Բովանդակության աղյուսակ
Մանկական կոլոնոսկոպը բժշկական էնդոսկոպիկ սարք է, որը հատուկ մշակված է երեխաների մոտ օգտագործելու համար: Ի տարբերություն մեծահասակների ստանդարտ կոլոնոսկոպների, այն ունի ավելի փոքր տրամագիծ, ավելի մեծ ճկունություն և մանկական անատոմիային հարմարեցված առանձնահատկություններ: Բժիշկները ապավինում են մանկական կոլոնոսկոպներին՝ ախտորոշիչ և թերապևտիկ կոլոնոսկոպիկ միջամտություններ կատարելու համար այն հիվանդների մոտ, որոնց տարիքը և մարմնի չափսերը պահանջում են մասնագիտացված սարքավորումներ: Սարքը կարևոր է երիտասարդ հիվանդների մոտ բորբոքային աղիքային հիվանդությունների, բնածին անոմալիաների, ստամոքս-աղիքային արյունահոսության և պոլիպների հայտնաբերման համար: Հիվանդանոցները, կլինիկաները և մասնագիտացված առողջապահական կենտրոնները մանկական կոլոնոսկոպը համարում են իրենց կոլոնոսկոպիկ համակարգի կարևորագույն բաղադրիչ և մանկական գաստրոէնտերոլոգիայի անփոխարինելի գործիք:
Մանկական կոլոնոսկոպը ճկուն էնդոսկոպ է, որը նախատեսված է երեխայի ամբողջ հաստ աղիքը հասնելու համար: Դրա աշխատանքային երկարությունը սովորաբար տատանվում է 133 սմ-ից մինչև 168 սմ, ավելի կարճ է, քան մեծահասակների կոլոնոսկոպներինը, իսկ ներդրման խողովակի տրամագիծը հաճախ կրճատվում է մինչև 9-11 մմ: Այս փոքր պրոֆիլը թույլ է տալիս տեղադրել առանց աղիքային պատերին ավելորդ վնասվածք պատճառելու, որոնք մանկական հիվանդների մոտ ավելի նեղ և ավելի զգայուն են: Չնայած իր կոմպակտ չափսերին, մանկական կոլոնոսկոպը պահպանում է կոլոնոսկոպիայի համակարգի ամբողջական ֆունկցիոնալությունը, ներառյալ բարձր թույլտվությամբ պատկերումը, ոռոգման խողովակները և պոլիպների հեռացման համար բիոպսիայի աքցաններ կամ թակարդներ տեղավորելու հնարավորությունը:
Մեծահասակների համար նախատեսված կոլոնոսկոպների համեմատ, մանկական տարբերակները ավելի թեթև են և օպտիմալացված են նեղ անատոմիական տարածություններում մանևրելու համար: Էրգոնոմիկ դիզայնը օգնում է բժիշկներին ճշգրտությամբ կողմնորոշվել հաստ աղիքում՝ միաժամանակ նվազեցնելով հիվանդի անհարմարությունը: Ժամանակակից սարքերը ներառում են տեսապրոցեսորներ, առաջադեմ լուսավորություն և պատկերման բարելավումներ, որոնք ապահովում են լորձաթաղանթի մակերեսների հստակ պատկերացում՝ ապահովելով ախտորոշման ճշգրտությունը երեխաների մոտ:
Տեղադրման խողովակ – Նեղ, ճկուն լիսեռ, որը նախատեսված է մանկական հաստ աղիքի միջով սահուն ծալվելու համար: Խողովակը պարունակում է օպտիկամանրաթելային փնջեր կամ թվային պատկերման մալուխներ, որոնք տեսողական տվյալները փոխանցում են տեսապրոցեսորին:
Կառավարման բռնակ – Տեղադրված մարմնից դուրս, այս սարքը թույլ է տալիս բժշկին կառավարել դիտակի ծայրը՝ օգտագործելով անկյունային լծակներ: Լրացուցիչ կոճակները կառավարում են օդի ներշնչումը, ջրի ոռոգումը և ներծծումը:
Պատկերագրական համակարգ – Մանկական կոլոնոսկոպները կարող են օգտագործել կամ օպտիկամանրաթելային ոսպնյակներ, կամ թվային CMOS/CCD սենսորներ: Թվային համակարգերը ապահովում են ավելի բարձր լուծաչափ և թույլ են տալիս օգտագործել առաջադեմ պատկերման հնարավորություններ, ինչպիսիք են նեղաշերտ պատկերագրությունը:
Լույսի աղբյուր – Ժամանակակից կոլոնոսկոպները ներառում են LED կամ քսենոնային լույսի աղբյուրներ՝ ապահովելով պայծառ և միատարր լուսավորություն: Մանկական մոդելները շեշտը դնում են լույսի մեղմ ինտենսիվության վրա՝ փոքր անատոմիական խոռոչներում չափազանց շողացումից խուսափելու համար:
Աշխատանքային ալիք – Կրճատված տրամագծին չնայած, մանկական դիտակները պահպանում են աշխատանքային ալիք (2.8–3.2 մմ), որը հնարավորություն է տալիս անցկացնել բիոպսիայի գործիքներ, հեմոստատիկ սարքեր և թերապևտիկ գործիքներ։
Տեսապրոցեսոր և մոնիտոր. Սկանդալը միացված է կոլոնոսկոպիկ համակարգին, որը մշակում է պատկերները և ցուցադրում դրանք բարձր թույլտվության մոնիտորների վրա: Մանկաբուժական տարբերակները պետք է համատեղելի լինեն հիվանդանոցային էնդոսկոպիկ աշտարակների հետ: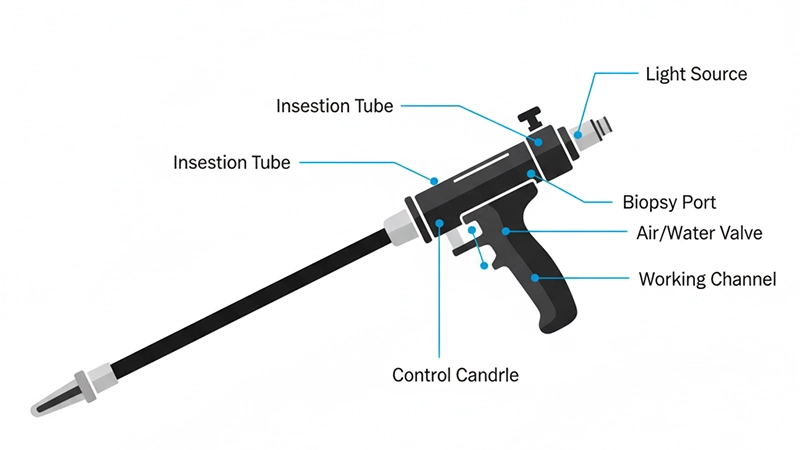
Նախապատրաստում – Մանկական հիվանդները ենթարկվում են աղիքների նախապատրաստման ընթացակարգի, որը սովորաբար իրականացվում է երեխաների համար անվտանգ լուծողականների և թափանցիկ հեղուկ դիետաների միջոցով: Պատշաճ նախապատրաստությունը կենսական նշանակություն ունի ընթացակարգի ընթացքում հստակ տեսողության համար:
Սեդացիա կամ անզգայացում. Երեխաները հաճախ կարիք ունեն թեթև սեդացիայի կամ ընդհանուր անզգայացման՝ անվտանգությունն ապահովելու և անհանգստությունը նվազագույնի հասցնելու համար: Անեսթեզիոլոգները կարևոր դեր են խաղում պրոցեդուրայի ընթացքում կենսական նշանների մոնիթորինգի գործում:
Ներդրում – Theկոլոնոսկոպզգուշորեն մտցվում է ուղիղ աղիքի միջով և դանդաղորեն առաջ մղվում հաստ աղիքով։ Փոքր տրամագծով ներդրման խողովակը նվազեցնում է անհարմարությունը և վնասվածքի ռիսկը։
Զննում և ախտորոշում. Բժիշկը զննում է հաստ աղիքի լորձաթաղանթը բորբոքման, խոցերի, արյունահոսության աղբյուրների կամ պոլիպների առկայության համար: Բարձր թույլտվությամբ պատկերումը և խոշորացման հնարավորությունները օգնում են հայտնաբերել աննշան աննշան անոմալիաները:
Թերապևտիկ միջամտություններ. Անհրաժեշտության դեպքում բժիշկը կարող է օգտագործել աշխատանքային ուղով անցկացվող գործիքներ՝ հյուսվածքը բիոպսիա կատարելու, արյունահոսող անոթները այրելու կամ փոքր պոլիպները հեռացնելու համար:
Ավարտում և վերականգնում – Հետազոտությունից հետո կոլոնոսկոպը հանվում է։ Հիվանդները վերականգնվում են հսկողության տակ, և նրանց մեծ մասը կարող է նույն օրը վերադառնալ տուն։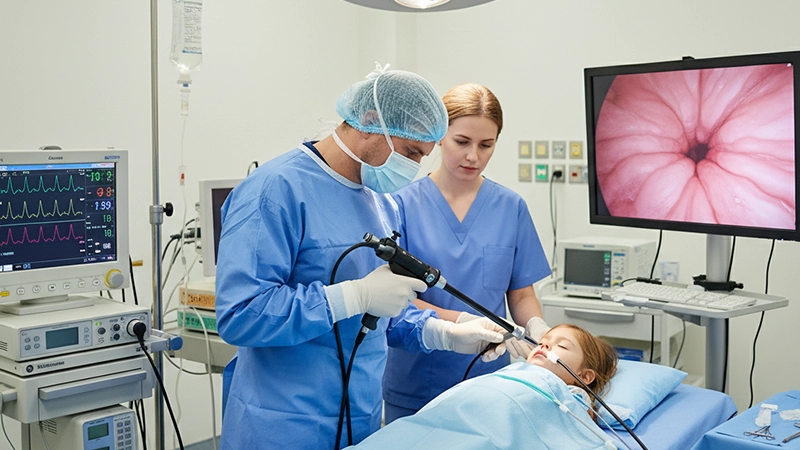
Անվտանգություն – Փոքր տրամագիծը նվազագույնի է հասցնում նուրբ աղիքային լորձաթաղանթի պերֆորացիայի և վնասվածքի ռիսկը։
Հարմարավետություն – Երեխաները ավելի քիչ ցավ և անհարմարություն են զգում էրգոնոմիկ դիզայնի և համապատասխան չափսերի շնորհիվ։
Ճշգրտություն. առաջադեմ պատկերագրական հետազոտությունը ապահովում է վաղ փուլի հիվանդությունների ճշգրիտ հայտնաբերում, որոնք այլապես կարող էին բաց թողնվել:
Բազմակողմանիություն. չնայած իր չափսերին, մանկական կոլոնոսկոպը թույլ է տալիս իրականացնել ինչպես ախտորոշիչ, այնպես էլ թերապևտիկ միջամտություններ՝ նվազեցնելով բազմակի միջամտությունների անհրաժեշտությունը:
Բարելավված արդյունքներ. Վաղ և ճշգրիտ հայտնաբերումը հանգեցնում է ժամանակին բուժման, ինչը կարևոր է մանկական հիվանդների մոտ, որոնց վիճակը կարող է արագ զարգանալ:
Մանկական կոլոնոսկոպի գինը տարբերվում է դիզայնից, տեխնոլոգիայի մակարդակից և գնման ուղուց կախված: Գնորդները սովորաբար հաշվի են առնում միավորի գնանշումը՝ կյանքի ցիկլի ծախսերի հետ միասին, ինչպիսիք են սպասարկումը, վերամշակումը, ուսուցումը և կոլոնոսկոպիայի համակարգի շրջանակներում ծրագրային ապահովման հնարավոր թարմացումները:
Կոլոնոսկոպի գինըմիջակայք. շատ հիվանդանոցներ մանկական կոլոնոսկոպների գնանշումները կազմում են մոտավորապես 8,000-25,000 ԱՄՆ դոլար՝ կախված տեխնիկական բնութագրերից և ապրանքանիշի դիրքորոշումից: Միանգամյա օգտագործման մանկական մոդելները կարող են գնանշվել յուրաքանչյուր օգտագործման համար, ինչը ծախսերը կապիտալ ծախսերից տեղափոխում է գործառնական ծախսերի:
Տեխնոլոգիական մակարդակ. Բարձր թույլտվության պատկերումը, բարելավված վիզուալիզացիան (օրինակ՝ նեղաշերտ կամ տոնային քարտեզագրում) և առաջադեմ պրոցեսորները, որպես կանոն, բարձրացնում են կոլոնոսկոպի գինը՝ ավելացված բաղադրիչների և վավերացման քայլերի շնորհիվ։
Բազմակի օգտագործման ընդդեմ միանգամյա օգտագործման. Բազմակի օգտագործման մանկական կոլոնոսկոպները պահանջում են նախնական ներդրումներ և վերամշակման ենթակառուցվածքներ, բայց կարող են նվազեցնել մեկ դեպքի արժեքը ծավալի առումով: Միանգամյա օգտագործման տեսապակիները նվազեցնում են վերամշակման ծանրաբեռնվածությունը և վարակի վերահսկման ռիսկը՝ միաժամանակ մեծացնելով մեկ պրոցեդուրայի համար ծախսերը:
Կոլոնոսկոպիայի համակցված համակարգ. Մանկական կոլոնոսկոպը լույսի աղբյուրի, տեսապրոցեսորի և մոնիտորի հետ միասին գնելիս գինը կարող է փոխվել, ինչը կարող է պարզեցնել համատեղելիությունը և սպասարկումը:
OEM/ODM տարբերակներ. կոլոնոսկոպների գործարանի հետ համագործակցությունը OEM կամ ODM-ի համար կարող է հնարավորություն տալ հիվանդանոցների և դիստրիբյուտորների համար ստեղծել անհատականացված կոնֆիգուրացիաներ և ծավալի վրա հիմնված գնանշումներ:
Մանկաբուժական հատվածը աջակցվում է կոլոնոսկոպների արտադրողների, տարածաշրջանային դիստրիբյուտորների և սպասարկման գործընկերների համաշխարհային ցանցի կողմից: Ճիշտ գործընկեր ընտրելը նպաստում է մատակարարման, ուսուցման և վաճառքից հետո աջակցության կայունացմանը:
Մանկաբուժական գծեր ունեցող արտադրողները սովորաբար պահպանում են ISO և CE համապատասխանությունը և առաջարկում են համապատասխան պարագաներ՝ ապահովելով համատեղելիությունը կոլոնոսկոպիկ համակարգի ողջ ընթացքում։
Սպեցիֆիկացիաների թափանցիկությունը (արտաքին տրամագիծը, աշխատանքային երկարությունը, անցքի չափը) օգնում է սարքերը համապատասխանեցնել մանկական ցուցումներին և սենյակների դասավորությանը։
Հուսալի կոլոնոսկոպների մատակարարը համակարգում է ցուցադրությունները, վարձակալությունները և կանխարգելիչ սպասարկումը՝ միաժամանակ համապատասխանեցնելով առաքման գրաֆիկը հիվանդանոցային դեպքերի ծավալին։
Դիստրիբյուտորները հաճախ միավորում են տեղադրումը, օգտագործողի ուսուցումը և երաշխիքային պայմանները, որոնք ազդում են կոլոնոսկոպի հիմնական գնից այն կողմ ընդհանուր արժեքի վրա։
Հիվանդանոցներն ու դիստրիբյուտորները կարող են ուղղակիորեն համագործակցել կոլոնոսկոպների գործարանի հետ՝ OEM/ODM արտադրանքի անհատականացման, մասնավոր պիտակավորման և լոգիստիկայի համախմբման համար։
Անմիջական ներգրավումը կարող է կրճատել դիզայնի ճշգրտումների համար հետադարձ կապի ցիկլերը (օրինակ՝ մանկական անկյունային պտտող մոմենտ, դիստալ ծայրի ճկունություն) և հեշտացնել պահեստամասերի պլանավորումը։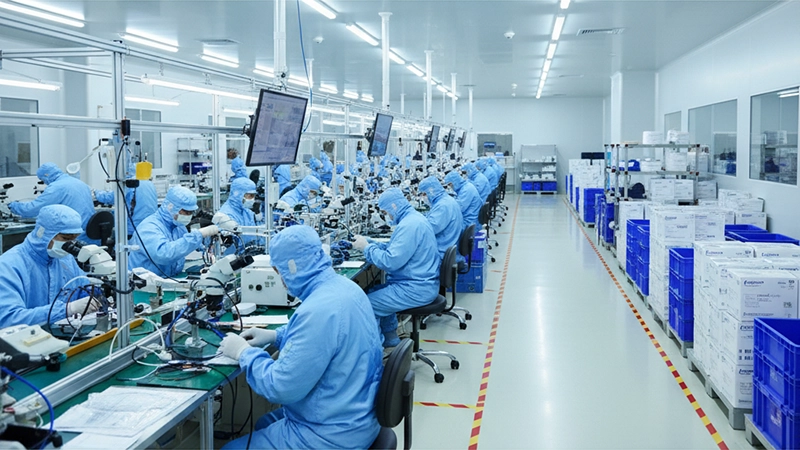
Կլինիկական համապատասխանություն. մանկական ցուցումներ, պատկերի որակ, ներդրման խողովակի ճկունություն և աշխատանքային ալիքի համատեղելիություն գործիքների հետ։
Տնտեսական համապատասխանություն. միավորի գնանշում, պարագաներ, վերամշակման ծախսեր, երաշխիք և սպասարկման արձագանքման ժամանակներ։
Համակարգի համապատասխանություն. փոխգործունակություն առկա էնդոսկոպիկ աշտարակների, EMR/VNA աշխատանքային հոսքերի և տեսանյութի ելքային ստանդարտների հետ։
Մատակարարի համապատասխանությունը. կարգավորող կարգավիճակ, ուսումնական ծրագրեր, տեղական ծառայությունների ծածկույթ և արդիականացման ճանապարհային քարտեզ:
Վերջին նորամուծությունները բարելավում են մանկական դեպքերի ախտորոշման վստահությունը և գործառնական արդյունավետությունը՝ միաժամանակ պահպանելով շրջանակի չափերը երեխային համապատասխան։
Բարձր թույլտվությամբ և բարելավված վիզուալիզացիա. HD սենսորները և օպտիկական ֆիլտրերը բարելավում են լորձաթաղանթի մանրամասները՝ նպաստելով նուրբ վնասվածքների վաղ հայտնաբերմանը։
Արհեստական ինտելեկտի օգնությամբ պատկերացում. իրական ժամանակում օրինաչափությունների ճանաչումը կարող է նշել կասկածելի տարածքները և ստանդարտացնել փաստաթղթավորումը թիմերի միջև։
Ջրային շիթի և ներծծման օպտիմալացում. ընթացակարգի ընթացքում ավելի լավ մաքրումը բարելավում է տեսանելիությունը և կարող է կրճատել հետազոտության ժամանակը:
Միանգամյա օգտագործման մանկական կոլոնոսկոպներ. Միանգամյա օգտագործման տարբերակները օգնում են լուծել վարակի վերահսկման քաղաքականությունը և նվազեցնել վերամշակման խոչընդոտները:
Մոդուլային կոլոնոսկոպիկ համակարգեր. Մանկական դիտակները, որոնք նախատեսված են առկա պրոցեսորների, լույսի աղբյուրների և մոնիտորների հետ միանալու և օգտագործելու համար, կարող են պարզեցնել տեղակայումը և ուսուցումը:
Համապատասխանեցնելով գնային նկատառումները մատակարարի կարողություններին և ժամանակակից տեխնոլոգիաներին՝ հիվանդանոցները կարող են ընտրել մանկական կոլոնոսկոպ, որը նպաստում է ինչպես կլինիկական արդյունքներին, այնպես էլ կայուն գործունեությանը։
Մանկական ճիշտ կոլոնոսկոպի ընտրությունը պահանջում է տեխնիկական բնութագրերի, հիվանդանոցային բյուջեների և կլինիկական կարիքների հավասարակշռություն: Մատակարարման մենեջերները և բժշկական տնօրենները սարքերը գնահատելիս հաճախ օգտագործում են կառուցվածքային ստուգաթերթիկ:
Կիրառման տեխնիկական բնութագրերը – Երկարությունը, տրամագիծը և աշխատանքային խողովակի չափը պետք է համապատասխանեն մանկական անատոմիային և կլինիկական օգտագործման դեպքերին:
Համատեղելիություն – Մանկական կոլոնոսկոպը պետք է սահուն ինտեգրվի հիվանդանոցի առկա կոլոնոսկոպիկ համակարգի հետ, ներառյալ պրոցեսորները, լույսի աղբյուրները և մոնիտորները:
Երկարակեցություն և կյանքի ցիկլի արժեք – Բազմակի օգտագործման հեռադիտակները պետք է դիմանան կրկնակի ստերիլիզացման ցիկլերին՝ առանց պատկերի որակի կամ կառուցվածքային ամբողջականության կորստի։
Սպասարկում և սպասարկում. Հուսալի կոլոնոսկոպների մատակարարը պետք է առաջարկի պահեստամասեր, սպասարկման պայմանագրեր և վերապատրաստում բժշկական անձնակազմի համար:
Երաշխիք և աջակցություն – Կոլոնոսկոպների արտադրողների կողմից տրամադրվող համապարփակ երաշխիքները երաշխավորում են սարքի վաղաժամ խափանումը։
Գնի գնահատում – Կոլոնոսկոպի գինը պետք է վերլուծվի ոչ միայն սարքի մակարդակով, այլև ամբողջ կյանքի ցիկլի ընթացքում, ներառյալ վերանորոգումը և ուսուցումը:
OEM/ODM անհատականացում – Կոլոնոսկոպների գործարանից անմիջապես գնումներ կատարող հիվանդանոցները կարող են խնդրել ապրանքանիշի, դիզայնի փոփոխություններ կամ սարքավորումների փաթեթներ։
Մանկական կոլոնոսկոպը սովորաբար ձեռք է բերվում որպես ավելի լայն կոլոնոսկոպիկ համակարգի մաս, որը ապահովում է կլինիկական արդյունավետություն և ստանդարտացում տարբեր բաժանմունքներում:
Էնդոսկոպիկ աշտարակ – Այստեղ տեղակայված են տեսապրոցեսորը, լույսի աղբյուրը և ոռոգման համակարգերը։
Մոնիտորներ – Բարձր թույլտվությամբ էկրաններ, որոնք ցուցադրում են կոլոնոսկոպի սարքավորումից իրական ժամանակում ստացված պատկերները:
Ներծծման և ոռոգման սարքեր – Թույլ են տալիս բժիշկներին մաքրել տեսադաշտը բարդ վիրահատությունների ժամանակ։
Աքսեսուարներ – Բիոպսիայի աքցաններ, թակարդներ և ներարկման ասեղներ, որոնք նախատեսված են մանկական օգտագործման համար:
Ստերիլիզացման և վերամշակման սարքավորումներ – Անհրաժեշտ են բազմակի օգտագործման կոլոնոսկոպների համար՝ ապահովելով վարակի վերահսկողությունը։
Մանկական այլ էնդոսկոպներից են վերին ստամոքս-աղիքային հետազոտությունների համար նախատեսված գաստրոսկոպները, միզուղիների ախտորոշման համար նախատեսված ցիստոսկոպները և բարձր թույլտվության պատկերման համար նախատեսված վիդեոկոլոնոսկոպները: Հիվանդանոցները հաճախ այս սարքերը միասին են ձեռք բերում՝ մատակարարների պայմանագրերը և ուսումնական ծրագրերը օպտիմալացնելու համար:
Միանգամյա օգտագործման մանկական կոլոնոսկոպների կիրառումը. Վարակների կանխարգելման վրա շեշտը դնում է միանգամյա օգտագործման դիտակների պահանջարկը խոշոր հիվանդանոցային ցանցերում։
Արհեստական բանականության ինտեգրում – Արհեստական բանականությամբ օժտված կոլոնոսկոպի սարքավորումները բարձրացնում են ախտորոշման ճշգրտությունը՝ կասկածելի հյուսվածքի վերաբերյալ իրական ժամանակի ահազանգերի միջոցով։
Մանրադիտացում և էրգոնոմիկա – Կոլոնոսկոպների արտադրողները մշակում են ավելի փոքր, ավելի ճկուն սարքեր՝ պրոցեդուրայի ժամանակը կրճատելու և հիվանդի հարմարավետությունը բարելավելու համար:
Մատակարարման շղթաների գլոբալ ընդլայնում – Ասիայի կոլոնոսկոպների գործարանները ընդլայնում են OEM/ODM արտադրությունը՝ առաջարկելով ծախսարդյունավետ գնման տարբերակներ։
Հեռաէնդոսկոպիա և հեռավար համագործակցություն. Ամպային միացված կոլոնոսկոպիկ համակարգերը հնարավորություն են տալիս իրական ժամանակում խորհրդատվություն ստանալ տարածաշրջաններում:
Կայունության նախաձեռնություններ – Էկոլոգիապես մաքուր վերամշակումը և վերամշակվող միանգամյա օգտագործման կոլոնոսկոպները մեծ ժողովրդականություն են վայելում։
Մանկական կոլոնոսկոպը մասնագիտացված սարք է, որը հարմարեցված է երեխաների անատոմիային և ապահովում է ախտորոշիչ և թերապևտիկ հնարավորություններ ժամանակակից կոլոնոսկոպիկ համակարգի շրջանակներում: Այն տարբերվում է մեծահասակների համար նախատեսված կոլոնոսկոպներից չափսերով, ճկունությամբ և դիզայնով՝ միաժամանակ պահպանելով լիարժեք ֆունկցիոնալություն:
Կոլոնոսկոպի սարքավորումների գնի վրա ազդում են տեխնոլոգիական մակարդակը, արտադրողի հեղինակությունը և գնման մոդելները՝ անկախ նրանից, թե դրանք դիստրիբյուտորների միջոցով են, թե ուղղակիորեն կոլոնոսկոպի գործարանից: Կոլոնոսկոպի մատակարարի հետ ամուր գործընկերությունը նպաստում է հուսալի սարքերի, մրցունակ կոլոնոսկոպի գների և արագ արձագանքող սպասարկման ապահովմանը:
Արհեստական բանականության միջոցով պատկերագրման, միանգամյա օգտագործման սարքերի և բարելավված վիզուալիզացիայի գործիքների նման առաջընթացները ձևավորում են մանկական կոլոնոսկոպիայի ապագան: Մատակարարներին ուշադիր գնահատելով, OEM/ODM լուծումները հաշվի առնելով և կյանքի ցիկլի ծախսերը պլանավորելով՝ առողջապահական հաստատությունները կարող են իրենց թիմերին հագեցնել հիվանդների խնամքի համար նախատեսված լավագույն մանկական կոլոնոսկոպիկ լուծումներով:
Մանկական կոլոնոսկոպը մասնագիտացված էնդոսկոպ է, որը նախատեսված է երեխաների համար, որն առանձնանում է փոքր տրամագծով, ավելի մեծ ճկունությամբ և մանկական անատոմիային հարմարեցված բաղադրիչներով:
Մեծահասակների կոլոնոսկոպների համեմատ, մանկական կոլոնոսկոպներն ունեն ավելի նեղ ներդրման խողովակ, կրճատված երկարություն և ավելի ճկուն դիզայն՝ երեխաների փոքր անատոմիայում անվտանգ տեղաշարժվելու համար:
Այն օգտագործվում է մանկական հիվանդների մոտ՝ բորբոքային աղիքային հիվանդությունների, պոլիպների, բնածին անոմալիաների, ստամոքս-աղիքային արյունահոսության և անհասկանալի որովայնի ցավի ախտորոշման և բուժման համար։
Գինը սովորաբար տատանվում է 8000-ից մինչև 25000 ԱՄՆ դոլար՝ կախված տեխնոլոգիայից, արտադրողից և մատակարարից: Միանգամյա օգտագործման տարբերակները կարող են արժենալ 500-1000 ԱՄՆ դոլար մեկ միավորի համար:
Առավելություններից են երեխաների անվտանգության բարելավումը, ախտորոշման ավելի բարձր ճշգրտությունը, վնասվածքի ռիսկի նվազեցումը և ինչպես ախտորոշիչ, այնպես էլ թերապևտիկ ընթացակարգեր կատարելու հնարավորությունը։
Հեղինակային իրավունք © 2025.Geekvalue Բոլոր իրավունքները պաշտպանված են։Տեխնիկական աջակցություն՝ TiaoQingCMS