?
Removal of loose fragments
Repair or suturing of ligaments or cartilage
Removal of inflamed tissue or foreign material
What to expect:
Typically performed under anesthesia, small incisions are made around the joint to insert the scope and instruments. Recovery is usually quick, making this ideal for sports injuries or minor joint repairs.
Endoscopy is a valuable diagnostic and therapeutic tool used across various medical specialties. The table below provides a quick overview of common endoscopy types and the specific areas of the body they are used to examine. This summary helps clarify which procedure is best suited for evaluating particular symptoms or conditions.
| Endoscopy Type | Examined Area | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Endoscopy (EGD) | Esophagus, stomach, duodenum | GERD, ulcers, bleeding, biopsies |
| Colonoscopy | Colon, rectum | Cancer screening, polyps, chronic bowel issues |
| Bronchoscopy | Lungs and airways | Cough, bleeding, lung infections |
| Cystoscopy | Urethra and bladder | UTIs, hematuria, urinary abnormalities |
| Laparoscopy | Abdomen and pelvic organs | Diagnosing pain, fertility issues, surgical procedures |
| Hysteroscopy | Uterine cavity | Abnormal bleeding, fibroids, infertility |
| Arthroscopy | Joints | Sports injuries, arthritis, surgical repair |
| Nasopharyngoscopy | Nose, throat, larynx | Voice problems, ENT infections, nasal blockage |
| Enteroscopy | Small intestine | Small bowel tumors, bleeding, Crohn’s disease |
| Capsule Endoscopy | Entire digestive tract (esp. small bowel) | Unexplained bleeding, anemia, non-invasive imaging |
Today’s medical field offers a wide array of endoscopic procedures designed to diagnose and treat specific regions of the body with minimal invasiveness. From bronchoscopy to colonoscopy, hysteroscopy, and beyond, the endoscope is a versatile tool that continues to transform patient care through early detection, targeted therapy, and reduced recovery time.
So, what is the endoscope? It’s more than just a camera on a tube—it’s a life-saving instrument that allows doctors to see, diagnose, and treat internal conditions without the trauma of open surgery. Whether you're undergoing an upper endoscopy, learning what is the procedure for an endoscopy, or carefully following your endoscopy prep, understanding the function and importance of the endoscope can help you make informed healthcare decisions.
The endoscope industry has grown into a multi-billion-dollar global market, driven by the dual forces of rising medical demand and continuous technological innovation. Hospitals, clinics, and research institutions increasingly depend on advanced endoscope systems to perform diagnostic and therapeutic procedures with higher accuracy and safety. At the same time, manufacturers are investing heavily in R&D to deliver devices that are smaller, more flexible, and better integrated with digital platforms. These dynamics not only shape procurement strategies for healthcare providers but also determine how suppliers compete in an increasingly consolidated global market.
The global endoscope market has maintained a steady growth rate of around 6–8% annually, with projections suggesting it will surpass USD 35 billion by the end of this decade.
Rising incidence of gastrointestinal disorders, colorectal cancer, and respiratory diseases significantly boosts demand for diagnostic endoscopy procedures.
Aging populations in developed regions, combined with rapid hospital infrastructure growth in emerging economies, fuel long-term market expansion.
Government initiatives and health insurance coverage improvements further accelerate the adoption of endoscope systems worldwide.
High-definition and 4K imaging: Advanced visualization technologies allow clinicians to detect micro-lesions that were previously invisible with standard resolution.
Disposable endoscopes: Single-use models are gaining traction as hospitals seek to reduce cross-infection risks and eliminate complex reprocessing steps.
AI integration: Artificial intelligence-assisted endoscopes are being developed to automatically highlight polyps, tumors, or early abnormal tissue changes during real-time procedures.
Miniaturization: Capsule endoscopes and ultra-thin flexible models open new possibilities for minimally invasive diagnostics.
North America currently leads the global endoscope market due to strong healthcare infrastructure, high adoption of innovative devices, and well-established reimbursement systems. Europe follows closely, particularly Germany, France, and the UK, where regulatory support and medical research play a key role. Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region, with China and India increasing procurement significantly in both public and private hospitals. Latin America and the Middle East are also showing steady demand, though at a smaller base, as governments expand investments in modern healthcare facilities.
The market is highly competitive, with major multinational corporations dominating through broad product portfolios and advanced R&D capabilities. At the same time, smaller manufacturers and specialized factories play an important role in producing cost-efficient solutions for regional buyers. Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships are common, allowing larger players to expand into new segments such as robotics-assisted endoscopy and AI-driven platforms. For hospitals and procurement managers, understanding the supply chain landscape is essential to balancing quality, cost, and long-term support.
Greater integration of robotics will enable more precise surgical interventions through endoscopes.
Portable and compact endoscopes designed for outpatient and rural settings will expand accessibility worldwide.
Customization and OEM/ODM production are expected to rise as healthcare systems demand tailored solutions for specific clinical needs.
Global regulations on patient safety and equipment sterilization will continue to shape manufacturing standards.
Overall, the endoscope market is shifting from traditional diagnostic tools to highly integrated systems that combine imaging, AI, and therapeutic capabilities. For healthcare providers, this means procurement decisions are no longer about choosing a single device but about investing in a future-ready platform. For manufacturers, staying competitive will require constant innovation, strong after-sales service, and compliance with evolving international standards. These market dynamics will continue to define the industry landscape over the coming decade.
An endoscope is a flexible tube equipped with a camera and light source, designed to provide real-time visualization of internal organs without the need for open surgery.
By transmitting high-quality images of organs such as the digestive tract and airways, an endoscope allows physicians to identify abnormalities like inflammation, polyps, or infections directly.
A typical endoscope includes a flexible insertion tube, an imaging camera, an illumination system, and working channels for tools such as biopsy forceps.
Endoscopes are widely used in gastroenterology, pulmonology, urology, gynecology, and minimally invasive surgery.
Endoscopic procedures reduce patient trauma, recovery time, and scarring by using small incisions or natural openings instead of invasive cuts.
Yes, endoscopes not only visualize organs but also support interventions such as tissue biopsy, polyp removal, and foreign object extraction.
Endoscopes improve diagnostic accuracy, enable minimally invasive treatments, and enhance patient safety, making them a critical tool in contemporary healthcare.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS