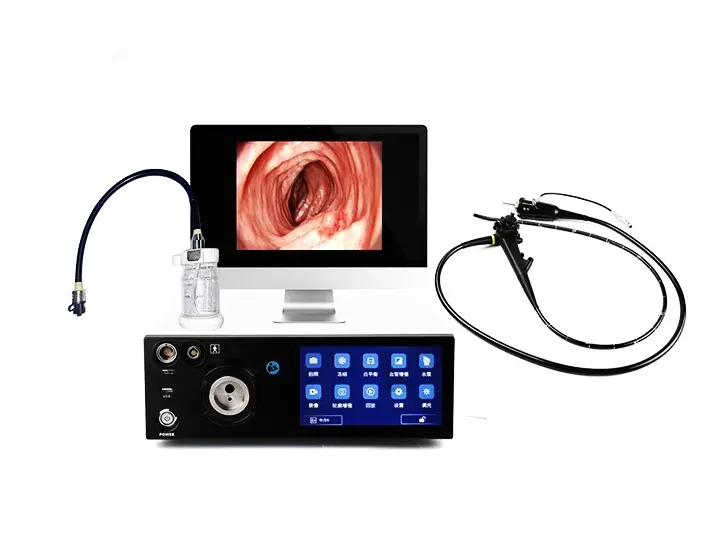
Medical Gastroscopy Equipment
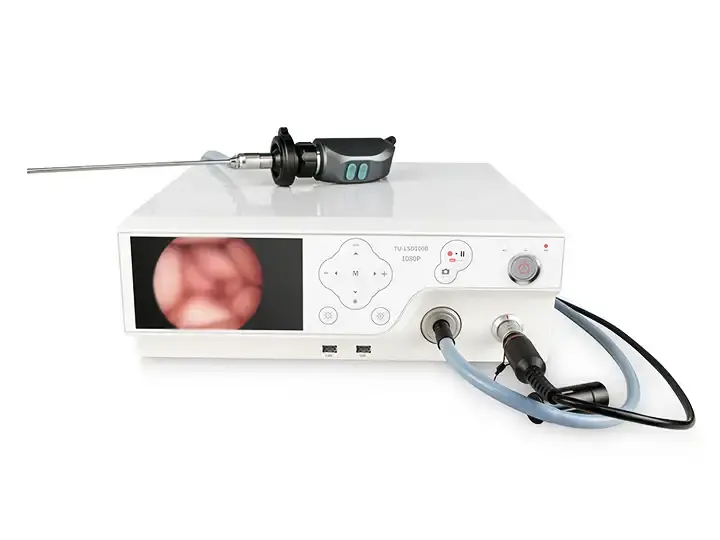
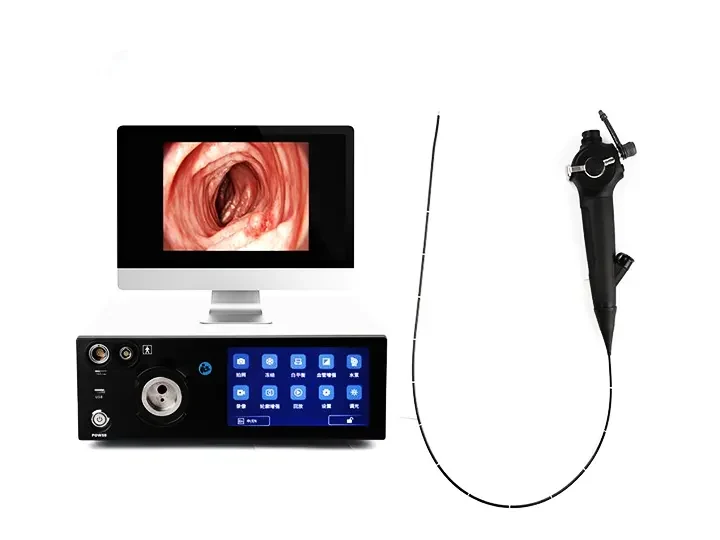
This desktop host provides HD imaging for endoscopy medical endoscopes, enabling clear visualization during gastroscopy procedures. Designed for clinical efficiency in endoscope medical diagnostics.
Technical Specifications
HD imaging resolution
Physical control knobs for sterile operation
Integrated carrying handle
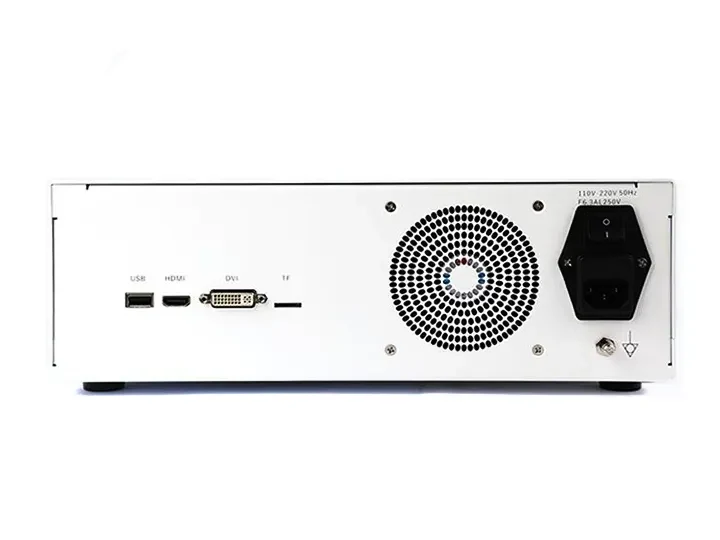
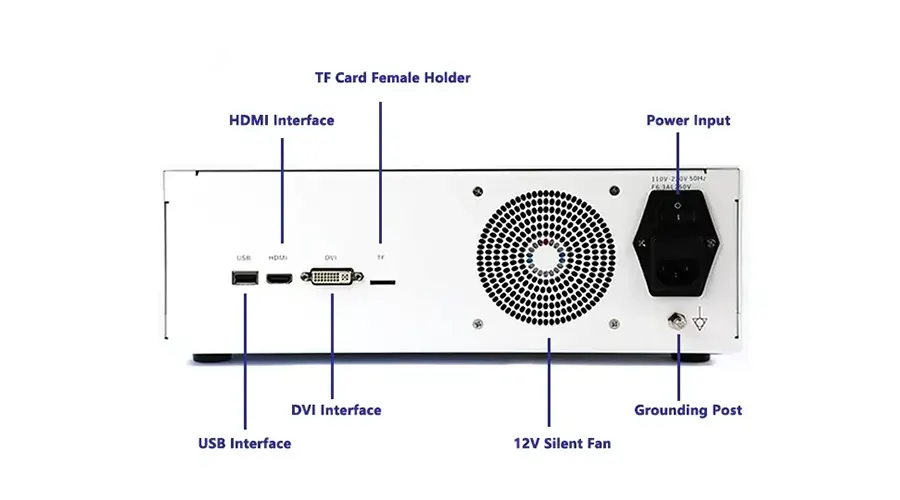
HDMI/USB video outputs
Desktop form factor
Clinical Applications
Gastric mucosa examination: Detailed tissue visualization
Lesion detection: Identification of abnormalities
Diagnostic procedures: Efficient clinical workflows
Operational Features
Stable performance for endoscopy medical endoscopes
Ergonomic interface for practitioner use
Compatibility with standard gastroscopes
Focused on essential functions for reliable gastroscopic imaging in clinical environments.
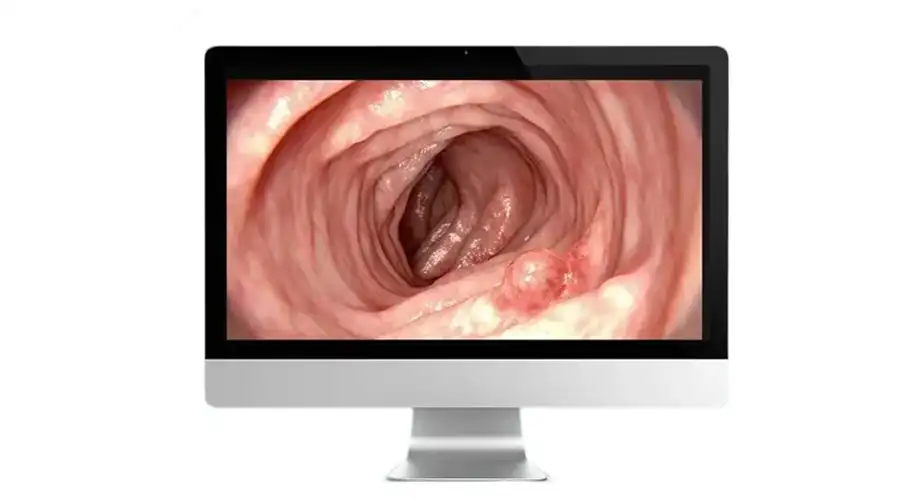
1920 1200 Pixel Resolution Image Clarity
With Detailed Vascular Visualization for Real-Time Diagnosis
Strong Compatibility
Compatible with Gastrointestinal Endoscopes, Urological Endoscopes, Bronchoscopes, Hysteroscopes,Arthroscopes, Cystoscopes, Laryngoscopes, Choledochoscopes, Strong Compatibility.
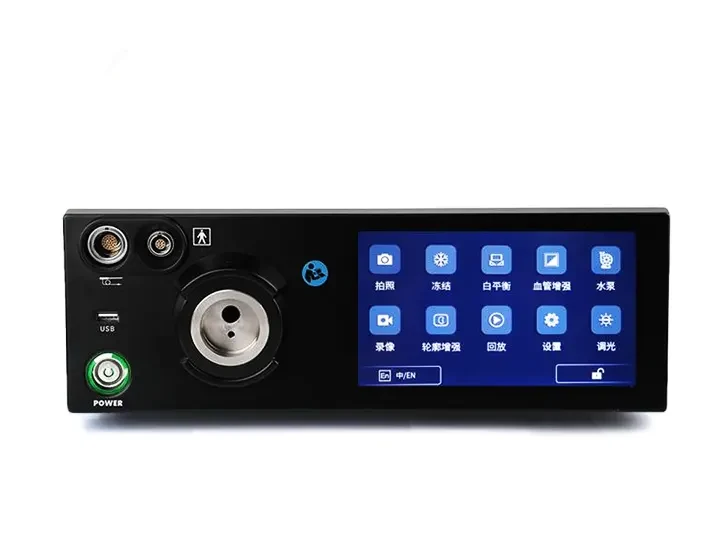
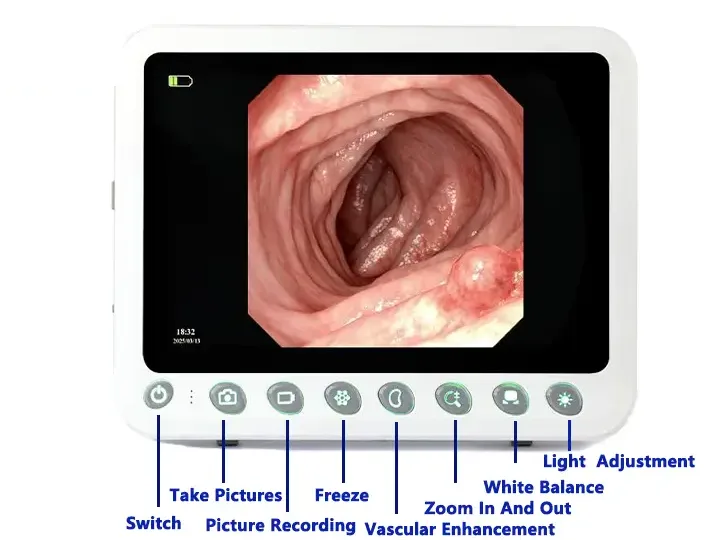
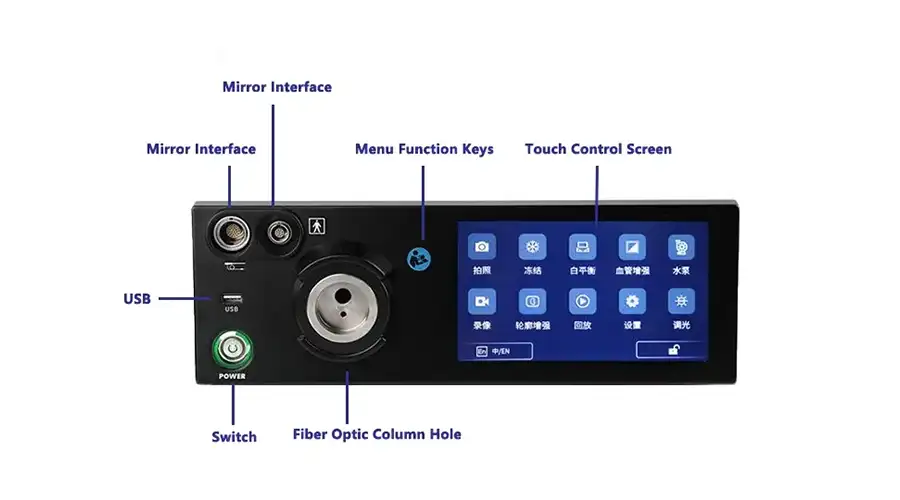
Capture
Freeze
Zoom In/Out
Image Settings
REC
Brightness: 5 levels
WB
Multi-Interface


High Sensitivity High-Definition Touchscreen
Instant Touch Response
Eye-comfort HD display
Dual LED Lighting
5 adjustable brightness levels, Brightest at Level 5
gradually dimming to OFF
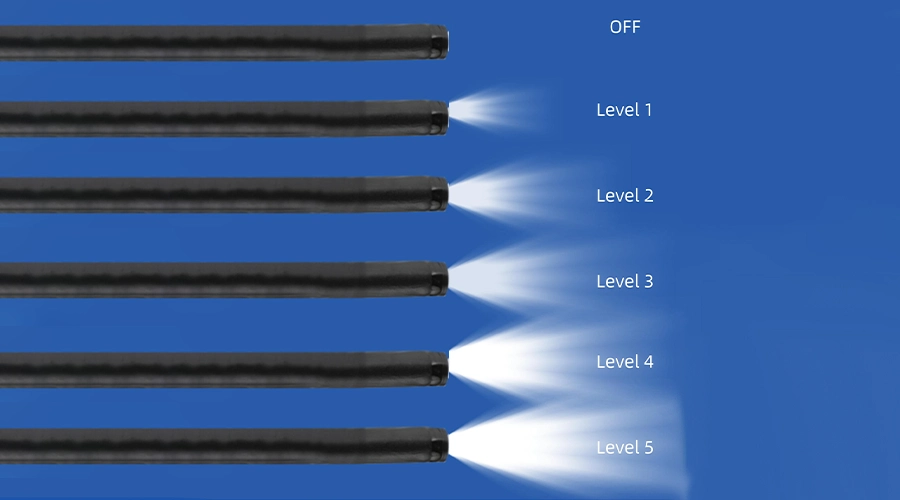


Brightest at Level 5
Brightness: 5 levels
OFF
Level 1
Level 2
Level 6
Level 4
Level 5
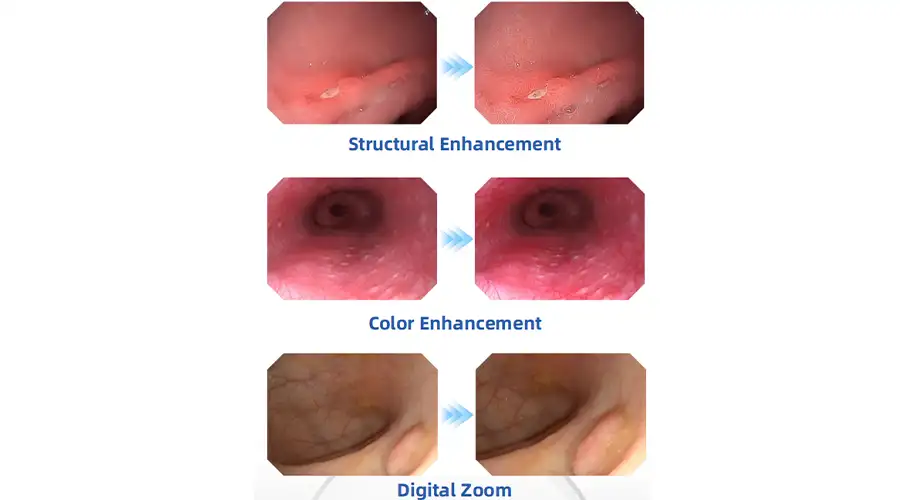
Vision Clarity for Confident Diagnosis
High-definition digital signals combined
with structural enhancement and color
enhancement technologies ensure
every image is crystal clear
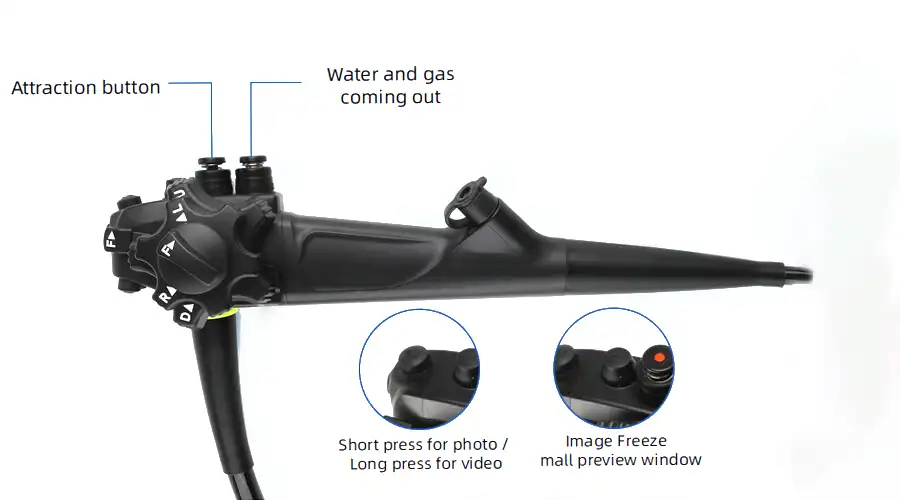
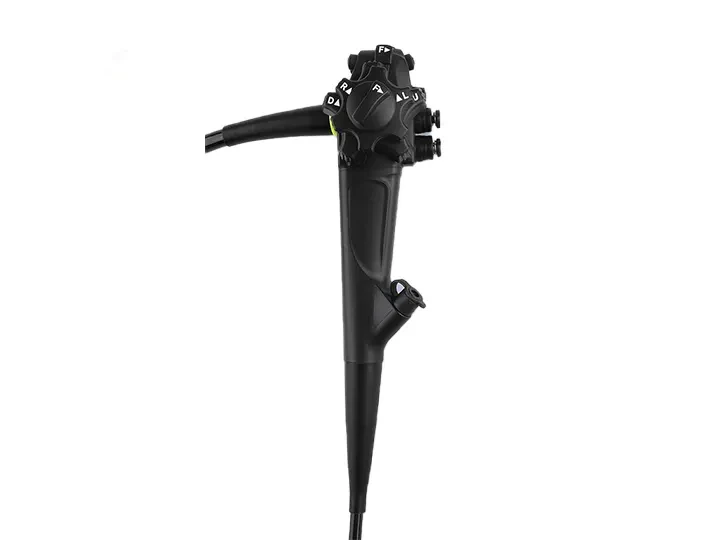
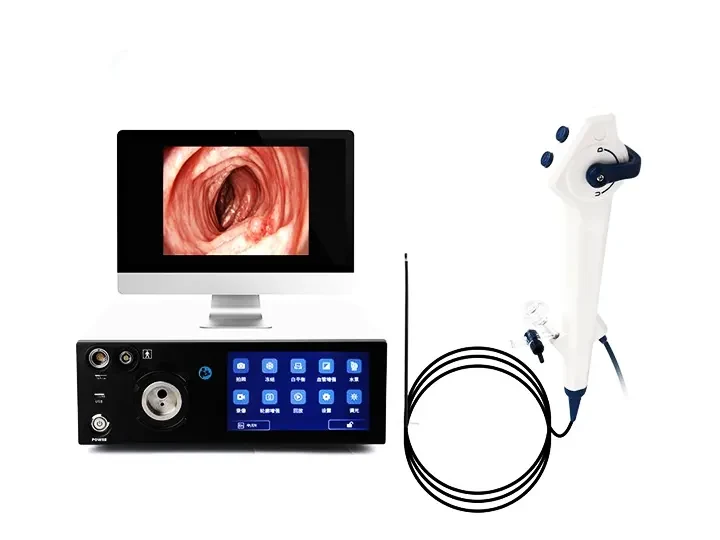
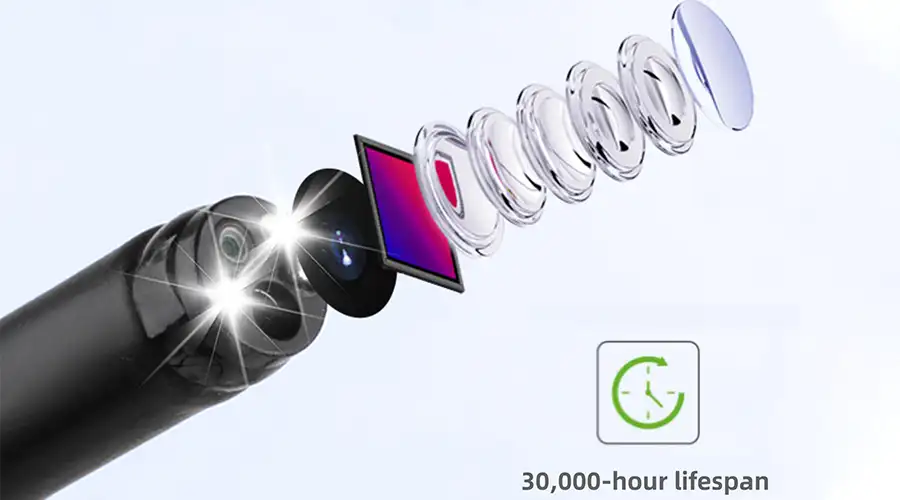
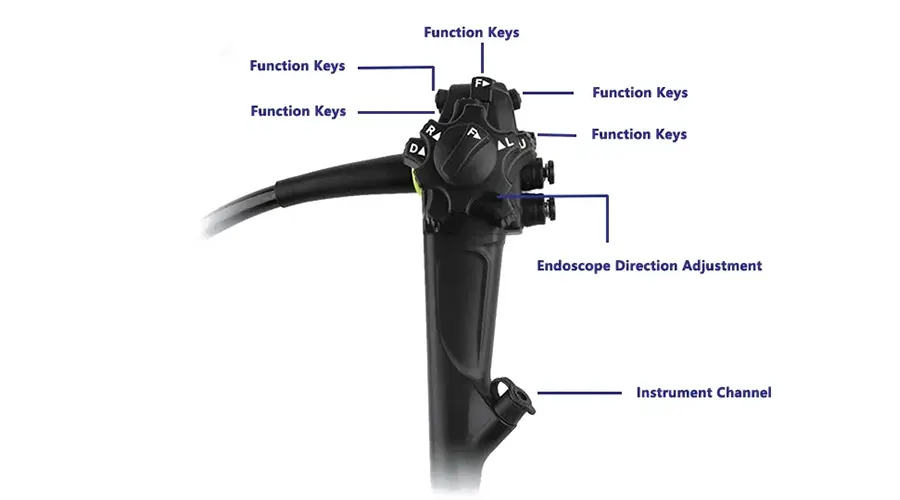
Lightweight handpiece
Superior handling for effortless operation
Newly upgraded for exceptional stability
Intuitive button layout enables
precise and convenient control


Gastroscopy is a medical examination technique that inserts an endoscope through the mouth or nose to directly observe lesions in the upper digestive tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum). It is mainly used to diagnose and treat the following diseases:
Diagnosis: gastritis, gastric ulcer, gastric cancer, esophagitis, esophageal cancer, Helicobacter pylori infection, etc.
Treatment: hemostasis, polypectomy, foreign body removal, stricture dilation, etc.
2. Types of Gastroscopes
Based on the number of uses and design, gastroscopes can be divided into disposable gastroscopes and reusable gastroscopes.
Comparison item Disposable gastroscope Reusable gastroscope
Definition Discarded after single use, no need for disinfection Can be used multiple times, strict cleaning and disinfection required each time
Material Medical grade plastic, low-cost optical components High-precision optical fiber or electronic sensor, durable material
Cost Low single cost, no disinfection cost High initial purchase cost, continuous maintenance and disinfection required
Infection risk Almost zero (avoid cross infection) There is a risk of infection due to incomplete disinfection
Image quality May be slightly lower than earlier products, but new technologies have improved High definition (such as electronic gastroscope), clearer images
Applicable scenarios Emergency, infectious disease patients, primary medical institutions Routine examinations, high-frequency use of tertiary hospitals
Environmental protection There are medical waste disposal problems More environmentally friendly (long-term use)
Representative brands Anhan Technology (China), Boston Scientific (USA) Olympus (Japan), Fuji (Japan)
III. Advantages and limitations of disposable gastroscopes
Advantages:
Eliminate cross infection (such as hepatitis B, HIV, Helicobacter pylori).
No need for complex disinfection process, saving time and manpower.
Suitable for resource-poor areas or public health emergencies.
Limitations:
Long-term use may increase the burden of medical waste.
Some cheap products have low image resolution.
IV. Advantages and challenges of repetitive gastroscopy
Advantages
Higher image quality (4K ultra-clear, NBI narrow-band imaging).
Support complex treatments (such as ESD, EMR and other surgeries).
Better long-term cost-effectiveness (high-frequency use scenarios).
Challenges:
Strict disinfection requirements (must follow WS/T 367 specifications).
High maintenance costs (such as lens damage, pipeline aging).
V. Technology development trends
Disposable gastroscope:
Material improvement (degradable plastic).
Integrated AI-assisted diagnosis (such as real-time lesion identification).
Repetitive gastroscope:
Intelligent disinfection robot.
Ultra-thin diameter design (reduce patient discomfort).
VI. Selection recommendations
Prioritize disposable gastroscopes: infectious disease prevention and control, emergency, and primary clinics.
Priority is given to repetitive gastroscopes: routine examinations in large hospitals and complex surgical needs.
VII. Regulations and standards
China: must comply with the "Medical Device Classification Catalog" (disposable is Class II, repetitive is Class III).
International: FDA (USA) and CE (EU) have strict requirements for disinfection and biocompatibility.
VIII. Future Outlook
With the advancement of materials science and microelectronics technology, disposable gastroscopes may gradually replace part of the repetitive gastroscope market, especially in the field of infection control sensitivity. However, high-end treatment scenarios still rely on repetitive high-definition gastroscopes.
Faq
-
What preparations need to be made before medical gas equipment examination?
Patients need to fast for 6-8 hours, take defoamers before examination, remove gastric mucus, ensure clear vision, and improve examination accuracy.
-
How can medical gastroscopy equipment achieve precise biopsy?
By using high-definition cameras to locate the lesion site, combined with rotatable forceps and intelligent positioning systems, fast and accurate sampling can be achieved, reducing patient discomfort.
-
What are the risks of incomplete disinfection of medical gastrointestinal equipment?
May cause cross infection and spread pathogens such as Helicobacter pylori, strict disinfection procedures must be followed, including cleaning, enzyme washing, soaking, and sterilization.
-
What are the precautions to be taken after inspecting medical gastrointestinal equipment?
Within 2 hours after the examination, fast and avoid water, and avoid spicy and irritating foods. If there is persistent abdominal pain or vomiting blood, seek medical attention immediately to investigate complications.
Latest articles
-
How XBX Cystoscope Supplier Ensures Quality and Precision for Hospital Procurement
Discover how the XBX Cystoscope Supplier provides hospitals with high-precision, OEM-ready endoscopy systems built for reliability, safety, and consistent imagi...
-
How XBX Bronchoscope Factory Delivers Reliable OEM Systems
Discover how the XBX Bronchoscope Factory ensures quality and reliability through advanced OEM manufacturing, optical precision, and strict quality control.
-
How XBX Laparoscope Minimizes Surgical Trauma in Abdominal Surgery
Discover how the XBX Laparoscope reduces surgical trauma through precision imaging, minimal incisions, and faster recovery in modern abdominal procedures.
-
How XBX Hysteroscope Detects and Removes Uterine Polyps
Discover how the XBX Hysteroscope enables precise detection and removal of uterine polyps, improving accuracy, safety, and comfort in women’s health care.
-
What Is an XBX Flexible Ureteroscope for Stone Removal?
Learn how the XBX flexible ureteroscope improves access, visibility, and efficiency in ureteral stone management with 4K imaging and ergonomic control.
Recommended products
-
4K Medical Endoscope Host
4K Medical Endoscope Host delivers ultra-HD imaging for medical endoscopes, enhancing diagnostic pre
-
Endoscope Image Processor Portable Host
The Endoscope Image Processor Portable Host enhances minimally invasive procedures with high-quality
-
XBX Repeating ENT Endoscope Equipment
Reusable ENT Endoscopes are medical optical instruments designed for examination of the ears, nose,
-
XBX Medical Repeating Bronchoscope
Reusable bronchoscope refers to a bronchoscope system that can be used multiple times after professi