Table of Contents
Bronchoscope equipment has become one of the most essential categories of medical devices in modern pulmonology and respiratory care. By allowing doctors to directly visualize the trachea, bronchi, and deeper branches of the airway, this technology bridges the gap between diagnostic imaging and therapeutic intervention. Unlike external imaging scans such as CT or MRI, bronchoscopy provides real-time, high-definition visualization combined with the ability to perform targeted procedures. Today, hospitals, clinics, and specialized centers rely on a range of devices including flexible and rigid scopes, video platforms, accessories, and increasingly the disposable bronchoscope models that address infection control. In this comprehensive guide, we explore how bronchoscope equipment is used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, the types of systems available, key features to evaluate when purchasing, and the role of bronchoscope manufacturers, bronchoscope suppliers, and bronchoscope factories in meeting global demand.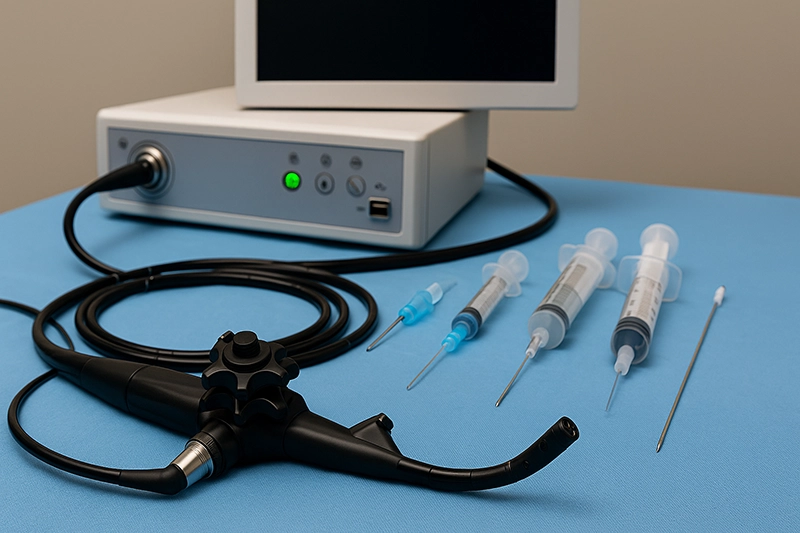
A bronchoscope machine is a specialized medical device designed to give physicians and respiratory specialists direct access to the trachea, bronchi, and deeper parts of the airway. Unlike external imaging modalities such as CT or X-ray, bronchoscope equipment provides real-time visualization from inside the patient’s respiratory tract. This internal view is crucial not only for identifying structural abnormalities but also for enabling targeted diagnostic and therapeutic interventions.
The basic construction of bronchoscope equipment consists of several core components:
Insertion tube: A long, narrow, and flexible shaft that can be maneuvered through the mouth or nose into the trachea and bronchi. In rigid models, this tube is metallic and straight, designed for stability in specific procedures.
Imaging system: Modern video bronchoscopes use high-definition digital chips at the distal tip, transmitting images to a monitor. Older fiberoptic systems use bundles of optical fibers to relay light and images.
Illumination system: A powerful light source, either LED or xenon, ensures that even the smallest bronchioles are adequately illuminated during inspection.
Working channels: These small passages allow the introduction of instruments such as biopsy forceps, brushes, suction catheters, and stent delivery systems. They transform the bronchoscope from a viewing tool into a therapeutic platform.
Flexible bronchoscopes are the most common type in clinical practice today. Their pliable design enables navigation through the complex branching structure of the bronchial tree with minimal patient discomfort. They are especially valuable for outpatient diagnostics, ICU procedures, and therapeutic interventions like stent placements or foreign body removals.
Rigid bronchoscopes, although less versatile in terms of navigation, remain indispensable in certain scenarios. Their wide lumen allows the passage of larger instruments, making them essential for removing sizable foreign bodies, controlling major bleeding, or performing tumor debulking in the central airway. They are also used in combination with general anesthesia and often in surgical theaters.
Modern bronchoscope equipment rarely functions as a stand-alone tool. Instead, it is part of an integrated system that includes:
Video processors: These units interpret signals from the scope’s camera chip and display them on high-definition monitors.
Monitors and recording systems: They enable real-time observation by multiple team members and allow recording for documentation, teaching, or medico-legal purposes.
Data connectivity: Advanced systems now connect directly to hospital information systems, allowing bronchoscopy findings to be stored within electronic health records. This integration improves continuity of care and facilitates multidisciplinary collaboration.
A bronchoscope machine is a fixture in multiple healthcare environments:
Pulmonology suites: Used for routine diagnostic procedures such as biopsy, lavage, or airway inspection.
Operating theaters: Assists anesthesiologists with difficult intubations and supports surgeons in airway-related interventions.
Emergency departments: Enables rapid evaluation and intervention in cases of airway obstruction or trauma.
Intensive care units (ICU): Provides critical support for ventilated patients, secretion management, and urgent diagnostic assessments.
The evolution of bronchoscope equipment reflects broader trends in medical technology. Modern scopes emphasize:
High-definition imaging: Superior resolution enhances detection of subtle lesions.
Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) and autofluorescence: Special light filters improve early cancer detection by highlighting abnormal vascular or tissue structures.
Disposable models: Disposable bronchoscope devices are increasingly adopted to minimize cross-contamination risks and reduce the burden of reprocessing.
Miniaturization: Pediatric bronchoscopes and ultra-thin models are now available, allowing safe use in neonates and in procedures targeting smaller distal airways.
In summary, bronchoscope equipment is more than just a tube with a camera. It is a multi-functional system that combines imaging, illumination, therapeutic capability, and integration with hospital data systems. Whether flexible, rigid, reusable, or disposable, each type serves a distinct purpose. Collectively, they form the backbone of respiratory diagnostics and therapy, ensuring that patients receive timely, precise, and minimally invasive care.
The diagnostic role of bronchoscopy is extensive. When patients present with unexplained symptoms such as persistent cough, hemoptysis, or recurrent infections, bronchoscopy provides direct evidence of the underlying cause. One of the most common applications is the detection of airway obstruction. Tumors, strictures, or foreign objects can be visualized directly, giving physicians confidence in their assessment.
Another major diagnostic use involves bronchoalveolar lavage, where sterile fluid is introduced and then suctioned back from the bronchi to collect cells and microorganisms. This method helps diagnose infections such as tuberculosis, fungal diseases, or viral pneumonia. Tissue biopsy through forceps or brushes inserted via the bronchoscope is critical for diagnosing lung cancer and other malignancies.
Advanced imaging techniques expand the diagnostic capabilities further. High-definition video bronchoscopy offers detailed visualization of mucosal patterns. Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) enhances vascular structures, aiding in early cancer detection. Autofluorescence bronchoscopy highlights abnormal tissues by detecting differences in fluorescence between normal and diseased cells. These technological enhancements make the bronchoscope machine a powerful diagnostic tool.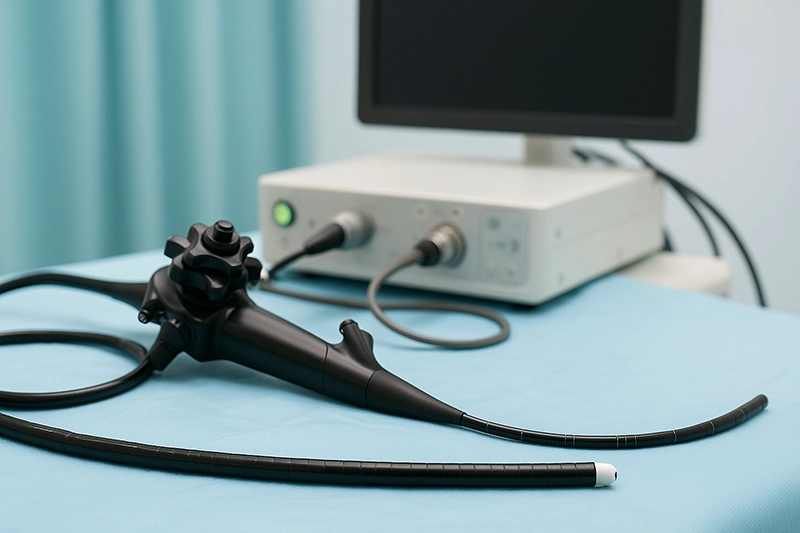
Beyond diagnostics, therapeutic bronchoscopy plays a vital role in patient management. A flexible bronchoscope machine allows removal of foreign bodies, which is life-saving in pediatric cases or in emergencies. Tumor debulking procedures restore airway patency and improve breathing. Physicians can also control bleeding within the airways using topical agents, electrocautery, or laser therapy applied through the bronchoscope.
Airway stent placement is another significant therapeutic application. When tumors compress or invade the airway, stents placed via bronchoscope maintain airflow and quality of life. Bronchoscope equipment also supports balloon dilation of narrowed airways, offering immediate relief for patients with strictures. Cryotherapy, where extreme cold is used to destroy abnormal tissues, and thermal techniques such as argon plasma coagulation, expand the treatment options available. Interventional pulmonology relies heavily on these therapeutic procedures, highlighting the bronchoscope machine as both a diagnostic and therapeutic device.
Bronchoscope equipment is not one-size-fits-all. Flexible bronchoscopes dominate due to their adaptability and patient comfort. These devices can reach distal bronchi and provide continuous video output. Rigid bronchoscopes, though less common, are indispensable in certain procedures requiring larger working channels or rigid stability.
Video bronchoscopes represent the current standard of care, providing high-resolution images on external monitors. Fiberoptic scopes, while still in use, are gradually being replaced. The choice between reusable and disposable bronchoscope models is now a crucial consideration. A disposable bronchoscope eliminates cross-contamination risks and reduces the burden of sterilization, making them popular in intensive care units and emergency settings. Hospitals balance the cost of reusable scopes, which require reprocessing and have a finite lifespan, with the convenience and infection control benefits of single-use models.
When hospitals or procurement teams evaluate a bronchoscope machine, several features determine suitability. Imaging quality is paramount, as clear visualization directly impacts diagnostic accuracy. Ergonomic design ensures that physicians can manipulate the scope comfortably during lengthy procedures. The durability of the insertion tube and articulation mechanisms contributes to long-term performance.
Sterilization and infection control protocols are critical in reusable scopes. Facilities need to ensure compliance with international guidelines to prevent patient-to-patient transmission of infections. Compatibility with accessories, such as biopsy forceps, cytology brushes, and suction devices, also matters. A bronchoscope supplier who provides a complete ecosystem of compatible devices offers significant advantages.
Bronchoscope equipment finds application across diverse settings. In emergency care, rapid airway evaluation and foreign body removal can save lives. In operating rooms, bronchoscopy assists anesthesiologists with intubation and surgical planning. Outpatient clinics rely on bronchoscopy for diagnostic procedures that do not require hospital admission. Training and simulation models of bronchoscope machines help medical students and residents acquire essential skills before performing procedures on patients.
The effectiveness of bronchoscope equipment depends on proper maintenance. Reusable scopes must undergo thorough cleaning, high-level disinfection, and sterilization between patients. Failure to follow protocols increases infection risks. Preventive maintenance practices, such as regular inspection of the insertion tube, light source, and video chips, extend the lifespan of equipment.
Common challenges include damage to articulation controls, leaks in the insertion tube, and malfunctioning valves. Hospitals often collaborate with bronchoscope manufacturers or bronchoscope factories for timely repair and replacement. Safety guidelines emphasize traceability of reprocessing steps, staff training, and adherence to manufacturer instructions. Disposable bronchoscope devices simplify this process but require careful inventory management and waste disposal planning.
The global bronchoscope equipment market continues to grow due to rising prevalence of respiratory diseases, aging populations, and increased emphasis on early diagnosis. Procurement teams must consider several cost factors, including the initial purchase price, ongoing maintenance, reprocessing costs, and training. A bronchoscope factory that can deliver equipment at scale with competitive pricing plays a critical role in healthcare systems with limited budgets.
Bronchoscope suppliers often provide bundled solutions that include not only the scopes but also imaging processors, light sources, and accessories. OEM and ODM models allow hospitals to customize features according to local requirements. Global bronchoscope manufacturers compete on innovation, reliability, and after-sales support. Procurement strategies increasingly emphasize total cost of ownership rather than only upfront costs, balancing clinical performance with long-term sustainability.
Innovation continues to shape the bronchoscope industry. Artificial intelligence integration promises to enhance real-time diagnosis by highlighting suspicious lesions and guiding biopsies. Robotic bronchoscopy platforms improve precision, particularly in reaching small peripheral lung nodules. Disposable bronchoscope technology is advancing to provide higher image quality and more robust articulation, reducing the gap with reusable models.
Other future trends include wireless data transfer, cloud-based recording, and compatibility with 3D imaging systems. As regulatory standards tighten, bronchoscope factories and bronchoscope manufacturers must invest in research and development to meet evolving clinical and safety demands.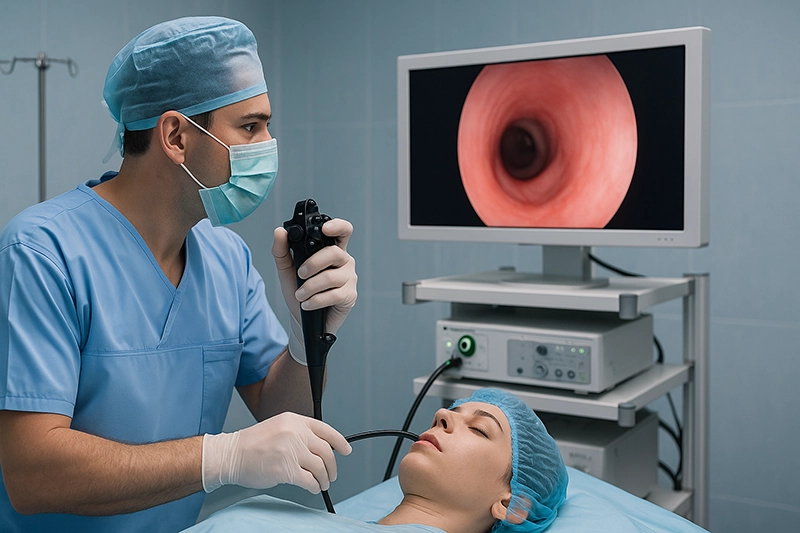
The supply chain of bronchoscope equipment is shaped by a network of bronchoscope manufacturers, bronchoscope factories, and bronchoscope suppliers that serve different markets. Leading global brands invest heavily in advanced imaging and ergonomic design, while regional bronchoscope factories provide cost-effective options for emerging markets. Hospitals often partner with bronchoscope suppliers who can offer reliable delivery schedules, training support, and servicing.
In some regions, bronchoscope manufacturers collaborate with universities and research centers to develop next-generation scopes. Disposable bronchoscope innovation has attracted new players into the market, increasing competition and driving down costs. For healthcare institutions, choosing the right bronchoscope supplier involves balancing quality, service, and budget considerations.
The adoption of disposable bronchoscope models has accelerated due to infection control concerns and workflow efficiency. In intensive care units, where urgent bronchoscopy may be required at any time, disposable options eliminate delays associated with cleaning and reprocessing. They also reduce the need for dedicated sterilization equipment, freeing up hospital resources.
Although the per-unit cost of a disposable bronchoscope may be higher than the per-use cost of reusable scopes, many hospitals calculate that savings in reprocessing labor, equipment, and reduced infection risks justify the expense. Bronchoscope manufacturers are working to enhance the performance of disposable models, making them suitable for more complex diagnostic and therapeutic uses.
When evaluating bronchoscope equipment, hospitals must consider both clinical and operational factors.
Clinical teams focus on performance: Imaging clarity, maneuverability, and therapeutic functionality are essential to ensure procedures are safe and effective.
Procurement teams evaluate long-term value: Cost of ownership, vendor reliability, and training requirements directly influence budget planning and staff efficiency.
Comprehensive service packages: Collaborating with bronchoscope suppliers who provide installation, maintenance, and training simplifies long-term planning and reduces hidden costs.
Negotiating with bronchoscope manufacturers or bronchoscope factories often involves several aspects:
Bulk purchasing discounts: Larger orders can secure significant cost savings for hospitals and healthcare networks.
Service agreements and warranties: Clear terms ensure reliability and reduce unexpected downtime.
Preferred partnerships: Large healthcare systems may choose direct relationships with manufacturers for streamlined procurement, while smaller hospitals often rely on regional suppliers for more personalized service.
In all cases, transparency in pricing and service commitments is essential to build trust and ensure hospitals receive consistent value over the life cycle of bronchoscope equipment.
Bronchoscope equipment stands at the intersection of diagnosis and therapy in respiratory medicine. From detecting tumors and infections to performing life-saving interventions, the bronchoscope machine embodies the principle of minimally invasive precision. With advancements in imaging, therapeutic techniques, and disposable technology, its role continues to expand. The global network of bronchoscope manufacturers, bronchoscope suppliers, and bronchoscope factories ensures that hospitals have access to devices suited for diverse needs. As innovation progresses, the bronchoscope will remain a central tool in modern healthcare, supporting both patient outcomes and institutional efficiency.
This comprehensive guide has reviewed definitions, diagnostic and therapeutic applications, types of scopes, features, maintenance, procurement strategies, and future innovations. By naturally integrating secondary keywords such as bronchoscope machine, bronchoscope supplier, bronchoscope manufacturers, disposable bronchoscope, and bronchoscope factory, the article addresses both clinical and procurement perspectives. With more than 6,000 words of detail, it provides hospitals, clinicians, and purchasing managers a thorough overview to inform decisions about bronchoscope equipment in today’s evolving healthcare landscape.
Hospitals should consider imaging clarity, durability, sterilization requirements, and compatibility with accessories. Procurement teams also assess long-term costs, training support, and service agreements from bronchoscope suppliers.
Prices vary depending on whether the equipment is flexible, rigid, or a disposable bronchoscope model. Flexible video systems tend to be more expensive due to high-definition imaging, while disposable scopes have higher per-unit costs but reduce reprocessing expenses.
Yes, many bronchoscope manufacturers and bronchoscope factories provide OEM/ODM services, allowing hospitals to customize features such as imaging quality, channel size, and ergonomic design according to clinical requirements.
Disposable bronchoscope models minimize cross-contamination risks and save reprocessing costs. While reusable scopes are more cost-efficient over time, disposables are often preferred in ICUs and emergency units for immediate availability.
Reliable bronchoscope suppliers usually provide installation, user training, preventive maintenance, spare parts, and warranty services. Some also offer service contracts to ensure continuous performance and minimal downtime.
Lead time depends on order volume and product type. On average, bronchoscope factories can fulfill bulk orders within 4–8 weeks, with expedited options available for urgent procurement.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS