Table of Contents
Bronchoscopy is a vital medical procedure that allows doctors to examine the airways, diagnose lung conditions, and perform therapeutic interventions. When discussing flexible vs rigid bronchoscopy, healthcare professionals often focus on the equipment used, patient comfort, and the clinical context that determines which method is appropriate. Flexible bronchoscopy has become the most common choice due to its adaptability and comfort, while rigid bronchoscopy remains essential for specific cases such as removing large obstructions or managing heavy bleeding. Understanding the differences, the technology behind bronchoscopy equipment, and how these devices fit into the broader medical equipment industry is essential for clinicians, hospitals, and procurement teams.
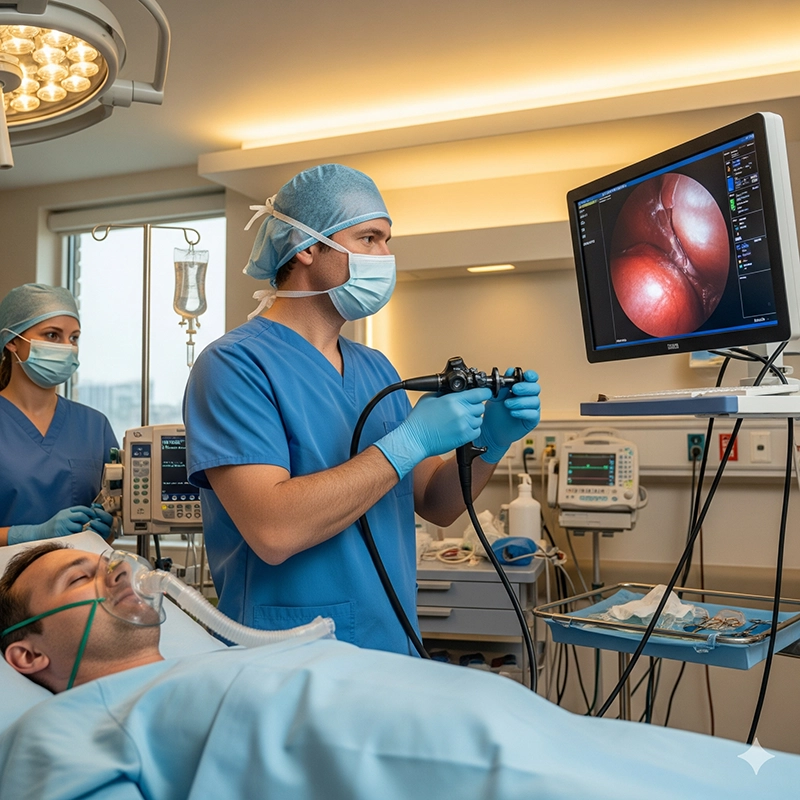
A bronchoscopy is a medical procedure performed using a specialized device called a bronchoscope, which provides a direct view of the airways and lungs. The device is inserted through the mouth or nose, passing down the throat into the trachea and bronchi. Physicians use it to diagnose diseases such as lung cancer, infections, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is also applied in therapeutic situations such as clearing blockages, suctioning secretions, or controlling bleeding.
Bronchoscopy is part of a broader category of endoscopic techniques, similar in principle to gastroscopy, colonoscopy, hysteroscopy, and arthroscopy. Each procedure involves inserting an endoscope into the body for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. While a colonoscope examines the colon, a laryngoscope is used to view the throat and vocal cords. Understanding what is the endoscope in general terms highlights its versatility across medical specialties.
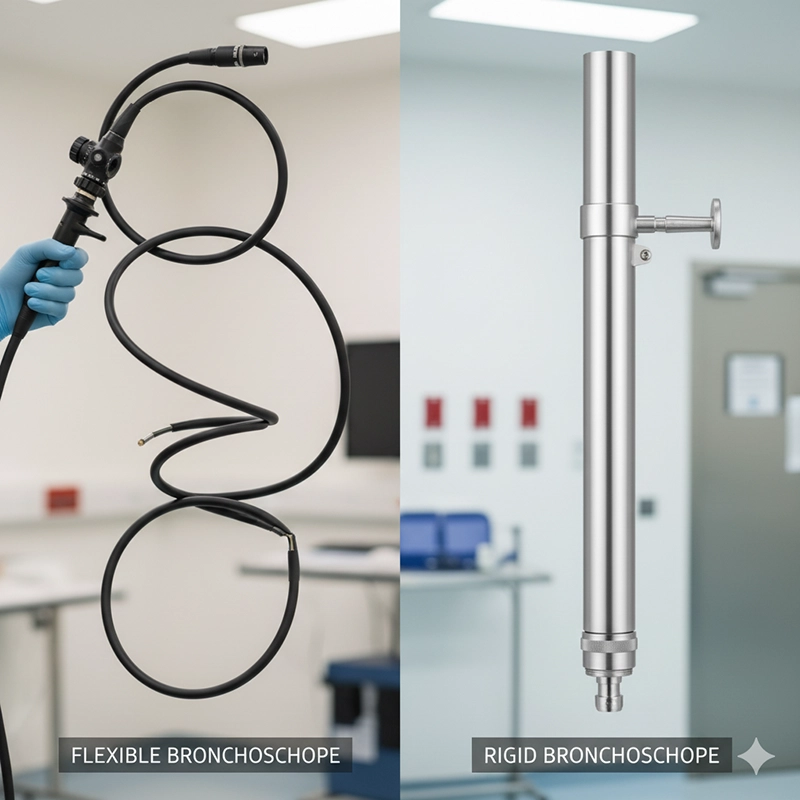
Flexible bronchoscopy is the most widely performed type. A flexible bronchoscope consists of a thin, maneuverable tube equipped with a light source and a camera. This design allows it to navigate through the intricate branches of the airways with minimal discomfort for the patient.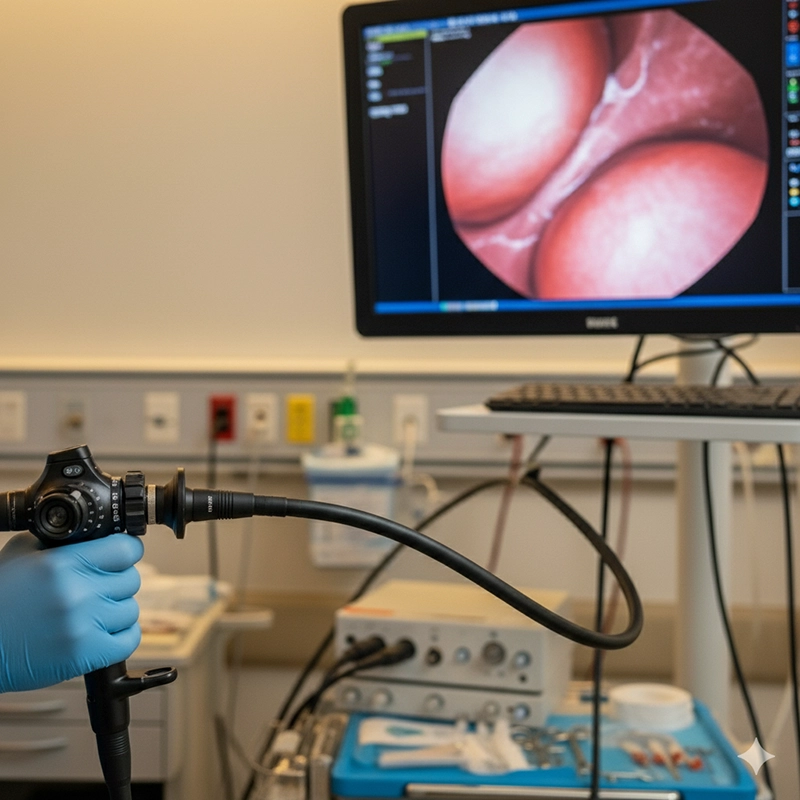
Equipped with fiberoptic or video technology for real-time imaging.
Small diameter enables passage through nasal airways.
Compatible with biopsy forceps, cytology brushes, and suction tools.
Flexible bronchoscopy is used to take tissue samples (biopsy) when lung cancer is suspected, to obtain fluid samples during infections, or to evaluate abnormal imaging findings. It is also used in therapeutic procedures such as removing mucus plugs, placing stents, or delivering medication directly to the lungs.
Less invasive and usually requires only local anesthesia with sedation.
Can be performed in an outpatient setting.
Provides a detailed view of peripheral airways that rigid bronchoscopy cannot reach.
Hospitals investing in flexible bronchoscopy equipment often prioritize video systems that connect seamlessly with electronic health records, improving workflow and documentation. Manufacturers like XBX produce medical devices in this category, catering to global demand for advanced bronchoscopy solutions.
Rigid bronchoscopy, while less common today, remains a critical tool in specific clinical scenarios. A rigid bronchoscope is a straight, hollow metal tube inserted through the mouth into the trachea. Because it does not bend, it requires general anesthesia and is performed in an operating room.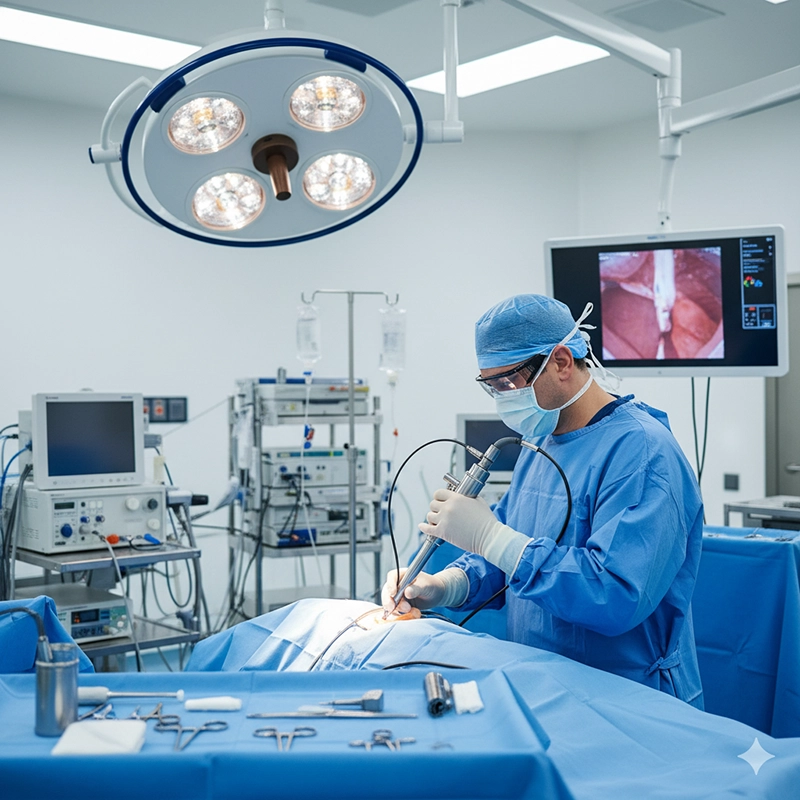
Provides a stable platform for surgical interventions.
Larger lumen allows insertion of bigger instruments.
Offers better suction capacity for managing bleeding.
Rigid bronchoscopy is particularly useful in emergency situations. For example, if a large foreign body obstructs the airway, a rigid bronchoscope allows for rapid removal. It is also used to manage massive hemoptysis (severe bleeding), to dilate airway strictures, and to place large airway stents.
Facilitates removal of large objects.
Provides secure control in life-threatening airway emergencies.
Enables surgeons to perform complex therapeutic interventions.
Hospitals and clinics still procure rigid bronchoscopy equipment as part of their surgical setup, particularly in centers specializing in thoracic surgery. Although more invasive, rigid bronchoscopy complements the flexible approach rather than competing with it.
When comparing flexible vs rigid bronchoscopy, several dimensions come into focus.
Flexible bronchoscopy: routine diagnostic procedures, outpatient evaluation, peripheral airway visualization.
Rigid bronchoscopy: emergencies, large foreign body removal, significant airway bleeding.
Flexible bronchoscopy: minor bleeding, transient hypoxia, or bronchospasm may occur.
Rigid bronchoscopy: requires general anesthesia, carries higher risk of complications but provides greater control.
| Aspect | Flexible Bronchoscopy | Rigid Bronchoscopy |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Flexible tube with camera and light | Rigid metal tube |
| Anesthesia | Local plus sedation | General anesthesia |
| Applications | Biopsy, stenting, infection diagnosis | Foreign body removal, bleeding control |
| Patient Comfort | Higher, less invasive | Lower, more invasive |
| Accessibility | Outpatient, diagnostic labs | Operating room only |

Modern bronchoscopy equipment includes scopes, processors, monitors, light sources, and accessories such as biopsy forceps and suction devices. Advances in endoscopic imaging have made high-definition video systems standard, improving diagnostic accuracy. Disposable bronchoscopes have also emerged, reducing the risk of cross-contamination and simplifying infection control.
As part of the wider medical equipment industry, bronchoscopy equipment parallels devices such as colonoscopes, laryngoscopes, hysteroscopes, and arthroscopes. Hospitals and clinics evaluate suppliers not only on price but also on training, after-sales service, and integration with existing medical devices. Global suppliers, including factories in Asia, offer competitive options for procurement. For example, colonoscope price is often considered alongside bronchoscope costs during endoscopy equipment acquisition. Procurement teams must weigh the balance between affordability and quality when selecting endoscope systems.
Clinical decision-making determines whether flexible or rigid bronchoscopy is chosen. Physicians consider the patient’s condition, the urgency of the procedure, and the tools required. Flexible bronchoscopy is chosen for routine diagnostics and less invasive therapies, while rigid bronchoscopy is reserved for emergency or surgical contexts.
From a procurement perspective, hospitals need both systems to cover all scenarios. XBX and other manufacturers of medical devices provide modular systems where flexible scopes connect to shared video processors, while rigid systems complement surgical suites.
Bronchoscopy belongs to the family of endoscopic examinations. Understanding this context is crucial:
Gastroscopy: Used to examine the stomach and upper digestive tract.
Colonoscopy: Performed with a colonoscope to examine the large intestine; questions like what age should you get a colonoscopy guide screening practices.
Hysteroscopy: Uses a hysteroscope to visualize the uterus.
Arthroscopy: Allows orthopedic surgeons to view joints.
Laryngoscopy: Involves a laryngoscope to view the larynx and vocal cords.
Each of these procedures relies on specialized medical equipment but shares the underlying concept of endoscopy. Knowing what is the endoscope reinforces the link between these tools.
High-definition imaging: 4K and beyond, improving diagnostic accuracy.
Disposable bronchoscopes: reducing the risk of cross-contamination and simplifying infection control.
AI-assisted diagnosis: using algorithms to identify lesions in real time.
Integration with electronic health records: enhancing data management.
Cross-specialty technology transfer: advances in colonoscopy, hysteroscopy, and arthroscopy influencing bronchoscopy design.
The global demand for bronchoscopy equipment is rising in parallel with other endoscopic procedures. Hospitals seek suppliers who can provide complete solutions, including colonoscopes, laryngoscopes, and hysteroscopes. Cost factors such as colonoscope price influence budgets, while long-term service agreements and training add value.
Evaluate the range of devices offered (bronchoscopy, gastroscopy, colonoscopy).
Verify quality certifications and compliance with international standards.
Consider OEM and ODM options from factories in regions like China and Korea.
Confirm compatibility with existing hospital infrastructure.
The endoscope market is highly competitive, requiring careful selection to ensure quality patient care.
Flexible vs rigid bronchoscopy remains a central discussion in respiratory medicine. Flexible scopes dominate for diagnostics and routine care, while rigid systems retain importance in emergencies and surgeries. Together, they form a complementary pair, ensuring physicians have the right tools for every clinical challenge.
In the broader context, bronchoscopy connects with other endoscopic specialties such as colonoscopy, hysteroscopy, arthroscopy, laryngoscopy, and gastroscopy. Understanding what is a bronchoscopy within the ecosystem of medical devices illustrates how crucial endoscopy is for modern healthcare.
Hospitals, clinics, and procurement teams evaluating bronchoscopy equipment must balance cost, including colonoscope price, with quality and innovation. Manufacturers like XBX provide solutions that integrate across specialties, helping institutions invest in reliable medical equipment that supports long-term patient care.
We provide both flexible and rigid bronchoscopy systems, including scopes, processors, monitors, and accessories such as biopsy forceps and suction devices.
Yes, hospitals often procure both types together to cover diagnostic and surgical needs. Bundled procurement options are available with shared video processors and modular components.
Yes, OEM and ODM manufacturing services are available. Custom branding, packaging, and specification adjustments can be provided according to hospital or distributor requirements.
Flexible bronchoscopes typically cost more due to imaging technology and accessories. Rigid bronchoscopes are less expensive but require operating room infrastructure. A detailed price list can be provided upon request.
Yes, our product line covers a wide range of endoscopes, including colonoscopes, hysteroscopes, arthroscopes, laryngoscopes, and gastroscopes. Hospitals can consolidate procurement across specialties.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS