Table of Contents
A hysteroscope is one of the most indispensable tools in modern gynecology. It allows physicians to directly visualize the uterine cavity, diagnose abnormalities, and perform precise treatments with minimal trauma. The importance of the hysteroscope in women’s health care lies in its ability to merge diagnosis and therapy into a single, minimally invasive procedure—reducing pain, shortening recovery time, and improving fertility outcomes. In hospitals and clinics worldwide, hysteroscopic technology has become the cornerstone of reproductive health management and early intervention.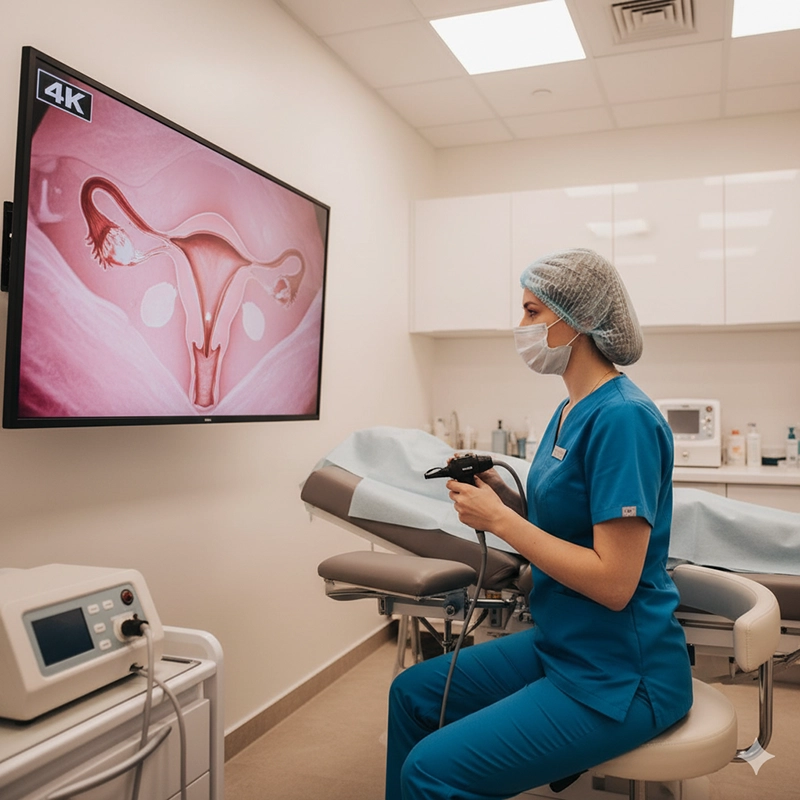
Before hysteroscopy became routine, uterine disorders were often diagnosed indirectly through imaging or exploratory surgery. These methods were either inconclusive or invasive. The introduction of the hysteroscope revolutionized gynecologic diagnostics by enabling direct visualization of the endometrium, polyps, fibroids, and adhesions. In real time, clinicians can evaluate uterine health, take biopsies, or treat abnormalities with precision instruments introduced through the same channel.
Traditional dilation and curettage (D&C) procedures offered limited visual feedback and higher risk of incomplete removal.
Hysteroscopy allows targeted treatment with minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
Patients experience faster recovery and lower rates of infection or uterine scarring.
This transition from “blind curettage” to “guided intervention” redefined patient outcomes. It reduced unnecessary hysterectomies and preserved fertility for millions of women, marking one of the most impactful technological evolutions in gynecology.
The versatility of the hysteroscope extends across nearly all stages of a woman’s reproductive life. It plays a crucial role in diagnosing abnormal uterine bleeding, investigating infertility, managing intrauterine adhesions, removing retained products of conception, and evaluating postmenopausal bleeding. Hysteroscopy bridges preventive medicine and reproductive care, making it a central component of women’s health programs worldwide.
| Clinical Indication | Hysteroscopic Application |
|---|---|
| Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) | Direct evaluation of endometrium and polyp removal |
| Infertility work-up | Detection of uterine septum, fibroids, or adhesions |
| Recurrent miscarriage | Assessment of uterine shape anomalies |
| Endometrial cancer screening | Targeted biopsy under direct vision |
| Intrauterine foreign body | Visual retrieval of IUD or retained tissue |
These applications underscore why hysteroscopy is not a niche technique but a multidisciplinary diagnostic and therapeutic platform. It connects reproductive endocrinology, oncology, and obstetrics under one minimally invasive discipline.
Modern hysteroscopy has evolved far beyond basic fiber-optic systems. Today’s devices employ HD and 4K video sensors, integrated LED illumination, and flexible control sheaths that allow physicians to maneuver within the uterine cavity safely. Manufacturers like XBX have pioneered digital hysteroscope systems combining compact camera heads with ultra-thin insertion tubes, offering superior clarity and reduced discomfort.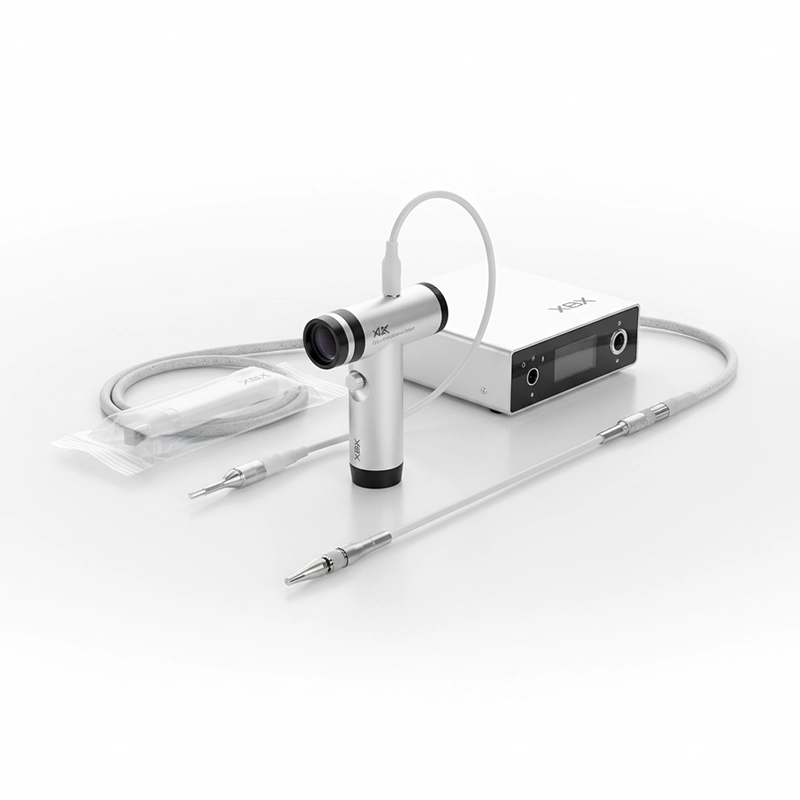
Full-HD or 4K CMOS sensors with natural color rendering.
Adjustable viewing angles from 0° to 30° for optimal visualization.
Anti-fog optics and waterproof connectors for sterile reprocessing.
Lightweight ergonomic handles that reduce surgeon fatigue.
The evolution of the hysteroscopic camera has paralleled that of general endoscopy—smaller, clearer, and more integrated. Digital transmission enables seamless recording and live teaching, while AI-assisted software now aids in detecting endometrial irregularities automatically. These advancements reduce diagnostic subjectivity and enhance patient safety.
From the patient’s perspective, hysteroscopy represents empowerment. Procedures once requiring general anesthesia and hospital stays can now be performed in outpatient settings under mild sedation. Pain levels are minimal, and recovery typically occurs within hours. Studies show that over 90% of women prefer office hysteroscopy over conventional surgical alternatives.
Reduced hospital admission and faster return to daily activities.
Minimized postoperative complications and infections.
Lower overall treatment costs per episode of care.
Preservation of fertility through uterine conservation.
In infertility treatment, hysteroscopy has become indispensable. Correcting uterine septa, removing fibroids, or treating adhesions under direct vision significantly improves implantation rates in assisted reproduction. In oncology, it allows early detection of precancerous changes, enabling preventive intervention long before symptoms appear.
For healthcare institutions, adopting advanced hysteroscopic systems offers clear operational advantages. Unlike laparoscopic or open gynecologic surgeries, hysteroscopy requires minimal infrastructure. A single outpatient room equipped with an HD monitor and hysteroscopy machine can handle dozens of procedures daily, dramatically improving patient throughput.
Minimal consumables compared with open or laparoscopic surgeries.
Shorter turnaround time between cases (15–20 minutes).
Reduced need for operating room scheduling and inpatient beds.
Compatibility with reusable and disposable instrument options.
In countries emphasizing value-based healthcare, such as the United States and Germany, hysteroscopy aligns perfectly with performance metrics: lower costs per diagnosis, fewer complications, and higher patient satisfaction. For hospital administrators, investing in a high-quality XBX hysteroscope system becomes both a clinical and financial decision—improving outcomes while optimizing operational efficiency.
Because hysteroscopy involves intrauterine access, device sterility and optical reliability are critical. Regulatory agencies including the FDA and EMA enforce stringent certification for all hysteroscopic systems. XBX hysteroscopes are CE and ISO13485 certified, ensuring compliance with European and global standards. Hospitals are encouraged to maintain validated sterilization cycles or adopt single-use sheaths to prevent cross-contamination.
Rinse immediately after use to remove biological debris.
Disinfect using enzymatic solutions followed by autoclaving.
Use protective storage trays to prevent optical misalignment.
Perform routine leak testing and lens inspection.
Some hospitals now employ semi-disposable hysteroscopic systems combining a reusable camera with sterile single-use sheaths. This hybrid model achieves both safety and sustainability, minimizing waste while maintaining infection control.
The role of hysteroscopy extends beyond diagnosis and treatment—it is a preventive instrument. Early hysteroscopic screening in women with unexplained bleeding or infertility can detect abnormalities at a reversible stage. Preventive hysteroscopy reduces healthcare burden by addressing pathologies before they evolve into chronic or malignant conditions.
Japan’s national infertility guidelines include routine hysteroscopic evaluation before IVF.
European reproductive centers recommend hysteroscopy for all women with recurrent miscarriage.
Developing regions increasingly use portable hysteroscopes for outreach gynecologic screening.
These public health strategies highlight hysteroscopy’s growing contribution to population-level well-being. By improving reproductive health and preventing cancer, hysteroscopy enhances quality of life for women worldwide.
The future of hysteroscopy is shaped by miniaturization, digital integration, and sustainability. Compact systems with integrated light sources and wireless video output are making the procedure more accessible even in small clinics. Artificial intelligence will play a larger role in automatic lesion recognition, documentation, and predictive analytics for uterine pathology.
3D hysteroscopic imaging for enhanced spatial orientation.
Wireless handheld hysteroscopes for remote gynecologic care.
Biodegradable single-use hysteroscope sheaths reducing medical waste.
Cloud-connected platforms for AI-assisted diagnosis and patient record storage.
In the next decade, the global hysteroscopy market is projected to exceed USD 2.8 billion, driven by rising fertility treatment demand and hospital digitization. Emerging economies will benefit most, as compact digital systems such as the XBX 4K Hysteroscope lower the entry barrier for modern uterine care.
For hospital decision-makers, integrating hysteroscopic systems requires evaluation beyond price. Considerations include image resolution, ergonomics, sterilization compatibility, and after-sales service. Reliable suppliers provide comprehensive training for physicians and nurses, ensuring safe operation and maintenance.
| Evaluation Criteria | Recommended Standard |
|---|---|
| Certification | ISO13485, CE, FDA |
| Image Quality | Full-HD or 4K CMOS sensor |
| Optical Diameter | ≤3.5 mm for diagnostic, ≤5 mm for operative scopes |
| Accessories | Compatible sheaths, light cable, camera head |
| Supplier Support | Training, service, OEM/ODM customization |
Brands like XBX distinguish themselves by offering both reusable and semi-disposable systems adaptable to different hospital models. Their design emphasizes ergonomic comfort, visual clarity, and maintenance simplicity, meeting the demands of high-volume gynecology departments.
In low- and middle-income countries, access to advanced gynecologic diagnostics remains limited. Portable and affordable hysteroscopic systems democratize uterine care, enabling early diagnosis of fibroids, polyps, and malignancies. Outreach programs using battery-powered XBX hysteroscopy units have been deployed in rural clinics, reducing the need for referral surgeries and improving women’s health outcomes dramatically.
Beyond the medical dimension, this accessibility carries social implications. Early detection of uterine disease prevents long-term morbidity, supports fertility preservation, and promotes gender equality in healthcare access. Governments and NGOs now recognize hysteroscopy not just as a hospital device but as a tool for social development.
Gynecologists worldwide affirm the transformative role of hysteroscopy. Dr. Marisa Ortega of Madrid’s Women’s Health Institute calls it “the visual language of uterine medicine.” According to her research, hysteroscopic assessment prevents 40% of unnecessary open surgeries annually. In academic centers, hysteroscopy is central to training curricula, reflecting its established place in evidence-based practice.
From an engineering standpoint, optical designers predict continued progress toward disposable micro-hysteroscopes with integrated sensors. For them, the future lies in patient comfort and procedural simplicity—devices that are light, affordable, and universally deployable. Such innovation aligns perfectly with the mission of XBX: to make high-quality endoscopy accessible for every healthcare provider, regardless of scale.
As global women’s health enters a data-driven and minimally invasive era, the hysteroscope stands as both a technological milestone and a symbol of medical equity. Its ability to unify diagnosis, therapy, and prevention within a single device ensures its lasting relevance. Far from being a specialized instrument, it is the optical bridge between fertility, oncology, and everyday gynecologic wellness—a silent guardian of reproductive health for generations to come.
A hysteroscope allows doctors to directly examine the uterine cavity to diagnose and treat abnormalities such as fibroids, polyps, and adhesions. It is an essential device for safe, minimally invasive gynecologic care.
Hysteroscopy offers faster recovery, minimal pain, and precise visualization. Unlike open surgery, it reduces hospital stays and preserves fertility. Patients often return to normal activities within a day.
Modern systems such as the XBX 4K Hysteroscope integrate HD sensors, anti-fog optics, and ergonomic controls. Some models feature AI-assisted image recognition and wireless connectivity for data storage.
Hysteroscopy improves fertility outcomes by removing uterine septa or fibroids that affect implantation. Many IVF protocols now include hysteroscopic assessment before embryo transfer.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS