Table of Contents
A video colonoscope captures real-time, high-definition images of the colon with a chip-on-tip camera, illuminates the lumen with a controlled light source, and routes signals to a processor and monitor while irrigation, suction, and accessory channels enable inspection, biopsy, and therapy in a single procedure.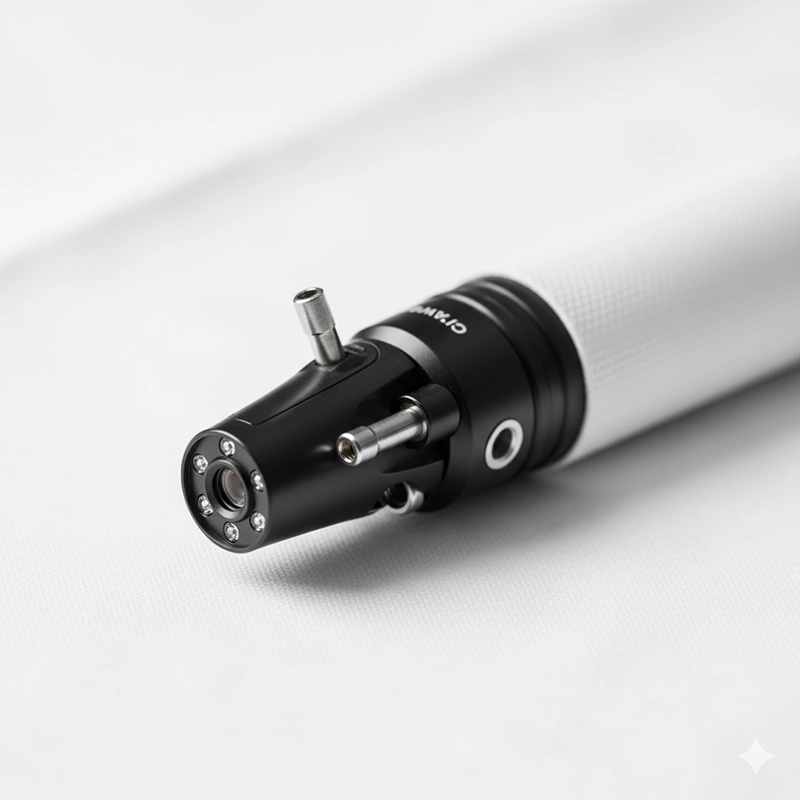
The complete workflow begins with patient and instrument preparation, continues through insertion, loop control, insufflation, imaging, careful withdrawal, documentation, and ends with validated reprocessing to return the device to clinical readiness.
Prepare patient, verify consent, confirm adequate bowel preparation, and complete time-out.
Leak test and function check the colonoscope, then white balance the optical system.
Insert with lubrication, minimize loops using torque steering and patient repositioning.
Use CO₂ for insufflation and targeted water exchange to keep the field clear.
Capture images via CCD/CMOS, process signals in the video processor, and display on the monitor.
Withdraw deliberately with enhanced imaging modes to maximize adenoma detection.
Perform biopsy or polypectomy when indicated; document with structured reports.
Clean, disinfect/sterilize, dry, and store according to validated protocols.
A modern colonoscope integrates optics, electronics, channels, and ergonomics to support both diagnosis and therapy. Throughout this article, “colonoscope” refers to a video-enabled instrument.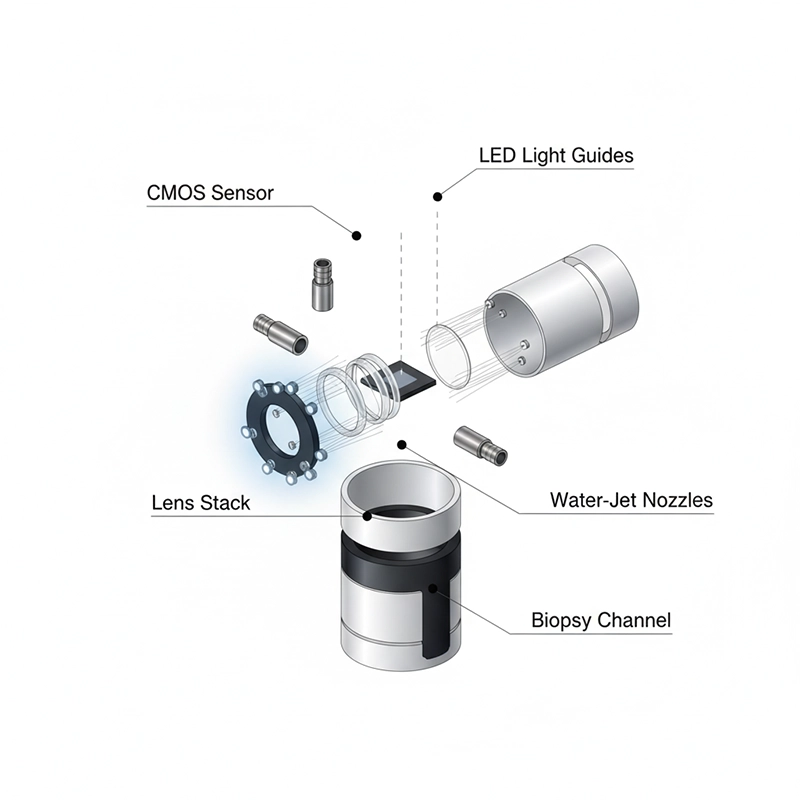
Back-illuminated CMOS or low-noise CCD provides high sensitivity and dynamic range.
Multi-element lens stack with anti-fog coatings preserves near-field detail on mucosa.
Nozzles deliver lens wash and targeted irrigation for debris removal.
LED or xenon light supplies a stable spectrum; LED reduces heat and maintenance.
Auto exposure and white balance preserve color fidelity for vascular patterns.
Layered construction combines torque wires, protective braid, and low-friction outer sheath.
Four-way angulation wheels and thumb levers allow precise tip control.
Tactile buttons control suction and insufflation; valves are removable for cleaning.
A working channel (≈3.2–3.7 mm) accepts biopsy forceps, snares, clips, and injection needles.
Video processor handles demosaicing, denoising, edge enhancement, and recording.
Light source and medical-grade monitor complete the imaging pipeline.
High-quality images depend on color accuracy, contrast, and motion clarity. The pipeline translates reflected photons into reliable pixels clinicians can interpret confidently.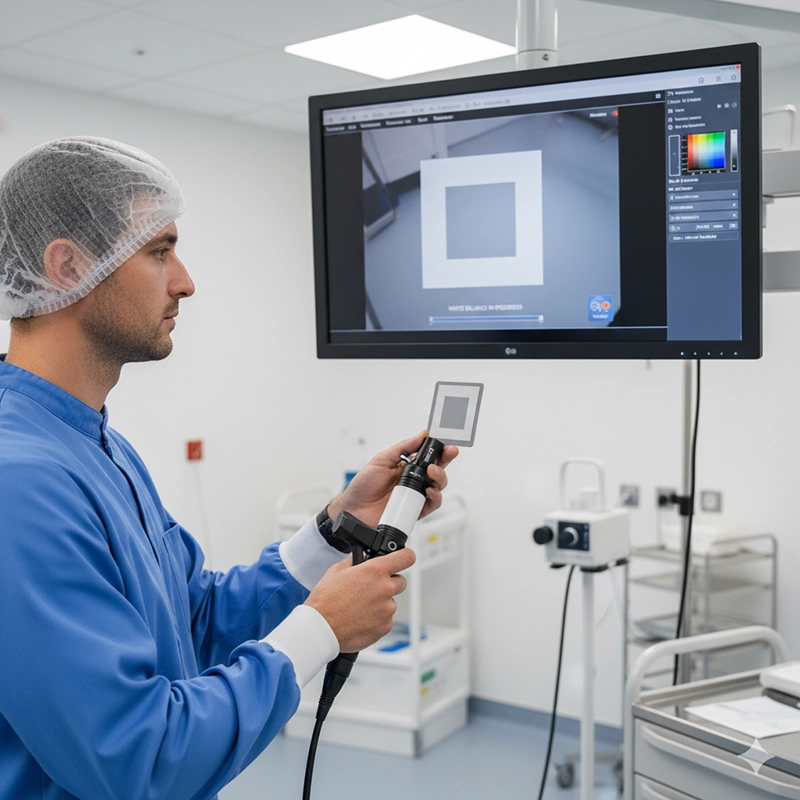
Technicians white-balance against a reference card to prevent color cast.
Balanced color reveals subtle erythema and pit patterns without artificial tint.
Demosaicing preserves micro-texture; gentle temporal denoise avoids waxy surfaces.
Edge enhancement remains moderate to avoid halos yet sharpen lesion borders.
Gamma mapping keeps deep folds and bright surfaces visible simultaneously.
Narrow Band Imaging emphasizes superficial vasculature and mucosal patterns.
Virtual or dye-based chromoendoscopy boosts contrast on flat lesions.
Magnification and close focus support pit-pattern assessment when available.
CO₂ insufflation reduces discomfort and speeds recovery compared with room air.
Water exchange floats folds open and rinses adherent mucus; the lens wash clears droplets.
| Mode / Tech | Typical Use | Visibility Gains | ADR Impact | Learning Curve |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD | Baseline white-light inspection | Clear mucosal texture, reduced blur | Associated with reliable baseline detection | Minimal |
| 4K | Fine-detail assessment, teaching | Sharper borders, improved microstructures | Associated with enhanced lesion recognition | Low |
| NBI | Vascular pattern evaluation | Highlights capillaries and pit patterns | Associated with improved flat lesion detection | Moderate |
| AFI | Metabolic contrast | Fluorescence differences between tissues | Adjunct in selected cases | Moderate |
| Chromo | Flat or subtle lesions | Enhanced surface contrast with dyes/virtual | Associated with improved delineation | Moderate |
Operators target cecal intubation, complete inspection during withdrawal, and minimize risk through standardized technique and checklists.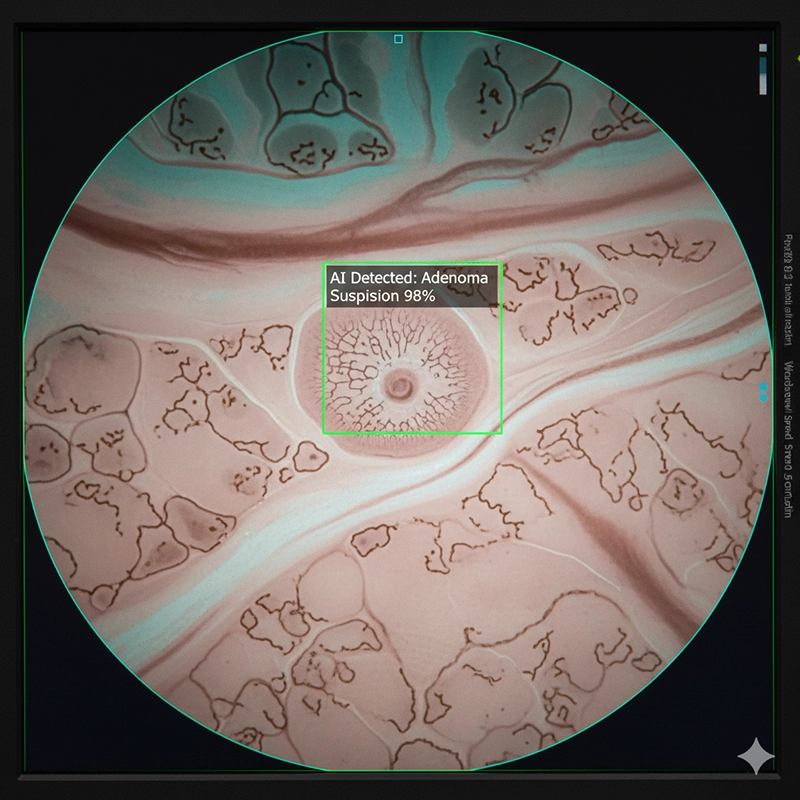
Split-dose bowel preparation increases mucosal visibility and detection rates.
Conscious sedation or anesthesiologist-led propofol enables comfort and stable vitals.
Scope function check confirms angulation, suction, irrigation, and image quality.
Use gentle torque steering rather than force; reduce loops early.
Reposition the patient to shorten the colon and expose hidden segments.
Identify cecal landmarks such as the appendiceal orifice and ileocecal valve.
Withdraw deliberately (often ≥6 min in average cases) while examining every haustral fold.
Alternate enhanced modes and white light; wash mucus and deflate overdistension.
Retroflex in the rectum when appropriate to evaluate the dentate line and distal folds.
Capture key images before and after intervention and append them to a structured report.
Sync stills and video to the hospital archive for audit and teaching.
Verify anticoagulation plan and thrombotic risk balancing before polypectomy.
Confirm equipment readiness: clips, injection needles, hemostatic tools available.
Use CO₂; avoid overinsufflation; reposition to reduce loops and wall stress.
Rinse frequently; maintain clear view to prevent blind advancement.
Standardize post-polypectomy instructions and contact pathways.
The working channel converts the colonoscope from a diagnostic camera into a therapeutic platform.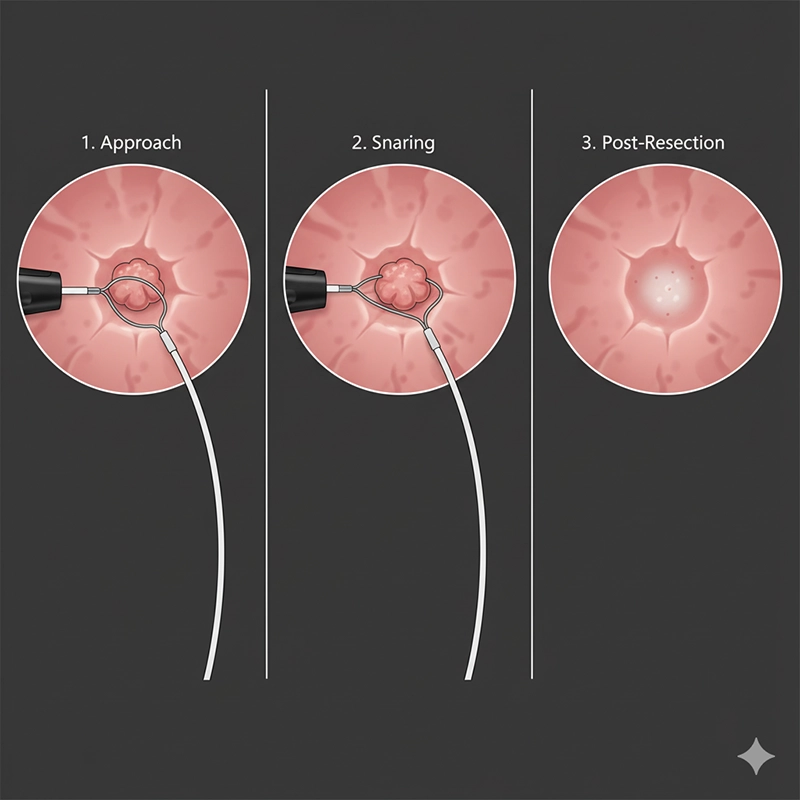
Cold snare suits diminutive and small sessile lesions.
Endoscopic mucosal resection lifts the lesion with submucosal injection before snaring.
Selected centers perform ESD for en bloc removal of superficial neoplasia.
Through-scope clips, coagulation forceps, and epinephrine injection control bleeding.
Tattooing with sterile carbon ink marks sites for surveillance or surgery.
Through-scope balloons dilate benign strictures under direct visualization.
Decompression techniques address sigmoid volvulus in appropriate cases.
Procurement and quality teams rely on objective metrics to compare systems and operators.
Cecal intubation rate reflects reliability of complete examinations.
Adenoma detection rate correlates with interval cancer risk reduction.
Withdrawal time, when paired with quality audits, promotes meticulous inspection.
Resolution, frame rate, and latency determine motion clarity during active suction and irrigation.
Channel diameter and suction flow influence debris clearance and tool compatibility.
Scope durability, bend-cycle testing, and repair incidence affect uptime.
Think beyond the sticker price of a colonoscope machine; total cost of ownership and outcomes drive value. Some buyers source directly from a colonoscope factory, while others prefer a colonoscope supplier for local service coverage. OEM endoscope and ODM endoscope options exist for tailored specifications.
HD/4K processing pipeline, latency, and monitor quality.
Ergonomics: wheel tension, button travel, weight distribution, handle shape.
Compatibility with existing processors, carts, and capture software.
Accessory ecosystem: snares, caps, injection needles, distal attachments.
Loaner availability, response time, and regional service teams.
Warranty scope across optics, angulation wires, and channels.
Training coverage for physicians, nurses, and reprocessing staff.
| Element | Driver | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition | Resolution tier, processor generation, bundle size | Sets depreciation baseline |
| Consumables | Valves, caps, snares, bite blocks | Predictable per-case cost |
| Reprocessing | Cycle time, chemistry, staffing | Determines true daily throughput |
| Maintenance | Angulation wire replacement, leak repairs | Impacts downtime and service calls |
| Training | Onboarding and refreshers | Improves safety and detection |
Processor compatibility with existing stacks and monitors.
Imaging tier (HD/4K) and available enhanced modes (NBI/virtual chromo).
Latency and frame rate under suction/irrigation load.
Working channel diameter and suction flow performance.
Distal tip profile, lens wash, and water-jet specs.
Handle ergonomics and control wheel tension adjustability.
Accessory ecosystem (snares, biopsy forceps, caps, injection needles).
Durability metrics (bend cycles, insertion tube abrasion resistance).
Sterilization/reprocessing compatibility and validated IFUs.
Unique device identification and serial tracking support.
DICOM/image export formats and EHR/PACS integration.
AI features: licensing model, on-processor vs cloud inference.
Service SLA: onsite response time, spare parts availability.
Loaner pool access and shipment logistics.
Preventive maintenance schedule and included calibrations.
Training coverage: physicians, nurses, reprocessing staff.
Warranty scope and exclusions (optics, angulation wires, channels).
Regulatory marks (FDA/CE/NMPA) for each model/stack pairing.
Energy efficiency and heat output (room HVAC impact).
Cart footprint and cable management accessories.
Total cost of ownership model and 5-year projections.
Trade-in/refresh options and roadmap alignment.
Option to source via colonoscope supplier vs colonoscope factory.
OEM/ODM customization options for branding or firmware.
Protecting the instrument protects the schedule, the budget, and patients. High-quality reprocessing is a clinical and economic imperative.
Flush channels and wipe exterior immediately to prevent biofilm formation.
Transport in closed, labeled containers to the decontamination area.
Leak test before immersion; document results for traceability.
Brush each lumen with the correct brush size; follow validated contact times.
Use compatible automated endoscope reprocessors with monitored chemistry.
Dry channels thoroughly; residual moisture threatens both safety and lifespan.
Avoid kinks: reduce loops early and respect angulation stops.
Prevent fogging: pre-warm scope and maintain a functional lens wash.
Eliminate blockages: never skip brushing; perform channel flow checks.
| Method | Cycle Steps | Typical Time per Scope | Consumables | Compliance Risk | Staff Dependency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual + HLD | Brush → Soak → Rinse → HLD → Rinse → Dry | Variable; depends on staff pace | Detergent, HLD chemistry, brushes | Higher (process variability) | High |
| AER | Manual clean → Automated cycle → Dry | Predictable per manufacturer spec | Validated chemistry cassettes | Lower (validated cycle parameters) | Moderate |
Standardized protocols and real-time readiness mitigate complications and improve patient experience.
Prefer CO₂ to lower discomfort and hasten recovery.
Track adverse events and review trends in quality meetings.
Keep rescue tools and medications immediately available.
Timely recognition and structured pathways reduce harm and support consistent care.
Assess flow and location; apply clip or coagulation as indicated.
Consider dilute epinephrine injection for oozing lesions.
Document photos pre/post hemostasis and plan for surveillance.
Provide clear post-procedure instructions and symptoms to watch.
Maintain rapid access pathway for return assessment and repeat endoscopy.
Record antithrombotic status and any bridging therapy used.
Stop advancement; decompress, assess size; clip closure if feasible.
Consult surgery early; arrange imaging as per protocol.
Capture images and complete incident documentation.
Evaluate for localized peritoneal signs without free air.
Manage supportively and monitor closely; escalate per protocol.
Follow sedation reversal and anaphylaxis algorithms.
Record agents, doses, onset time, and response in the report.
Integration with enterprise systems transforms images into durable, shareable clinical evidence and accelerates learning.
Store images and clips in DICOM where possible to simplify archiving and retrieval.
Use structured dictionaries for lesion descriptions and resection summaries.
Curate anonymized video colonoscope libraries for peer learning and resident training.
Simulation programs standardize loop reduction and withdrawal technique.
Sensor architecture and spectral techniques influence what the clinician can see and how reliably they can see it.
Modern CMOS brings low power, fast readout, and improved low-light sensitivity.
Back-illuminated designs increase quantum efficiency for dim, narrow lumens.
Future stacked sensors may integrate on-chip AI for real-time detection.
NBI narrows bands to accentuate capillaries and microvasculature.
Autofluorescence imaging contrasts metabolic differences in tissue.
Confocal endomicroscopy approaches cellular-level visualization in selected centers.
Units perform best when they optimize not only speed but also detection and documentation quality.
Balanced cecal intubation times and disciplined withdrawal improve ADR.
Throughput depends on reprocessing capacity and reliable staffing.
Dashboards that track ADR, withdrawal time, and complication rates drive improvement.
ADR: set an internal target above benchmark; review monthly.
CIR (cecal intubation rate): maintain high reliability across operators.
Photo-documentation completeness: define required landmarks per case.
Average withdrawal time: monitor by indication to avoid under-inspection.
Reprocessing compliance: audit cycle logs and drying documentation.
Scope turnaround time: align staffing to case start times.
Different acquisition paths trade cost for convenience and customization.
Lower unit price and custom shaft stiffness profiles.
Requires robust logistics and plans for on-site service coverage.
Faster service response, local training, immediate spares.
Typically higher upfront price due to distribution markup.
Private-label branding and standardized QC across fleets.
Stable long-term roadmap and predictable refresh cycles.
Firmware or processor features tailored to hospital workflows or AI overlays.
Best suited for group purchasing organizations and large clinic chains.
Compliance ensures patient safety and uninterrupted service.
Verify FDA, CE, or NMPA approvals for each model and processor pairing.
Align reprocessing with AAMI ST91 and ISO 15883; maintain complete cycle logs.
Conduct periodic audits and competency assessments for staff.
Modern systems embed intelligence to support detection, documentation, and education.
Real-time polyp detection highlights suspicious areas during withdrawal.
Quality analytics compute withdrawal time and photo documentation completeness.
Cloud-based review supports cross-site standardization in multi-hospital networks.
Although this article centers on colonoscopy, procurement often spans adjacent specialties to simplify service contracts and training.
Gastroscopy for upper GI work shares processors and carts.
Bronchoscopy equipment and the bronchoscope machine support airway visualization; some facilities source from a bronchoscope factory for consistency.
ENT endoscope equipment provides slim, maneuverable optics for sinonasal and laryngeal procedures.
Uroscope devices and uroscope equipment serve the urinary tract with compatible reprocessing workflows.
Orthopedic teams procure instruments from an arthroscopy factory, sometimes aligning carts and monitors across departments.
Demand continues to grow with population aging and expanding screening programs. Pricing varies by feature set and acquisition path.
Entry tiers focus on dependable HD at accessible pricing for community centers.
Mid tiers add advanced image modes, stronger processors, and broader accessory sets.
Premium tiers deliver 4K, advanced optics, and real-time AI assistance.
The following illustrative model helps procurement teams translate features into outcomes and costs. Figures are placeholders for planning and should be replaced with local data.
| Parameter | Baseline | Optimized | Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cases per day | 16 | 18 | Improved reprocessing turnaround and scheduling |
| Average withdrawal time | 6–7 min | 8–10 min | Quality protocol with imaging adjuncts |
| Scope turnaround | Unpredictable | Predictable | AER validation and staffing alignment |
| Cost Element | Share of TCO | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition | 35–45% | Depends on tier and bundle size |
| Reprocessing | 20–30% | Chemistry, water, staff time, AER maintenance |
| Maintenance/Repairs | 15–20% | Angulation wires, leak repairs, optics |
| Training | 5–10% | Onboarding, refreshers, competency checks |
| Consumables | 10–15% | Valves, caps, snares, bite blocks |
Adopt 4K + NBI and a standardized withdrawal protocol.
Track ADR monthly; target incremental improvement with coaching and water-exchange adoption.
Use dashboards to correlate detection with withdrawal time, bowel prep quality, and reprocessing readiness.
High-quality equipment achieves its potential only when clinicians and staff train systematically.
Simulation shortens learning curves for loop reduction and torque steering.
Video libraries built from the video colonoscope improve peer review and case conferences.
Credentialing tracks procedure numbers, ADR, and complication rates over time.
Innovation will improve visibility, safety, and efficiency while expanding compatibility across specialties.
Disposable insertion segments promise infection-control benefits with procurement trade-offs.
Modular tips may carry AI chips, spectral modules, or magnification optics.
Unified processors could drive colonoscopes, gastroscopes, bronchoscopes, uroscopes, and ENT scopes from a single video stack.
Procurement teams often evaluate the broader ecosystem after defining colonoscope needs. Positioning this section here preserves narrative focus on the video colonoscope through the earlier parts of the article.
Gastroscopy equipment supports esophagus, stomach, and duodenum examinations using compatible processors and accessories.
Bronchoscopy equipment, including the bronchoscope machine, visualizes the airway; standardized carts and monitors simplify cross-department training. Some hospitals buy from a bronchoscope factory to match connectors and service plans.
ENT endoscope equipment covers sinonasal and laryngeal exams with slim, highly maneuverable instruments.
Uroscope and uroscope equipment enable urology teams to diagnose and treat urinary tract conditions with shared reprocessing infrastructure.
Orthopedic services rely on devices from an arthroscopy factory; shared displays and capture software reduce IT complexity.
Depending on strategy, hospitals may work with a colonoscope supplier for fast local service or partner directly with a colonoscope factory for custom specifications. OEM endoscope and ODM endoscope pathways allow branding or firmware customizations that harmonize with the broader endoscopic fleet.
A modern video colonoscope blends optics, electronics, channels, and ergonomics to deliver precise diagnosis and therapy in one pass. Choose equipment by outcomes and lifetime economics, align with reliable partners, and maintain rigorous reprocessing and training. With the right system and processes, teams raise adenoma detection, reduce complications, and deliver efficient, patient-centered care.
Buyers should confirm whether the device supports HD or 4K output, enhanced modes such as Narrow Band Imaging, and request test videos from the supplier for direct comparison.
Direct factory sourcing often allows customization of insertion tube stiffness and lower unit prices, but hospitals must plan for international logistics and slower on-site service.
A supplier typically offers faster response times, loaner scopes, and local training, though with slightly higher acquisition costs.
Yes, OEM/ODM endoscope partners can modify branding, presets, or even integrate AI-assisted features. MOQ and development timelines should be clarified.
Suppliers should include accessory kits and clinical guidelines for bleeding, perforation, or post-polypectomy syndrome management, ensuring patient safety.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS