Table of Contents
By 2026, the medical endoscope industry is undergoing one of the most significant transformations in its history. Hospitals, manufacturers, and distributors are no longer competing only on image clarity or durability — they are redefining how imaging intelligence, sustainability, and workflow efficiency coexist within modern healthcare systems. The most influential trends in the medical endoscope field include the integration of artificial intelligence, the rise of disposable and eco-friendly designs, the widespread adoption of 4K and ultra-HD imaging, stricter infection control compliance, and a new focus on cybersecurity and lifecycle cost management. These changes are reshaping procurement strategies and redefining value for both clinicians and patients worldwide.
Artificial intelligence has evolved from a supporting feature into a critical capability within modern endoscopic systems. AI-assisted medical endoscopes now help physicians detect abnormalities, predict tissue pathology, and optimize visualization in real time. By 2026, AI adoption has become a top priority in hospital investment strategies, supported by mounting clinical evidence and strong regulatory momentum.
AI-driven image recognition models can automatically identify polyps, ulcers, or abnormal vascular patterns during endoscopic procedures. In gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy, computer-aided detection (CADe) systems can highlight potential lesions with color overlays or bounding boxes, alerting the physician in milliseconds. This reduces human fatigue and minimizes the risk of missing subtle early-stage disease signs.
Polyp detection accuracy: Studies show AI-assisted colonoscopy can increase adenoma detection rates by 8–15% compared with manual observation.
Time efficiency: Algorithms automatically capture key frames and generate instant reports, reducing procedure documentation time by up to 25%.
Standardization: AI maintains consistent diagnostic criteria across multiple operators, supporting training and benchmarking.
Companies such as XBX have integrated deep learning modules directly into their 4K camera control units. These systems perform onboard AI inference without relying on external servers, ensuring real-time analysis without data latency or privacy risks. For hospital buyers, the critical consideration in 2026 is not only whether AI is included but also whether it is validated by peer-reviewed studies and compliant with local regulatory frameworks such as the FDA or CE-MDR.
Despite the enthusiasm, integrating AI into daily endoscopy practice remains complex. Algorithm performance can drop if lighting conditions, tissue types, or patient demographics differ from the training data. To ensure reliability, hospitals must demand transparent documentation on AI training datasets, algorithm retraining frequency, and software update cycles. Vendors like XBX now offer AI audit logs and traceability dashboards that allow hospital IT departments to monitor model drift and ensure sustained accuracy over time.
Image quality remains the foundation of diagnostic confidence. In 2026, 4K and ultra-high-definition (UHD) endoscope systems are becoming standard across operating rooms and teaching hospitals. The transition from Full HD to 4K is more than a resolution upgrade — it represents a complete transformation in sensor design, illumination, and digital signal processing.
Advanced CMOS sensors: Modern endoscope cameras use back-illuminated CMOS chips that deliver higher sensitivity with lower noise in dim environments.
Optical lens coatings: Anti-reflective multilayer coatings minimize glare from mucosal surfaces, improving visibility in narrow lumens.
HDR signal processing: High dynamic range imaging balances bright and dark areas, ensuring consistent exposure even when transitioning between organs.
Digital chromoendoscopy: Spectral enhancement algorithms such as NBI, FICE, or LCI improve tissue differentiation without dyes.
Manufacturers like XBX have developed 4K endoscope camera heads capable of producing 4096×2160 pixel resolution at 60 frames per second. When combined with precision optical couplers and medical-grade monitors, these systems enable surgeons to identify vascular networks and lesion margins with unparalleled clarity. For laparoscopic and arthroscopic surgeries, real-time digital zoom and automatic white balance correction are now essential features.
The adoption of 4K endoscopy has a direct impact on clinical outcomes and medical education. Surgeons report reduced eye strain during prolonged procedures and greater precision in identifying microanatomical details. For teaching hospitals, 4K visualization allows multiple trainees to observe detailed tissue reactions during interventions, supporting remote learning and case reviews. As telemedicine expands, high-resolution live streaming also supports multidisciplinary collaboration across hospitals and continents.
Disposable medical endoscopes are rapidly changing hospital workflows and infection control policies. Once considered niche products, single-use bronchoscopes, ureteroscopes, and ENT endoscopes are now widely adopted in intensive care units and emergency departments. Their main advantage is the elimination of cross-contamination risks associated with reusable scopes, especially in high-turnover environments.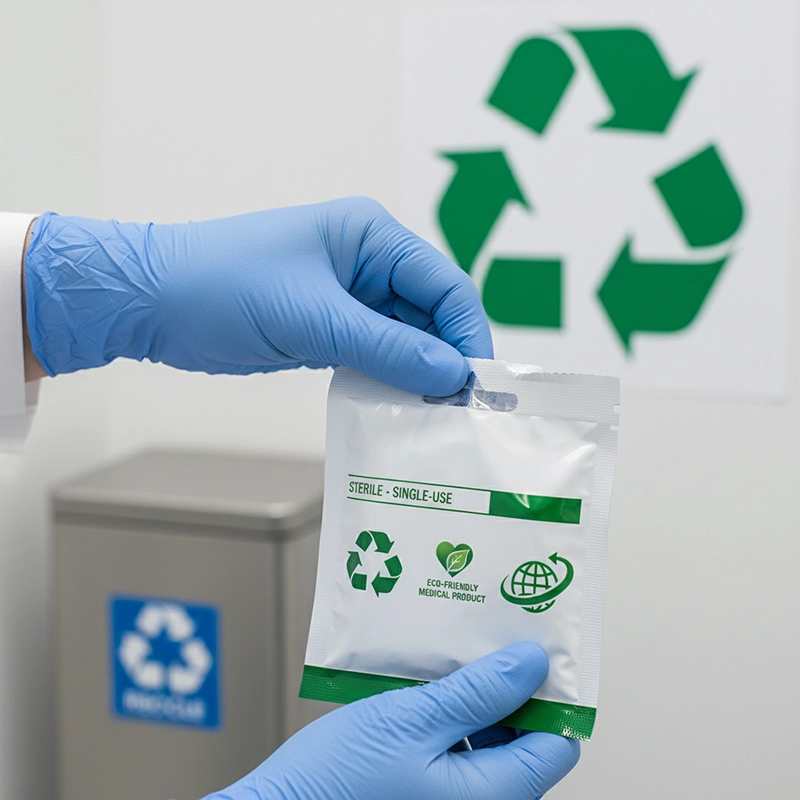
Zero cross-infection: Each unit is sterile and used for a single patient, removing the need for high-level disinfection.
Faster turnover: No downtime between procedures due to cleaning or drying processes.
Consistent image quality: Each device offers new optics and lighting, avoiding image degradation caused by wear and tear.
For smaller hospitals and outpatient centers, disposable endoscopes reduce infrastructure requirements since they eliminate the need for complex reprocessing rooms or drying cabinets. However, the higher per-unit cost remains a concern for large facilities performing high procedure volumes. Procurement teams are now balancing infection control benefits with long-term budget impact.
The environmental impact of disposable devices has become a major discussion point. Single-use endoscopes generate significant plastic and electronic waste. Some countries have introduced extended producer responsibility (EPR) regulations, requiring manufacturers to handle post-use recycling. XBX has responded by developing partially recyclable endoscope components and lightweight packaging that reduces overall waste volume. In parallel, hospitals are encouraged to establish internal recycling programs or partner with certified waste management services to align with global sustainability goals.
Even with improved design and automation, infection control remains a primary challenge in endoscopy. Between 2015 and 2024, several major outbreaks were traced to improper reprocessing of duodenoscopes and bronchoscopes. As a result, international standards such as ISO 15883, AAMI ST91, and FDA guidance now require stricter documentation and validation of cleaning, disinfection, and drying procedures.
Modern endoscope reprocessing units have shifted from manual soaking to fully automated cleaning systems. These machines track parameters such as water temperature, detergent concentration, and cycle duration to ensure consistency. Advanced tracking software assigns unique identifiers to each endoscope, recording every cleaning cycle and operator ID for regulatory audits.
Smart drying cabinets: Maintain HEPA-filtered airflow at controlled humidity levels to prevent bacterial regrowth.
RFID integration: Links each scope to its cleaning history for end-to-end traceability.
ATP monitoring: Rapid bioluminescence testing confirms surface cleanliness in seconds before reuse.
XBX’s reprocessing-compatible medical endoscopes are engineered with smooth, low-friction insertion tubes that minimize biofilm adherence. Their accessories include universal connection adapters compatible with major automated cleaning systems. This ensures that hospitals can integrate XBX products seamlessly without additional infrastructure investments.
Technology alone cannot prevent contamination. Staff training remains the cornerstone of infection prevention. Reprocessing technicians must follow validated workflows, monitor detergent expiry dates, and perform daily quality checks. In 2026, hospitals increasingly adopt digital training platforms and video-assisted supervision to maintain competency. Vendors like XBX support these initiatives through e-learning modules and on-site workshops, reinforcing safe handling practices and compliance.
As medical endoscope systems become increasingly digital and interconnected, cybersecurity has emerged as a non-negotiable factor in equipment procurement. Many of today’s AI-assisted endoscopes connect to hospital networks for data transfer, remote diagnostics, or cloud-based analysis. While this connectivity improves efficiency, it also creates vulnerabilities that can expose sensitive patient information if not properly secured. In 2026, healthcare cybersecurity standards are evolving rapidly to keep up with these risks.
Endoscopic imaging systems store patient identifiers, procedural data, and video files that often exceed several gigabytes. If intercepted, this information could lead to privacy violations or ransomware attacks. Hospitals must ensure that every network-connected endoscope and recording device meets industry cybersecurity benchmarks, such as ISO/IEC 27001 and FDA premarket cybersecurity guidance.
Encryption: All patient images and videos should be encrypted both at rest and in transit.
Access control: User authentication and role-based permissions must be enforced within the system.
Software lifecycle management: Regular firmware updates and vulnerability scans are essential to maintain system integrity.
Manufacturers such as XBX have responded by embedding secure firmware modules within their endoscopic platforms. These modules protect against unauthorized software changes and encrypt all communications between camera heads, processors, and hospital networks. In addition, XBX’s diagnostic consoles now feature customizable access logs, enabling IT administrators to track user activities for audit purposes.
The convergence of medical technology and IT security means hospitals can no longer treat endoscopes as isolated devices. Cross-department collaboration is now critical. Biomedical engineers must coordinate with IT departments to conduct security risk assessments before deploying new systems. In large hospitals, dedicated cybersecurity committees are being established to review and approve all connected medical devices. The result is a stronger governance structure that protects clinical operations from digital threats.
Purchasing a medical endoscope system in 2026 requires more than comparing price tags. Hospitals are adopting a lifecycle cost approach — evaluating not only the purchase price but also maintenance, training, energy use, spare parts, and end-of-life disposal. The global focus on sustainability and regulatory compliance has made procurement teams more analytical and risk-aware than ever before.
A comprehensive TCO model includes four main categories: acquisition, operation, maintenance, and disposal. When applied to endoscopy, this model helps hospitals predict long-term financial impact rather than short-term savings.
Acquisition: Equipment cost, installation, and initial staff training.
Operation: Consumables, energy consumption, and software licensing.
Maintenance: Service contracts, spare parts, and calibration.
Disposal: Recycling costs and data sanitization for electronic components.
For instance, an advanced 4K endoscopy tower may have a higher initial cost but deliver savings through longer lifespan and reduced reprocessing expenses. XBX provides hospitals with transparent TCO calculators that simulate operational expenses over a 7–10 year period, enabling procurement officers to make data-driven decisions.
When evaluating vendors, hospitals now emphasize service continuity as much as product quality. Manufacturers are expected to provide guaranteed parts availability, remote diagnostics, and 24/7 technical support. Multi-year service contracts with defined response times are becoming standard in tenders. XBX distinguishes itself through modular system design, allowing hospitals to upgrade specific components — such as light sources or processors — without replacing the entire setup. This flexibility significantly extends system life and reduces capital expenditure.
Procurement teams must also ensure compliance with environmental and ethical standards. Regulations such as the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and RoHS directives require traceability of materials and environmentally responsible disposal of electronic waste. Hospitals are encouraged to include sustainability scoring in vendor evaluation criteria. Manufacturers like XBX publish detailed environmental product declarations (EPDs), demonstrating carbon footprint reduction and recyclable content percentages for each model.
The global medical endoscope market is projected to surpass USD 45 billion by 2026, driven by technological innovation, aging populations, and expanded healthcare infrastructure. However, regional dynamics differ considerably, influencing procurement strategies and product preferences.
Asia-Pacific remains the fastest-growing region for medical endoscope adoption, fueled by increasing healthcare investment in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Government initiatives promoting early cancer screening and minimally invasive surgery are creating strong demand for endoscopic systems. Local manufacturers are emerging rapidly, but international brands like XBX maintain an edge through reliability, after-sales service, and regulatory expertise. Many regional distributors are partnering with OEM/ODM producers to meet custom hospital requirements at competitive prices.
North America continues to lead in advanced imaging and AI integration. Hospitals in the United States and Canada focus on upgrading from HD to 4K systems while integrating AI analytics into existing networks. The European market, on the other hand, is emphasizing environmental sustainability and data compliance under GDPR. EU hospitals now demand documented carbon reduction strategies from vendors. XBX’s European division has implemented a closed-loop recycling initiative, reclaiming used components and repurposing metals from returned devices.
In emerging markets, affordability and reliability remain the main concerns. Public hospitals prioritize durability, local service presence, and multi-functionality. Portable or battery-powered endoscopes are increasingly popular for field diagnostics and outreach programs. Organizations like the WHO are supporting these regions through grants that subsidize endoscopy equipment. To meet these demands, XBX offers scalable system configurations that combine core imaging modules with regional voltage and connectivity standards.
The next frontier in medical endoscopy lies in combining mechanical precision with intelligent imaging. Robotic-assisted endoscopy platforms are entering operating rooms, offering enhanced dexterity and control in confined anatomical spaces. Capsule endoscopy, once limited to gastrointestinal imaging, is now evolving into steerable, sensor-rich capsules capable of targeted biopsy and drug delivery.
Robotic platforms integrate 3D visualization, AI-guided movement, and haptic feedback to assist surgeons during complex procedures. These systems minimize tremor and improve ergonomics while allowing precise instrument control through micro-motors. Hospitals investing in robotic endoscopy should assess not only upfront costs but also ongoing software licensing and sterilization requirements. XBX’s research division collaborates with robotics startups to develop hybrid systems that combine flexible scopes with robotic arms for ENT and urology applications.
Wireless capsule endoscopy has evolved into a mainstream diagnostic tool for gastrointestinal disorders. The new generation of capsules features higher-resolution sensors, multi-band transmission, and AI-based localization to pinpoint lesions within the digestive tract. Integration with hospital data management platforms enables seamless review and remote consultation. In 2026, capsule endoscopy will likely expand beyond GI diagnostics into cardiology and pulmonary fields through micro-robotic advancements.
Hybrid systems that combine diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities are emerging as a practical trend. These devices allow clinicians to visualize and treat within the same session, reducing patient discomfort and procedure time. The integration of AI, robotics, and cloud analytics will define the future ecosystem of medical endoscopy. Manufacturers like XBX are actively investing in R&D partnerships with AI developers and sensor manufacturers to create interoperable, upgradeable platforms that evolve with hospital needs.
The medical endoscope industry in 2026 stands at the intersection of technology, sustainability, and clinical excellence. Hospitals and procurement teams must evaluate products not only for performance but also for long-term adaptability, cybersecurity, and environmental compliance. AI-driven diagnostics, 4K imaging, and eco-conscious design are becoming baseline expectations rather than premium features.
Brands such as XBX are redefining the role of the manufacturer — not merely as a supplier but as a strategic partner supporting hospitals through digital transformation. By prioritizing transparency, modularity, and compliance, XBX exemplifies the direction in which the entire medical endoscope industry is heading: toward smarter, safer, and more sustainable healthcare.
Hospitals that embrace these technological and operational principles will not only enhance diagnostic accuracy but also achieve long-term cost efficiency and patient trust, leading the way into a new era of minimally invasive medicine.
The most influential trends include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into endoscopic imaging, widespread 4K and ultra-HD visualization, rapid growth of disposable and eco-friendly scopes, enhanced infection control systems, and increasing attention to cybersecurity. Hospitals are also adopting lifecycle cost analysis when purchasing medical endoscopes, focusing on sustainability and long-term performance.
AI-enabled endoscopes analyze real-time video to highlight potential lesions, polyps, or abnormal tissue patterns. This reduces human error and shortens reporting time. Modern systems, such as those developed by XBX, include onboard AI processors that provide instant detection without relying on external servers, improving both speed and data security.
4K medical endoscopes deliver four times the resolution of traditional HD systems, revealing microvascular structures and subtle mucosal textures. This improves diagnostic accuracy and surgical precision. In addition, 4K systems reduce eye strain for surgeons during long operations and allow hospitals to stream and record high-quality educational content for training.
Disposable endoscopes are growing rapidly, particularly in emergency and ICU settings, due to their zero cross-contamination risk and faster turnover. However, reusable scopes still dominate in high-volume departments where total cost of ownership (TCO) is a concern. Many hospitals adopt a hybrid model, using single-use scopes for high-risk cases while maintaining reusable systems for routine procedures. XBX provides both categories, ensuring clinical flexibility and environmental responsibility.
Copyright © 2025.Geekvalue All rights reserved.Technical Support:TiaoQingCMS