Table of Contents
A bronchoscopy is a diagnostic and therapeutic medical procedure that allows doctors to directly visualize the inside of the airways, including the trachea and bronchi, using a specialized device known as a bronchoscope. The bronchoscope is a thin, flexible or rigid tube equipped with a camera and light source, which provides real-time imaging of the respiratory tract. Physicians use bronchoscopy to investigate unexplained symptoms such as persistent cough, lung infections, or abnormal imaging findings, and to collect tissue samples for laboratory analysis. The procedure plays an essential role in modern pulmonology, critical care, and oncology.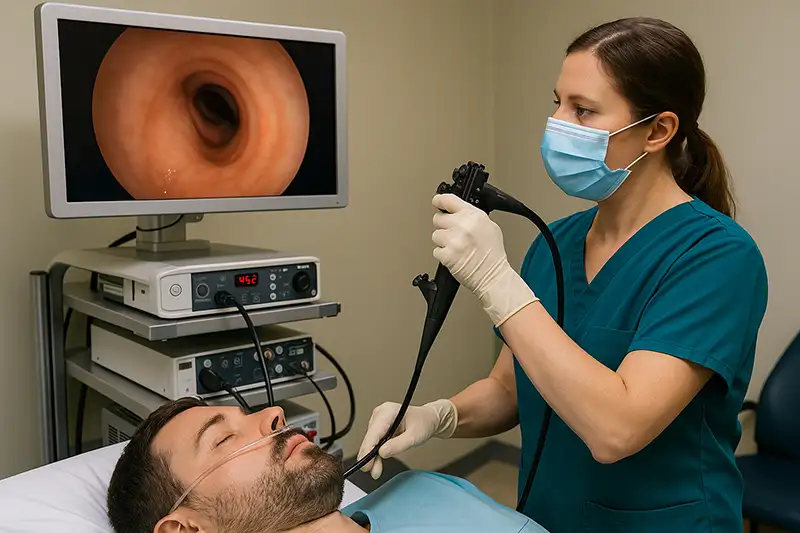
Bronchoscopy represents one of the most important advancements in respiratory diagnostics. Before its development, physicians relied on indirect imaging such as X-rays or on invasive surgical procedures to assess lung problems. With bronchoscopy, clinicians can enter the airways through the mouth or nose with minimal discomfort, observing abnormalities, collecting biopsies, or performing therapeutic interventions.
The value of bronchoscopy extends beyond simple diagnosis. In intensive care units, it is indispensable for airway management, suctioning secretions, and confirming the placement of endotracheal tubes. In oncology, it enables the direct visualization of lung tumors and guides biopsy procedures for precise staging. Across the world, bronchoscopy has become a standard of care in pulmonology and critical medicine.
Bronchoscopy is performed using either a flexible or rigid instrument. Flexible bronchoscopes are the most common, used for routine diagnostics and minor interventions, while rigid bronchoscopes are preferred for advanced therapeutic procedures.
The procedure begins with preparation, including fasting and adjusting medications. Local anesthesia or mild sedation ensures comfort, while continuous monitoring safeguards safety.
Preparation and patient positioning
Insertion of the bronchoscope
Visualization of airways
Tissue sampling or suction if required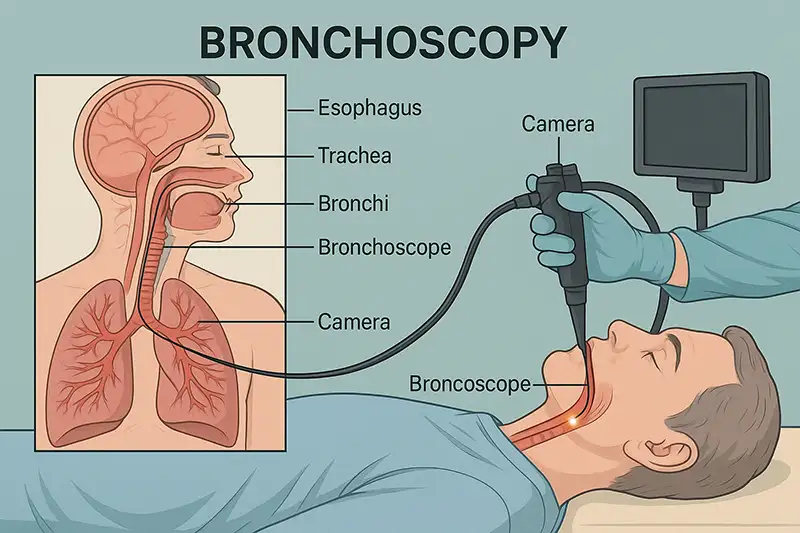
Bronchoscopy is a versatile diagnostic tool. Physicians use it to evaluate persistent symptoms, investigate abnormal chest imaging, and confirm suspected diseases. It provides direct access to tissues that cannot be adequately evaluated by imaging alone.
Lung cancer and tumors
Tuberculosis, pneumonia, and fungal infections
Airway narrowing or obstruction
Chronic cough or unexplained bleeding
Indications include abnormal imaging, infections not responding to treatment, unexplained shortness of breath, chronic cough, or hemoptysis. It is also useful for preventive screening in high-risk individuals and monitoring chronic lung diseases.
Most patients do not find bronchoscopy painful. Sedation and anesthesia minimize discomfort. Some may feel mild pressure, coughing, or gagging, but these are brief. Afterward, a sore throat or temporary cough may occur but resolve quickly.
The duration depends on the purpose. Diagnostic bronchoscopies last 15–30 minutes, while complex interventions may extend to 45 minutes. Observation afterward adds recovery time.
Biopsy results usually take 2–7 days. Routine histology requires several days, microbiological cultures can take weeks, and molecular testing for cancer may take longer. These results guide precise treatment planning.
Modern bronchoscopy relies on precision engineering and digital imaging.
Flexible bronchoscopes for diagnostics
Rigid bronchoscopes for therapeutic use
Light source and high-definition imaging systems
Biopsy and suction tools for tissue and airway management
Bronchoscopy is safe but not risk-free. Minor side effects include sore throat, cough, and nosebleeds. Rare complications include bleeding, infection, or collapsed lung. Proper monitoring and sterile technique minimize risks.
Compared to CT, MRI, or X-rays, bronchoscopy allows direct visualization and tissue sampling. It combines imaging with intervention, making it indispensable for diagnosis and treatment.
Modern innovations include HD imaging, narrow-band imaging, AI-assisted diagnostics, robotic bronchoscopy for precision, and single-use scopes to improve infection control.
Bronchoscopy is essential worldwide. In high-income countries, it supports cancer screening and ICU care. In developing regions, affordable scopes and training are expanding access. It also contributes to research in lung cancer, tuberculosis, and chronic respiratory diseases.
The bronchoscopy market is expanding due to rising lung disease rates and innovations in disposable scopes. OEM/ODM services allow hospitals and distributors to obtain customized systems. Compliance with CE, FDA, and ISO13485 ensures global safety and reliability.
Bronchoscopy remains a cornerstone of pulmonary medicine. With advances in imaging, robotics, and AI, its future promises even greater precision, safety, and accessibility for patients worldwide.
It helps detect lung cancer, infections, tuberculosis, and airway blockages.
It takes 15–45 minutes depending on complexity and whether biopsies are performed.
With sedation and anesthesia, most patients report mild discomfort rather than pain.
Routine pathology takes 2–7 days, while special cultures may take weeks.
Mild sore throat, cough, or bleeding may occur, but serious complications are rare.
They commonly use HD or 4K cameras, with optional narrow-band imaging for enhanced visibility.
Flexible scopes are for routine diagnostics, while rigid scopes are for complex therapeutic procedures.
Yes, OEM/ODM options allow logo placement, private labeling, and packaging customization.
Yes, rigid bronchoscopy is often used in emergencies to extract inhaled foreign bodies.
It cannot always reach the smallest peripheral airways, and some findings may still require complementary imaging like CT scans.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS