Table of Contents
Video laryngoscopes are advanced airway devices that visualize the larynx and vocal cords during intubation. By combining a camera and display, a video laryngoscope improves first-pass success, reduces complications, and supports safer procedures in operating rooms, ICUs, and emergency settings. Global hospital adoption reflects technology progress, procurement preferences, and the evolving role of laryngoscope equipment in modern care.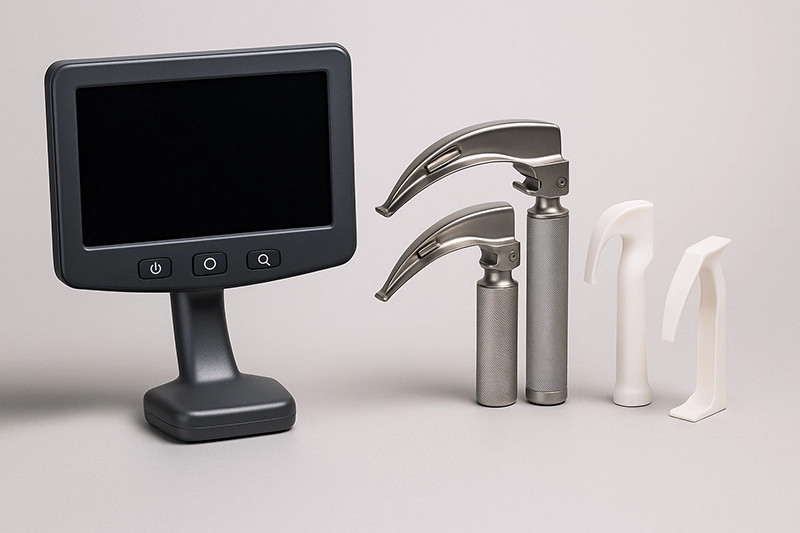
Demand for video laryngoscope solutions has grown as hospitals modernize airway protocols and replace conventional laryngoscope equipment. Compared with a direct laryngoscope, a video laryngoscope offers indirect visualization and shared viewing for training, making it valuable for anesthesiology, emergency medicine, and otorhinolaryngoscope practice. Hospital leaders evaluate where to transition from a traditional laryngoscope machine to a video-enabled platform that supports consistency, safety, and teaching.
High-definition optics and anti-fog design maintain image clarity during intubation.
Blade options include disposable and reusable formats to balance infection control and cost.
Portable, wireless, and battery-powered video laryngoscope units expand prehospital use.
Preference for safer airway techniques compared with direct laryngoscopes.
Standardization across OR, ICU, and ED improves difficult-airway response.
Integrated screens allow supervisors and trainees to observe the airway in real time.
North America and Europe: high adoption driven by patient-safety benchmarks.
Asia–Pacific: rapid expansion of surgical capacity and investment in laryngoscope equipment.
Emerging markets: affordability programs and stepwise upgrades from basic laryngoscope machines.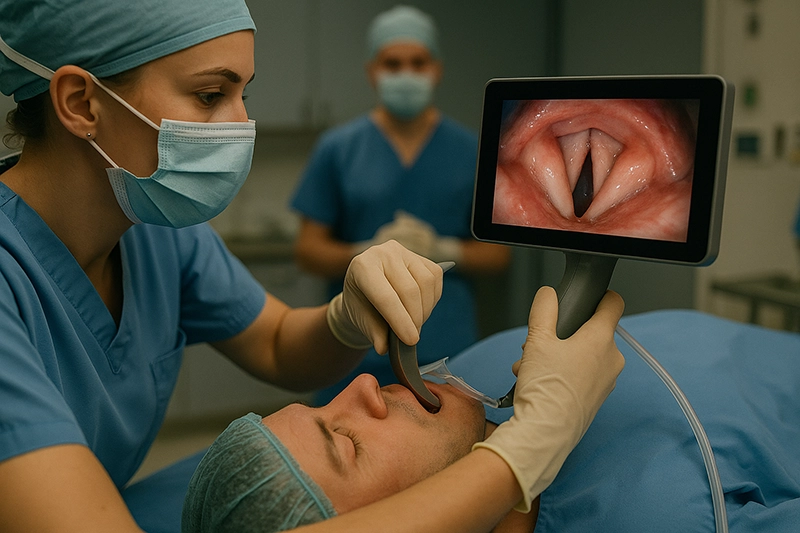
Higher first-pass success reduces hypoxia, aspiration, and airway trauma.
Improved visualization assists in cervical spine injury, obesity, and pediatric cases.
Shared view enhances team communication during critical procedures.
Upfront purchase vs. lifecycle value when replacing a legacy laryngoscope machine.
Ongoing costs for blades, batteries, maintenance, and staff training.
Disposable blades favored for infection control; reusable options lower long-term spend.
Compliance with national and international accreditation standards.
Evaluation of laryngoscope manufacturers for reliability, warranties, and service.
Selection of a laryngoscope supplier with stable logistics and clinician training support.
Simulation-based curricula for residents and emergency physicians.
Device-specific competency checklists to standardize technique and troubleshooting.
Use of recorded cases for debriefing and quality improvement.
Close coordination among anesthesia, ICU, ED, and otorhinolaryngoscope teams.
Shared protocols guiding blade choice, preoxygenation, and backup plans.
Peer teaching supported by the screen of a video laryngoscope during live cases.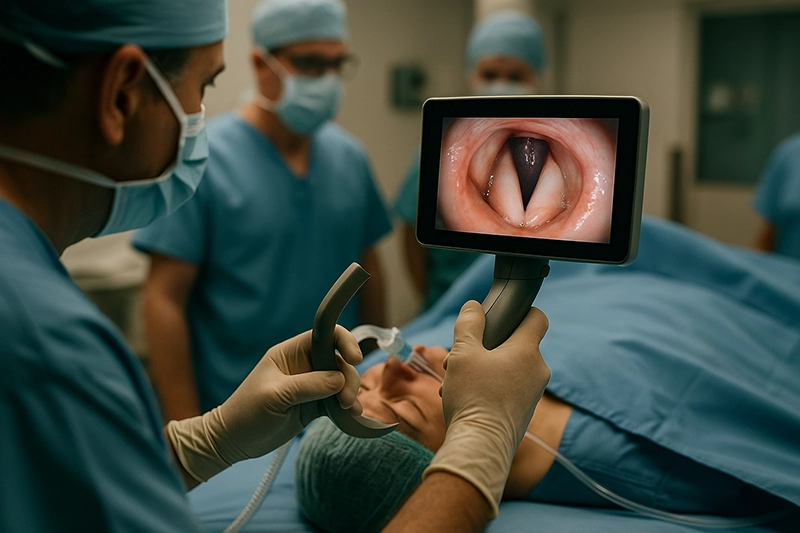
Budget constraints in small hospitals and resource-limited regions.
Fleet management of mixed laryngoscope equipment across departments.
Variation among models complicates stocking, reprocessing, and training.
Uneven availability of devices and consumables affects care equity.
Lack of standardized blade sizes and connectors across brands.
Need for unified documentation to streamline onboarding for rotating staff.
AI-assisted airway landmark recognition and decision support.
Lighter, more durable handheld units with extended battery life.
Integration with hospital data systems for audit, training, and QI analytics.
Gradual replacement of legacy laryngoscope machines with video-first platforms.
Public–private partnerships to improve access to essential laryngoscope equipment.
Tiered product lines enabling adoption from primary hospitals to tertiary centers.
Regulatory credentials (e.g., ISO-aligned quality systems) and transparent test data.
OEM/ODM customization from laryngoscope manufacturers to fit clinical workflows.
Responsive laryngoscope supplier support: onboarding, troubleshooting, and spare parts.
Forecasting blades and accessories to prevent stockouts during peak demand.
Service-level agreements covering uptime, repair turnaround, and loaner devices.
Total cost of ownership modeling across training, maintenance, and disposables.
Diagnostic visualization for vocal fold pathology and airway lesions.
Support for pediatric and difficult-airway protocols in ENT clinics and ORs.
Adjunct to teaching in otorhinolaryngoscope departments through shared displays.
Unified guidance for preoxygenation, device selection, and backup supraglottic airways.
Checklists for rapid sequence intubation incorporating a video laryngoscope.
Post-case reviews using recorded footage for team learning.
As hospitals expand advanced airway programs, a video laryngoscope complements traditional laryngoscope equipment and raises the standard of care. Partnering with capable laryngoscope manufacturers and a reliable laryngoscope supplier ensures availability, training, and service continuity, helping teams deliver safer intubation across anesthesia, critical care, emergency medicine, and otorhinolaryngoscope practice.
A qualified manufacturer must show ISO 13485, CE/MDR compliance, and in some regions FDA clearance. These ensure the video laryngoscope meets global safety and performance standards.
Yes. Many models are lightweight, battery-operated, and designed for rugged environments, making them ideal for emergency and pre-hospital intubation scenarios.
Although the initial investment is higher, savings come from reduced complications, fewer ICU transfers, lower training costs, and extended device longevity, making the video laryngoscope cost-effective over time.
Most require routine battery checks, blade inspection, and cleaning compatible with hospital sterilization workflows. Advanced models may need periodic software updates.
Some advanced systems allow video recording and data export into hospital databases for training, quality control, and legal documentation.
Yes. Single-use blades reduce cross-contamination risk, especially valuable in emergency or pandemic settings, though they increase disposable costs.
Bundled contracts can secure volume discounts, include both capital equipment and consumables, guarantee service coverage, and standardize training across departments, lowering the per-case cost of video laryngoscope use.
Reliable suppliers provide 24/7 technical support, rapid spare part delivery, training sessions for clinicians, and preventive maintenance programs. This reduces downtime and ensures consistent hospital use of the video laryngoscope.
By creating a structured evaluation matrix that scores each model on imaging quality, blade compatibility, sterilization workflow, service warranty, and overall cost, hospitals can objectively select the most suitable video laryngoscope.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS