Table of Contents
A colonoscope is a highly specialized instrument that combines flexibility, illumination, and imaging to allow physicians to examine the colon and rectum in detail. Unlike general endoscopes, the colonoscope is designed specifically for colonoscopic procedures. It enables detection of early disease, removal of polyps, control of bleeding, and tissue sampling—all within a single examination. This dual diagnostic and therapeutic capability makes colonoscopy a cornerstone in colorectal cancer prevention, which remains one of the leading causes of cancer mortality worldwide (World Health Organization, 2024).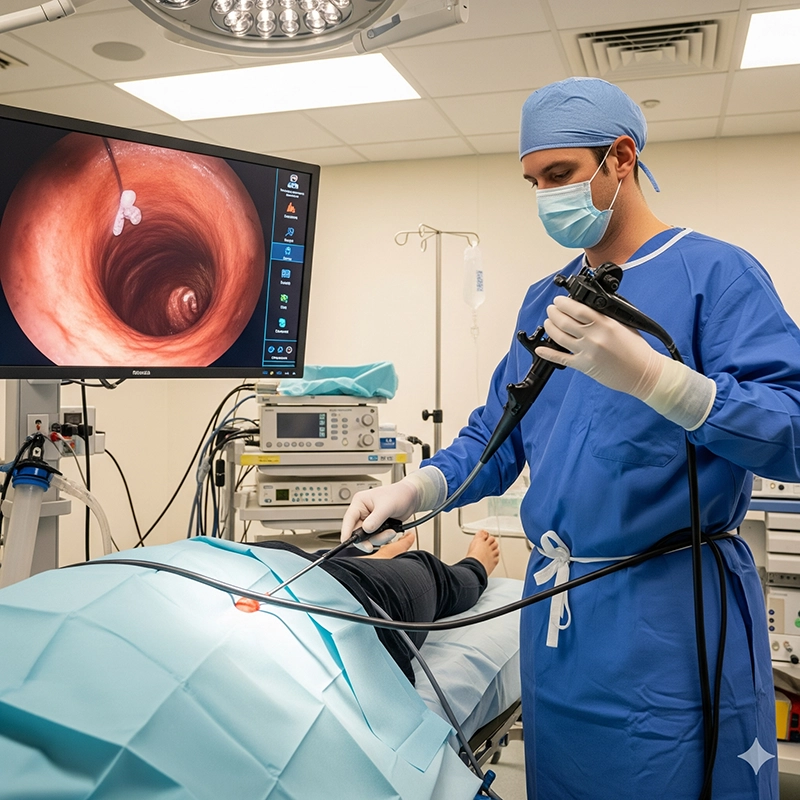
The colonoscope is a long, slender, and flexible colonoscope designed to reach the entire length of the colon. The typical colonoscope length ranges from 130 to 160 centimeters, long enough to navigate from the rectum to the cecum.
Colonoscope definition: It is a type of endoscope intended specifically for colonoscopy. While “endoscope” is the broad category, the colonoscope is the precise instrument for large bowel examinations. A colonoscope diagram usually shows:
A control head with angulation knobs, suction and irrigation controls.
An insertion tube with flexibility to traverse loops and curves.
A video colonoscope camera and light source for real-time imaging.
Working channels for instruments like biopsy forceps, snares, or injectors.
Compared to other instruments—such as the gastroscope for the upper GI tract, the bronchoscope for lungs, or the hysteroscope for the uterus—the colonoscope’s design emphasizes length and flexibility. This structural adaptation is essential for navigating the colon’s turns.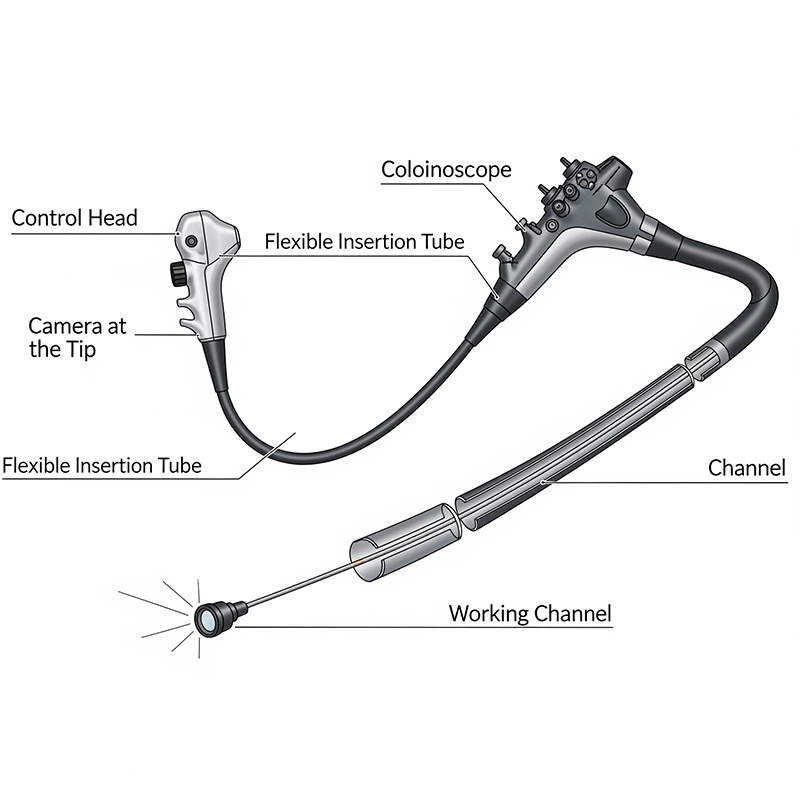
Colonoscopy is more than just inserting a tube. It is a carefully orchestrated process involving preparation, sedation, controlled insertion, and imaging.
Bowel cleansing: Adequate preparation is critical. Patients drink laxatives or bowel prep solutions to clear the colon of waste. Inadequate prep reduces detection rates of adenomas by 25% or more (American Cancer Society, 2023).
Dietary restrictions: Clear liquid diets are common, with fasting 12–24 hours before the procedure.
Medication management: Adjustments may be required for patients taking anticoagulants, insulin, or blood pressure medications.
Patients typically receive conscious sedation, though deeper anesthesia may be used in some hospitals.
Sedation ensures relaxation and minimizes discomfort while allowing responsiveness.
Continuous monitoring of vital signs provides safety.
The colonoscope is introduced into the rectum and carefully advanced.
How long is a colonoscope? Its usable length (~160 cm) is sufficient to visualize the entire colon, including the cecum.
Air or CO₂ is insufflated to open the colon for clear visualization.
Gentle manipulation and angulation reduce patient discomfort and prevent complications.
Modern video colonoscopes provide high-definition imaging, enabling clearer identification of subtle lesions.
Narrow-band imaging (NBI) enhances vascular detail.
Recording capability supports documentation and teaching.
Mild bloating or cramping may occur due to insufflation.
The colonoscope transmits images while passing through, giving a complete view of mucosa.
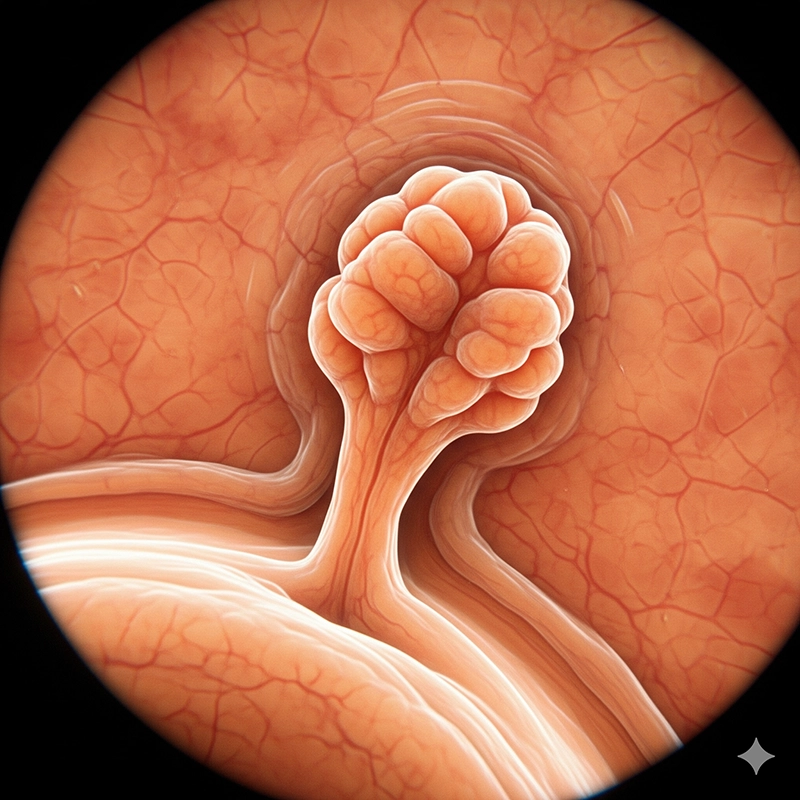
If suspicious lesions are seen, immediate biopsy or removal is possible.
Designed to bend with anatomy, improving both comfort and maneuverability.
Equipped with advanced torque transmission and control knobs.
Widely used in both routine and complex colonoscopic procedures.
Adult colonoscope: standard tool, length ~160 cm, diameter suitable for most adults.
Pediatric colonoscope: thinner, shorter; useful for children or adults with narrow colons.
Device selection depends on anatomy and clinical context.
4K imaging provides unmatched resolution.
AI-assisted systems flag potential polyps in real time (IEEE Medical Imaging, 2024).
Disposable components reduce infection risk.
Colonoscopy combines pre-procedure preparation, intra-procedure actions, and post-procedure care.
Detailed history is taken to assess risk (family history, symptoms).
Informed consent ensures patients understand risks, benefits, and alternatives like virtual colonoscopy or stool DNA testing.
Patients are positioned on their left side to facilitate insertion.
Diagnostic evaluation: The mucosa is examined for ulcers, tumors, inflammation, diverticula.
Therapeutic uses:
Polypectomy removes polyps that may become cancerous.
Biopsies allow microscopic evaluation.
Hemostasis controls active bleeding with clips or cautery.
Comparisons with other endoscopic procedures:
Gastroscopy: targets stomach and duodenum.
Bronchoscopy: visualizes lungs and trachea.
Hysteroscopy: examines uterine cavity.
Laryngoscopy: inspects vocal cords and larynx.
Uroscopy: evaluates the bladder and urinary tract.
ENT Endoscope: applied in sinus or ear assessments.
Patients are monitored until sedation wears off.
Minor bloating or discomfort may persist temporarily.
Light meals are generally permitted the same day.
Biopsy results are usually available in days; therapeutic results (like polyp removal) are explained immediately.
Large cohort studies (New England Journal of Medicine, 2021) confirm colonoscopy lowers colorectal cancer mortality rates by up to 60%.
Device type: fiberoptic vs video colonoscope.
Accessories: snares, biopsy forceps, cleaning equipment.
Brand reputation and after-sales service.
Flexible colonoscopes are the standard choice due to safety and diagnostic accuracy.
Adult colonoscopes are most widely purchased, though pediatric versions are necessary for special cases.
Hospitals weigh total ownership cost, including training and service contracts.
Expanding screening programs drive global demand.
AI-assisted colonoscopes and disposable models are emerging.
Forecasts indicate the global colonoscope market may exceed USD 3.2 billion by 2030 (Statista, 2024).
Perforation occurs in fewer than 0.1% of procedures (Mayo Clinic, 2023).
Post-polypectomy bleeding risk is <1%.
Sedation-related risks are minimized with continuous monitoring.
Proper bowel prep enhances visualization and lowers risks.
Experienced endoscopists reduce adverse event rates.
Disposable insertion components decrease infection transmission.
AI-assisted colonoscopes improve polyp detection.
Video colonoscopes with 4K and augmented imaging raise accuracy.
Integration with digital patient records streamlines data collection and screening efficiency.
| Instrument | Main Target | Application Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Colonoscope | Colon & rectum | Screening, polyp removal, cancer prevention |
| Gastroscope | Esophagus, stomach | Ulcer detection, gastric cancer, GERD evaluation |
| Bronchoscope | Airways, lungs | Diagnosis of lung disease, airway obstruction |
| Hysteroscope | Uterine cavity | Fibroid detection, infertility assessment |
| Laryngoscope | Vocal cords, throat | ENT diagnosis, airway surgery |
| Uroscope | Bladder, urinary tract | Tumor detection, stone evaluation |
| ENT Endoscope | Ear, nose, throat | Chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps, otitis evaluation |
The colonoscope continues to serve as one of the most effective preventive and diagnostic tools in modern medicine. By enabling real-time visualization, immediate treatment, and accurate tissue sampling, it not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces long-term healthcare burdens. With advances in video colonoscope technology, AI-enhanced detection, and global screening initiatives, colonoscopic practice is expected to expand further. Alongside instruments like the gastroscope, bronchoscope, hysteroscope, laryngoscope, uroscope, and ENT endoscope, the colonoscope demonstrates how minimally invasive tools are reshaping healthcare for both diagnostics and therapeutic interventions.
Our standard adult colonoscope length ranges from 130 cm to 160 cm, suitable for complete colonoscopic examinations. Pediatric and customized lengths are also available on request.
Yes, we provide both adult colonoscope models for routine procedures and pediatric versions for patients with smaller anatomy. Detailed specifications can be included in the quotation.
Standard packages may include biopsy forceps, snares, cleaning brushes, and irrigation valves. Additional accessories for colonoscopic procedures can be quoted separately.
Yes, we offer OEM/ODM solutions for distributors and hospitals. Options include branding on video colonoscopes, packaging design, and customized colonoscope specifications.
The typical colonoscope length is about 130–160 cm. This length is necessary to examine the entire large intestine, from the rectum to the cecum. Shorter pediatric versions are also available for children or adults with narrower colons.
An endoscope is a general term for instruments used to look inside the body, such as a gastroscope for the stomach or a bronchoscope for the lungs. A colonoscope, on the other hand, is specifically designed for the colon, making it longer and more flexible.
A video colonoscope has a tiny camera at its tip that sends real-time images to a monitor. This allows doctors to carefully examine the lining of the colon. Modern models may include high-definition or even 4K imaging, making small abnormalities easier to spot.
A flexible colonoscope bends with the natural curves of the colon, which makes the procedure safer and more comfortable. Rigid instruments were used in the past, but flexible models have become the global standard.
An adult colonoscope is the standard instrument for most patients. A pediatric colonoscope is thinner and shorter, designed for children or adults with narrow colons. Using the right size ensures accurate and safe examinations.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS