Table of Contents
The imaging technology of medical endoscopes has undergone a leapfrog development from standard definition (SD) to high definition (HD), and now to 4K/8K ultra high definition+3D stereoscopic imaging. This technological revolution has greatly improved surgical accuracy, lesion detection rate, and doctor operating experience. The following provides a comprehensive introduction to the technical principles, core advantages, clinical applications, representative products, and future trends.
1. Technical principles
(1) 4K/8K Ultra High Definition Imaging
resolving power:
4K: 3840 × 2160 pixels (approximately 8 million pixels), which is 4 times that of 1080P (Full HD).
8K: 7680 × 4320 pixels (approximately 33 million pixels), with a 4x increase in clarity.
Core Technology:
High density CMOS sensor: larger photosensitive area, improving imaging quality in low light environments.
HDR (High Dynamic Range): enhances contrast between light and dark, avoiding overexposure or underexposure.
Image processing engine: real-time noise reduction, edge enhancement (such as Olympus VISERA 4K's "Ultra HD signal processing").
(2) 3D Stereoscopic Imaging
Implementation method:
Dual lens system: Two independent cameras simulate human eye disparity and synthesize 3D images (such as Stryker1588 AIM).
Polarized light/time-division display: Stereoscopic vision is achieved through special glasses (some laparoscopic systems).
Core advantages:
Depth perception: Accurately judge the spatial relationship between organizational levels (such as nerves and blood vessels).
Reduce visual fatigue: closer to natural vision, reduce the "plane operation" error of 2D surgery.
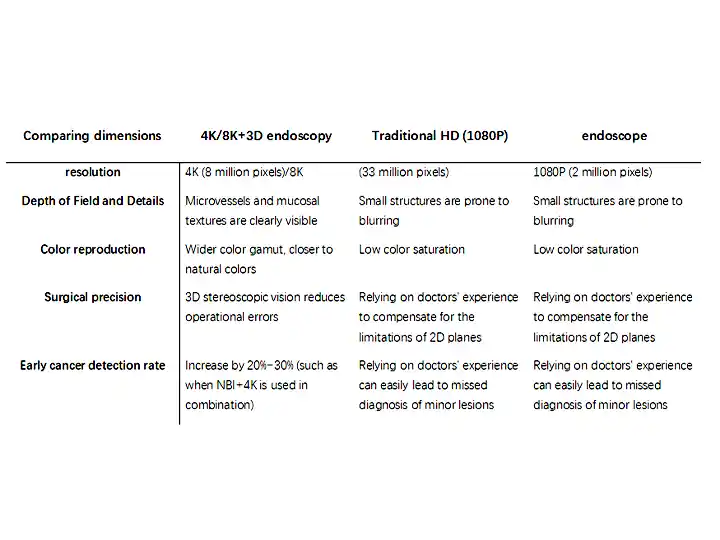
2. Core advantages (vs traditional high-definition endoscopy)
3. Clinical application scenarios
(1) The core application of 4K/8K ultra high definition
Early diagnosis of tumors:
In colorectal cancer screening, 4K can identify tiny polyps<5mm (which are easily overlooked by traditional endoscopy).
Combined with narrowband imaging (NBI), the early cancer detection rate has been increased to over 90%.
Complex minimally invasive surgery:
Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: 4K clear display of neurovascular bundles reduces the risk of urinary incontinence.
Thyroid surgery: 8K resolution of recurrent laryngeal nerve to avoid damage.
(2) The core application of 3D stereoscopic imaging
Narrow space operation:
Transnasal pituitary tumor resection: Avoid touching the internal carotid artery with 3D vision.
Single port laparoscopic surgery (LESS): Depth perception improves instrument manipulation accuracy.
Suture and anastomosis:
Gastrointestinal anastomosis: 3D suturing is more precise and reduces the risk of leakage.
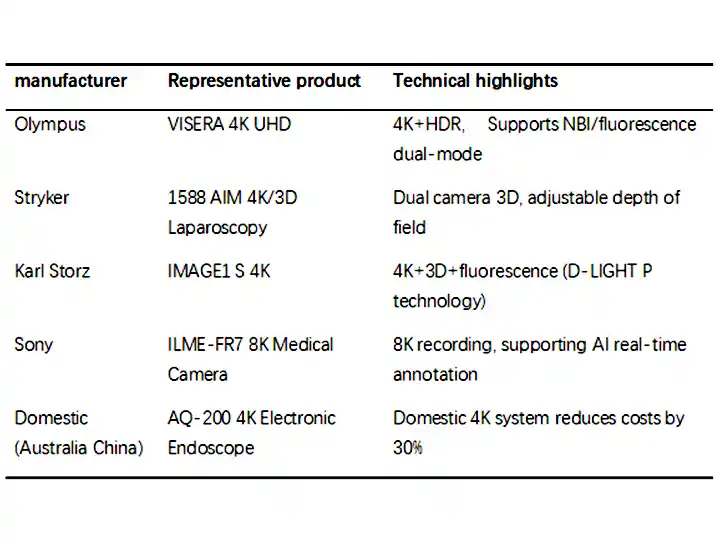
4. Representing manufacturers and products
5. Technical challenges and solutions
(1) The amount of data has increased dramatically
Problem: 4K/8K video traffic is high (4K requires ≥ 150Mbps bandwidth), and traditional devices experience transmission latency.
Solution:
Fiber optic signal transmission (such as Karl Storz's TIPCAM protocol).
Compression algorithm (HEVC/H.265 encoding).
(2) 3D dizziness problem
Problem: Some doctors are prone to fatigue when using 3D for a long time.
Solution:
Dynamic focal length adjustment (such as Stryker's AIM system, which can switch between 2D and 3D).
Naked eye 3D technology (experimental stage, no need for glasses).
(3) High cost
Problem: The price of a 4K endoscope system can reach 3 to 5 million yuan.
Breakthrough direction:
Domestic substitution (such as opening medical 4K endoscopes at a price only 50% of imported ones).
Modular design (only upgrading the camera, retaining the original host).
6. Future Development Trends
8K popularization+AI enhancement:
8K combined with AI for real-time lesion labeling (such as Sony's collaboration with Olympus to develop 8K+AI endoscopy).
3D holographic projection:
Intraoperative holographic image navigation (such as Microsoft HoloLens 2 integrating endoscopic data).
Wireless 4K/8K transmission:
5G network supports remote 4K surgical live streaming (as piloted by the General Hospital of the People's Liberation Army).
Flexible 3D endoscope:
Flexible 3D electronic endoscope (suitable for narrow airways such as bronchi and bile ducts).
summarize
4K/8K+3D endoscopic technology is reshaping the standard of minimally invasive surgery:
At the diagnostic level, the detection rate of early cancer has significantly increased, reducing missed diagnoses.
Surgical level: 3D vision reduces operational difficulty and shortens the learning curve.
In the future, the integration with AI, 5G, and holographic technology will usher in a new era of "intelligent surgery".
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS