Table of Contents
A hysteroscopy machine in 2025 generally costs between $5,000 and $20,000 depending on brand, equipment configuration, and supplier terms. Prices vary with features such as HD/4K imaging, integrated fluid management, and whether the hospital purchases directly from a hysteroscopy manufacturer or through a hysteroscopy supplier. Total cost of ownership also includes reusable or disposable hysteroscopy equipment, training, warranty, and maintenance from the hysteroscopy factory or distributor.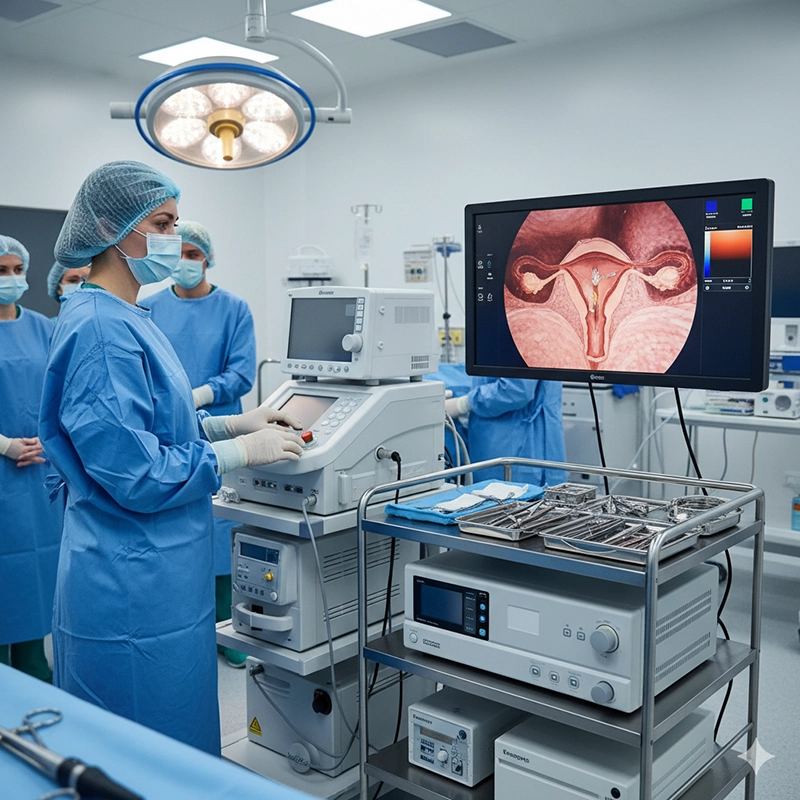
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive gynecological procedure that allows direct visualization of the uterine cavity using a thin endoscope called a hysteroscope. It is used to investigate abnormal uterine bleeding, evaluate infertility, confirm or remove intrauterine lesions such as polyps and submucosal fibroids, and guide operative procedures like adhesiolysis or septum resection. Because the approach is transcervical and incision-free, recovery is faster and perioperative risks are reduced compared with open surgery.
Diagnostic assessment of abnormal bleeding and suspected structural anomalies
Polypectomy and targeted biopsy under direct vision
Myomectomy for appropriately selected submucosal fibroids
Adhesiolysis for Asherman’s syndrome
Septum resection to improve reproductive outcomes in selected patients
Removal of retained products of conception or intrauterine devices
Hospitals invest because hysteroscopy combines diagnosis and therapy in one session, shortens length of stay, improves patient satisfaction, and expands service lines in minimally invasive gynecology. Standardized workflows, reprocessable or single-use accessories, and digital documentation make hysteroscopy equipment a cost-effective addition for both tertiary centers and community clinics.
Hysteroscope: rigid or flexible optical instrument that enters the uterine cavity.
Light Source: LED or xenon illumination delivered through fiber optics.
Camera System: HD/4K sensor, control unit, and image processing.
Fluid Management: pump and pressure regulation for uterine distension using saline.
Visualization: medical monitor and recording/archiving unit.
Accessories: sheaths, electrodes, scissors, graspers, and single-use or reusable instruments.
Diagnostic systems prioritize small-diameter scopes, portability, and quick setup. Operative systems add larger working channels, energy delivery, and advanced fluid management for longer procedures. Selection depends on procedure mix, staffing, and throughput expectations.
Unlike laparoscopy, hysteroscopy accesses the uterine cavity without abdominal ports. Compared with colposcopy, hysteroscopy provides intrauterine rather than cervical visualization. The hysteroscopy machine is optimized for fluid distension, narrow-lumen optics, and fine instruments suited to endometrial and intrauterine pathology.
Entry-level diagnostic hysteroscopy machine: $5,000–$8,000
Mid-range HD system with recording and compact pump: $10,000–$15,000
Advanced operative hysteroscopy equipment with integrated fluid management: $15,000–$20,000+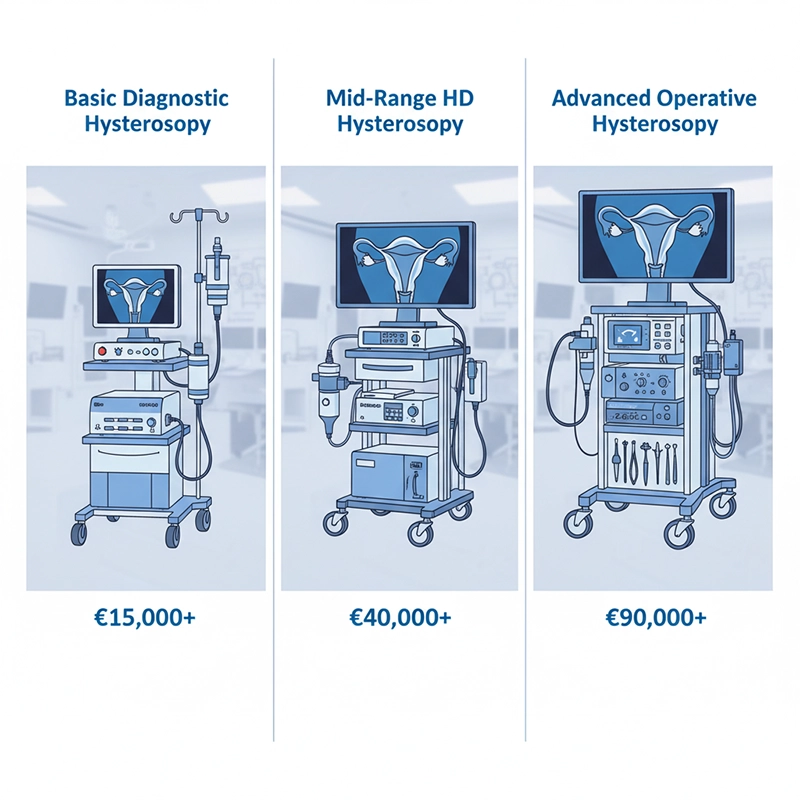
Gradual shift toward HD/4K imaging and digital connectivity increases base prices.
Broader availability of single-use hysteroscopes elevates per-procedure costs while reducing reprocessing.
OEM/ODM from regional hysteroscopy manufacturers keeps mid-range pricing competitive.
United States and Europe: highest baseline due to regulatory compliance and premium service packages.
Asia-Pacific: strong competition from local hysteroscopy factories offers 20%–30% lower capital prices.
Middle East, Africa, and Latin America: pricing depends on import duties, distributor margins, and tender requirements.
Established brands command premiums based on proven reliability, long service life, and extensive service networks. Emerging manufacturers may offer similar optical performance at lower cost but require careful due diligence on quality systems and spare-parts availability.
Sensor resolution, low-light performance, and color accuracy
Fluid pump precision, pressure safety limits, and alarm logic
Scope diameter and working channel options for operative work
Recording formats, DICOM/HL7 connectivity, and cybersecurity features
Reusable accessories lower consumable spend but require robust sterilization. Disposable options simplify workflow, reduce turnaround time, and avoid cross-contamination, at the cost of higher per-case expenditure. Many hospitals adopt a hybrid approach to balance safety and budget.
Direct factory purchasing can reduce capital price and enable OEM customization. Working with a regional hysteroscopy supplier adds value through local stock, loaner units, staff training, and faster repairs. The best option depends on the buyer’s case volume, technical staff, and geographic location.
ISO 13485 quality management
Regulatory clearances such as CE and FDA where applicable
Documented process validation for optics, electronics, and sterilization compatibility
Optical polishing, coating, and assembly tolerances for consistent image quality
Burn-in and environmental testing for camera heads and control units
Traceability of parts and serial numbers to enable rapid service actions
For large networks and distributors, OEM/ODM programs allow private labeling, accessory kits tailored to local protocols, and bundled training materials. Contract terms should specify firmware ownership, spare-parts SLAs, and end-of-life support windows.
Factory-direct: lower price per unit, deeper engineering access, potential MOQs.
Distributor: localized inventory, multilingual training, financing, and shorter response times.
Clinical in-service training and proctorship for first cases
Extended warranty, swap programs, and preventive maintenance contracts
Loaner scopes to protect uptime during repair cycles
Resilient suppliers maintain regional service hubs, multi-sourced components, and clear logistics pathways for time-sensitive parts like camera sensors and light-engine modules.
Match configuration to case mix. Diagnostic clinics emphasize compact systems and small-diameter scopes; tertiary centers prioritize operative capability, advanced pumps, and robust recording. Value is achieved when image quality, safety controls, and workflow support meet clinical demand without over-specifying unused features.
Request multi-year pricing for accessories to stabilize per-case costs.
Bundle training, spare scopes, and service into the capital quote.
Compare total five-year costs from at least three vendors before award.
Confirm certifications and test reports for the exact model offered.
Verify fluid pump safety limits and pressure monitoring accuracy.
Assess monitor specifications and recording formats required by IT.
Review warranty terms, uptime guarantees, and loaner availability.
Estimate sterilization throughput or disposable usage by monthly volume.
AI-assisted lesion highlighting and real-time documentation templates
4K sensors in compact camera heads with improved low-light performance
Smarter pumps with automatic deficit tracking and alarm analytics
Cloud-ready video storage with role-based access and audit trails
Demand grows as minimally invasive gynecology expands to community settings. Mid-range systems capture much of the volume, while premium platforms differentiate with image quality, digital workflows, and robust safety features. Distributors who combine competitively priced devices with strong clinical support will gain share.
Standardize kits across sites to reduce training complexity and inventory
Negotiate accessory price caps tied to volume milestones
Leverage factory partnerships for tailored OEM bundles
Capital: camera, control unit, light source, pump, monitors
Operating: accessories, sterilization, software licenses, service
Hysteroscope (rigid or flexible): $2,000–$6,000
Pump and tubing set: $1,000–$4,000 plus disposables per case
HD monitor and recorder: $800–$3,000
Reusable instruments set: $800–$2,500 per room
Single-use accessories (optional): $20–$200 per procedure
When modeled over five years, service contracts and accessories often equal or exceed the initial capital outlay, making supplier transparency on pricing and consumption rates essential.
Premium image quality, cybersecurity compliance, and EMR integration are decisive. Hospitals favor vendors with rapid field service and comprehensive device histories, even at higher prices. Teaching institutions seek recording features suitable for education and research.
Local hysteroscopy factories and regional brands deliver attractive price-performance. Private hospitals adopt hybrid models using reusable scopes for routine diagnostics and disposable options for time-critical or high-risk cases.
Tender processes emphasize certifications, bundled training, and warranty. Distributors that maintain local stocks of scopes and light cables improve uptime and win renewals.
Currency volatility and import duties influence purchase timing. Leasing and pay-per-procedure models from suppliers help clinics manage cash flow while upgrading to HD imaging.
Adopt standardized operative platforms across operating rooms
Negotiate OEM accessory kits and long-horizon service rates
Establish in-house biomed training with supplier certification
Choose compact diagnostic systems with quick startup and low footprint
Evaluate disposable scopes for overflow days or when sterilization is constrained
Use distributor financing and trade-in programs to manage capital budgets
Maintain demo fleets to accelerate clinical adoption
Offer structured onboarding: site survey, first-case support, and follow-up audits
Balance portfolio with one premium brand and one cost-optimized factory OEM
Annual inspection of optics, seals, and electrical safety
Firmware updates and calibration for camera control units
Pump pressure verification and alarm testing with documented records
Hot-swap loaners to minimize downtime
Serialized tracking of scopes and accessories for trend analysis
Clear turn-around targets in supplier SLAs
Define refresh cycles at three to five years for monitors and recorders and five to seven years for camera heads and pumps, or earlier when repair costs exceed residual value.
Device setup and safe use of fluid management
Scope handling to prolong optical life
Integration with video routing, storage, and EMR workflows
Simulation-based practice for diagnostic and operative steps
Proctored initial cases and competency sign-off
Periodic refreshers aligned with updated protocols
Biomed teams coordinate with suppliers for parts and calibration, while IT enables secure storage, retrieval, and transmission of procedure videos following hospital policies.
Documented compliance with ISO 13485 and applicable regional regulations
Risk management files and post-market surveillance plans
Unique device identification and traceability for recalls
Clear reimbursement for diagnostic and operative hysteroscopy increases utilization, justifying investment in higher-end systems. Where reimbursement is limited, mid-range equipment with carefully managed accessory costs is preferred.
The hospital selected a premium hysteroscopy machine with 4K camera heads and advanced fluid management. Despite a higher purchase price, reduced complication rates and faster procedures improved throughput and resident education metrics.
The clinic chose a compact diagnostic platform plus a small inventory of disposable scopes for high-risk infection scenarios. The balanced approach controlled costs while meeting patient safety expectations.
A distributor partnered with an Asia-Pacific hysteroscopy factory for OEM systems and a European brand for premium tenders, covering a wider price and feature spectrum. Shared training assets and standardized service processes improved customer satisfaction.
Define clinical scope: diagnostic only or operative capability required
Map sterilization capacity to choose reusable, disposable, or hybrid
Demand five-year TCO models with accessory consumption assumptions
Pilot units and collect user feedback before framework awards
Negotiate software, cybersecurity updates, and data-export rights upfront
Hysteroscopy: endoscopic visualization of the uterine cavity
What is hysteroscopy: explanatory content defining indications and benefits
Hysteroscopy machine: integrated system including camera, light, and pump
Hysteroscopy equipment: scopes, instruments, and accessories used in procedures
Hysteroscopy manufacturer: company designing and producing devices
Hysteroscopy factory: production site with quality and regulatory controls
Hysteroscopy supplier: distributor or reseller offering local service and training
In 2025, a hysteroscopy machine typically ranges from $5,000 to $20,000+. True value is realized when hospitals and distributors align configuration with case mix, choose a reliable hysteroscopy manufacturer or supplier, and secure training and service that sustain performance. By evaluating total cost of ownership, negotiating accessory pricing, and planning lifecycle refreshes, buyers can deliver safe, efficient, and scalable hysteroscopy services for their communities.
In 2025, a hysteroscopy machine typically costs between $5,000 and $20,000, depending on specifications, whether it is diagnostic or operative, and whether it is purchased from a hysteroscopy manufacturer, factory, or supplier.
Price differences are influenced by manufacturer reputation, machine technology, imaging quality, fluid management features, and whether accessories are reusable or disposable. Supplier services such as training and warranty also affect overall cost.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy machines are smaller and used mainly for observation and minor procedures, while operative systems include larger working channels, advanced pumps, and instruments for complex intrauterine surgeries.
Hospitals should check for certifications (ISO 13485, CE, FDA), confirm factory quality standards, compare product specifications, and evaluate the manufacturer’s after-sales service, warranty, and training support.
Common hysteroscopy equipment accessories include rigid or flexible scopes, light cables, camera systems, fluid management tubing, and instruments such as scissors, forceps, or electrodes. These can be reusable or single-use.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS