Table of Contents
Gastroscopy and upper endoscopy are essential diagnostic procedures used in hospitals to examine the upper digestive tract with minimal invasiveness. While the terms are often used interchangeably, their applications, scope, and clinical contexts can vary. In professional healthcare environments, understanding the differences and overlaps between gastroscopy vs upper endoscopy supports better decision-making in equipment procurement and procedural planning.
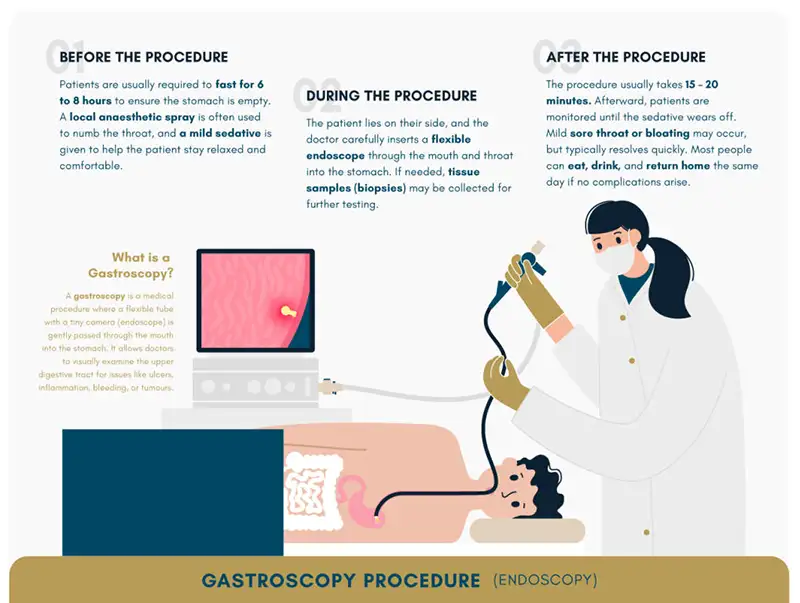
A What Is an Upper Endoscopy procedure—formally called esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)—is a minimally invasive exam of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum using a flexible endoscope. It enables direct visualization of mucosa, real-time biopsy, bleeding control, dilation of strictures, and stent placement under high-definition imaging. Modern platforms may add narrow-band imaging and other enhancements to improve early detection of dysplasia or Barrett’s esophagus. From a hospital procurement perspective, selecting What Is an Upper Endoscopy systems involves assessing image quality, ergonomics, reprocessing compatibility, disposable versus reusable accessory workflows, and connectivity with reporting software to optimize lifecycle cost and clinical throughput.
What Is a Gastroscopy focuses on endoscopic assessment of the stomach—often extending to the esophagus and duodenum—to evaluate conditions such as gastritis, ulcers, and early gastric cancer. During What Is a Gastroscopy, clinicians can perform targeted biopsies, Helicobacter pylori testing, and localized therapy in the same session. Newer gastroscopy solutions support water-jet lens cleaning, cap-assisted access, and optional disposable sheaths to reinforce infection control. For hospitals, evaluating What Is a Gastroscopy equipment set includes verifying diagnostic accuracy, operator comfort, modular expansion for evolving indications, reprocessing efficiency, and service coverage, with hybrid systems allowing interchangeable components to balance performance and long-term value.
In hospital settings, gastroscopy vs upper endoscopy comparisons are often based on anatomical reach, procedural intent, and device configurations. Gastroscopy typically refers to the examination of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum using a flexible endoscope. Upper endoscopy, while similar in equipment, is a broader term encompassing diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the same anatomical region and sometimes extending slightly beyond. For hospital procurement, the choice between the two often depends on the department’s case mix and required therapeutic capabilities.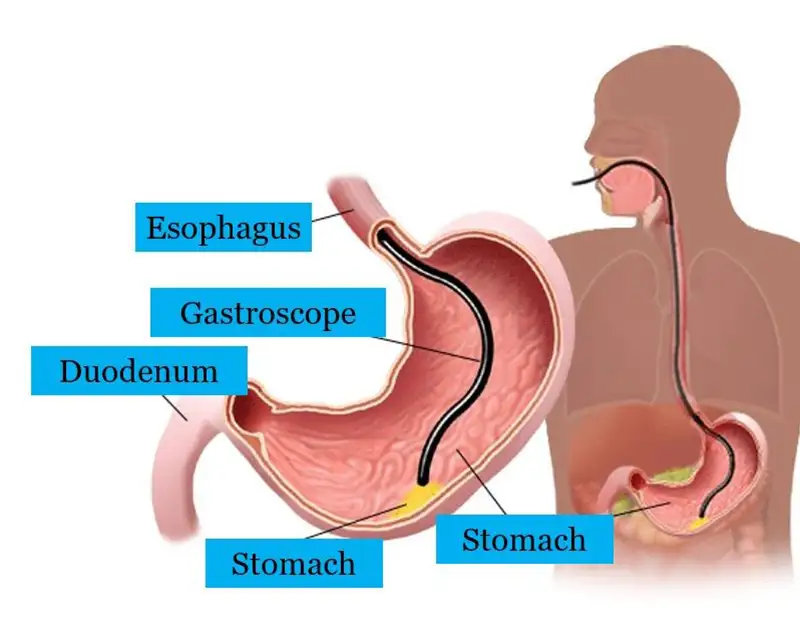
Upper endoscopy vs gastroscopy assessments focus on the versatility of the equipment and the types of conditions addressed. Both can detect ulcers, inflammation, bleeding sources, and abnormal growths. However, upper endoscopy is frequently used as a term in multidisciplinary contexts, such as when integrating with ENT or respiratory endoscopy procedures in shared facilities. In contrast, gastroscopy is more often referenced in gastroenterology-specific units.
Gastroesophageal reflux complications
Gastric ulcers or erosions
Duodenal pathology
Biopsy collection for histopathology
Foreign body retrieval in the upper GI tract
Hospitals and distributors evaluating gastroscopy vs upper endoscopy equipment must account for device flexibility, image resolution, and compatibility with sterilization systems. Some systems are optimized for rapid deployment in emergency settings, while others are tailored for high-volume diagnostic clinics. Procurement teams may also prioritize modular systems that can be used for both terminology contexts without duplication of capital investment.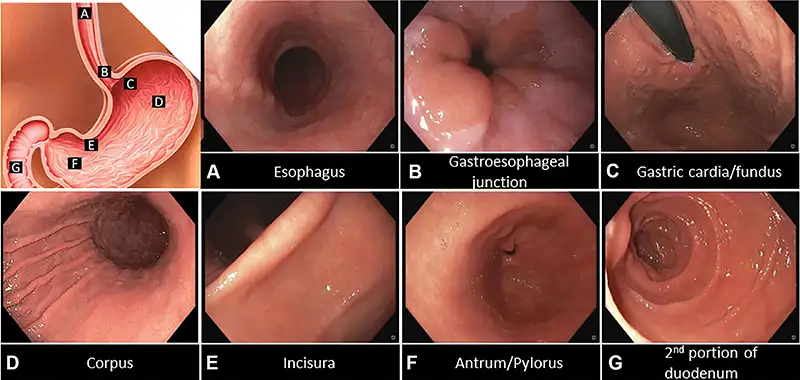
When deciding between devices labeled for upper endoscopy vs gastroscopy, hospitals often assess:
Diameter and length of insertion tube for patient comfort and reach
High-definition imaging systems for improved visual clarity
Integrated channels for suction, irrigation, and instrument passage
Ergonomic design to reduce operator fatigue during long lists of procedures
In large hospitals, the choice between gastroscopy vs upper endoscopy equipment can also impact training schedules and workflow integration. A single versatile platform may streamline cross-specialty use, whereas specialized gastroscopy units may offer dedicated functionality for gastroenterology. Distributors working with procurement teams often provide training modules to ensure staff are proficient in both diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Gastroscopy excels in targeted examination of the stomach and adjacent structures. It allows gastroenterologists to perform biopsies, remove polyps, and treat bleeding lesions within the stomach lining. In B2B procurement, gastroscopy systems are often selected for gastroenterology departments that perform high volumes of these focused interventions.
Clinical Applications of Upper Endoscopy in Multidisciplinary Departments
Upper endoscopy offers the same core capabilities as gastroscopy but with a broader procedural description. This is particularly useful in hospitals where the same device might be used for both gastroenterology and ENT procedures. For procurement, upper endoscopy equipment can be positioned as a versatile asset across multiple clinical service lines.
Hospital administrators and surgeons may differentiate gastroscopy vs upper endoscopy primarily in terms of procedural coding, patient referral patterns, and departmental equipment allocation. In facilities with specialized units, gastroscopy systems may be reserved for gastroenterology wards, while upper endoscopy equipment is shared across departments.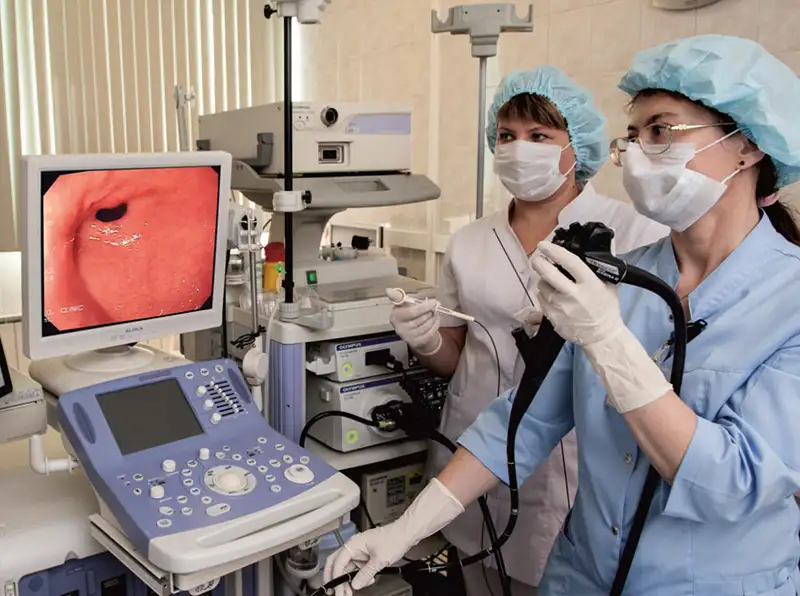
Modern hospital systems integrate high-definition imaging from both gastroscopy and upper endoscopy procedures into electronic medical records. Equipment that supports seamless data transfer, video capture, and remote consultation can add value for procurement teams, especially in large healthcare networks.
Faster diagnosis through real-time image review
Standardized reporting formats across departments
Archival of images for long-term patient monitoring
Easier multidisciplinary case discussions
In the gastroscopy vs upper endoscopy procurement decision, after-sales service is as important as initial purchase cost. Hospitals benefit from suppliers who offer preventive maintenance, rapid part replacement, and training for in-house biomedical staff. Durable construction and easy reprocessing compatibility reduce downtime and enhance long-term value.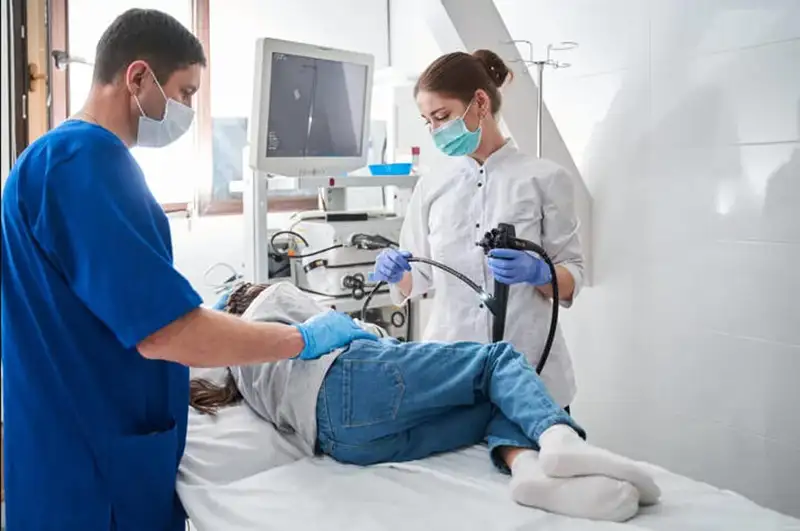
For global hospital networks and distributors, upper endoscopy vs gastroscopy equipment must comply with multiple regulatory frameworks. Devices that meet ISO and local health authority standards allow smoother procurement and cross-border deployment. This compliance also reassures hospital administrators about quality and safety.
Emerging trends include AI-assisted lesion detection, ultra-slim scopes for enhanced patient comfort, and advanced therapeutic capabilities within the same device. Hospitals may increasingly seek equipment that bridges the gastroscopy vs upper endoscopy gap, offering maximum procedural versatility.
Both gastroscopy vs upper endoscopy systems play vital roles in hospital diagnostics and treatment of upper gastrointestinal conditions. While the terminology differs, the underlying technology often overlaps, and procurement teams must evaluate features, durability, and service support in line with institutional needs. For advanced gastroscopy and upper endoscopy solutions tailored to hospital applications, XBX offers equipment designed for professional healthcare environments.
Hospitals should examine imaging resolution, insertion tube diameter, working channel size, and compatibility with existing sterilization systems.
Upper endoscopy systems are often more versatile, allowing use across gastroenterology and other specialties, while gastroscopy systems focus on targeted gastrointestinal procedures.
Ergonomic control handles, quick reprocessing capability, and durable construction enhance performance in high-volume diagnostic and therapeutic sessions.
Gastroscopy offers specialized focus for the stomach and duodenum, supporting precise diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in targeted areas.
Modular systems allow cross-procedure use, reduce duplication of equipment, and simplify maintenance and training across departments.
Commonly requested accessories include biopsy forceps, cytology brushes, injection needles, and therapeutic devices compatible with the scope’s working channel.
Devices should be compatible with the hospital’s reprocessing units, resistant to disinfectant wear, and easy to disassemble for cleaning.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS