Indholdsfortegnelse
Et stift ØNH-endoskop giver lige billeddannelser i høj opløsning og bruges primært i kirurgiske procedurer, mens et fleksibelt ØNH-endoskop tilbyder manøvredygtighed og komfort, hvilket gør det velegnet til diagnostiske næse- og halsundersøgelser. Begge spiller en væsentlig, men adskilt rolle i ØNH-hals- og halskirurgi, og hospitaler anskaffer ofte begge typer afhængigt af kliniske krav.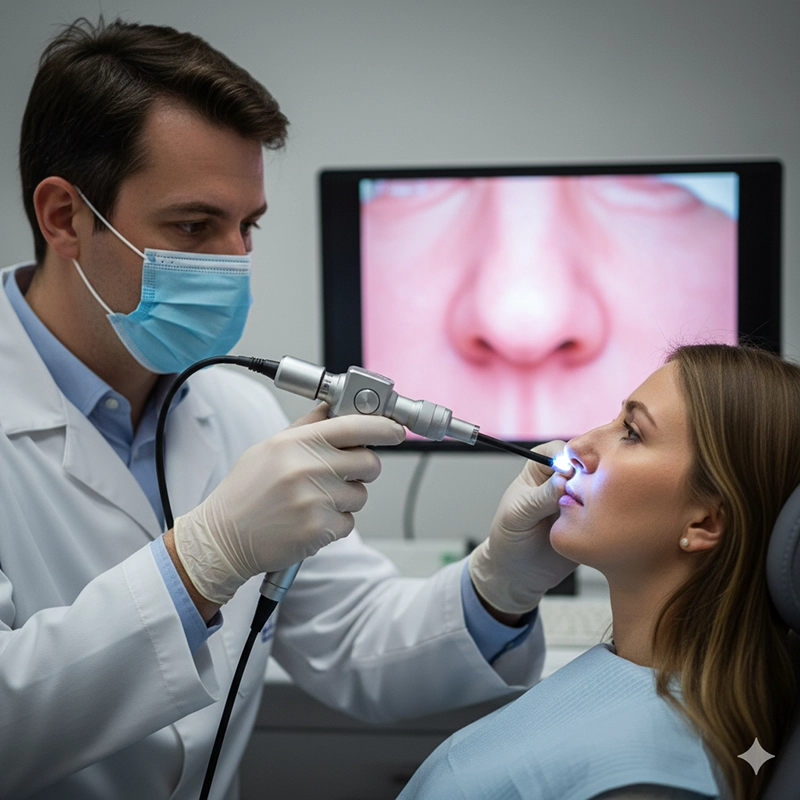
ØNH-endoskopet er et af de mest værdifulde værktøjer inden for moderne øre-næse-hals-kirurgi. Ved at tilbyde et direkte indblik i smalle anatomiske strukturer gør det det muligt for læger at udføre både diagnostiske vurderinger og terapeutiske indgreb uden store snit. Systemet består typisk af selve endoskopet, en lyskilde og i mange tilfælde et ØNH-endoskopkamera, der overfører billedet til en skærm.
Nasal endoskopi: bruges til at evaluere kronisk bihulebetændelse, næseblokering eller strukturelle afvigelser.
Diagnostisk nasal endoskopi: hjælper læger med at identificere årsager til tilbagevendende næseblod eller kronisk rhinitis.
Bihuleendoskopi: hjælper med at opdage infektioner, evaluere bihuledræning og planlægge kirurgiske tilgange.
Da disse procedurer er rutinemæssige på hospitaler og ØNH-klinikker, prioriterer indkøbsteams ØNH-endoskopudstyr, der er holdbart, brugervenligt og bakkes op af pålidelige producenter.
Et stift ØNH-endoskop er bygget af rustfrit stål med et lige skaft, der opretholder en fast vinkel. Dets konstruktion giver overlegen billedklarhed og holdbarhed, hvilket gør det uundværligt i kirurgiske procedurer.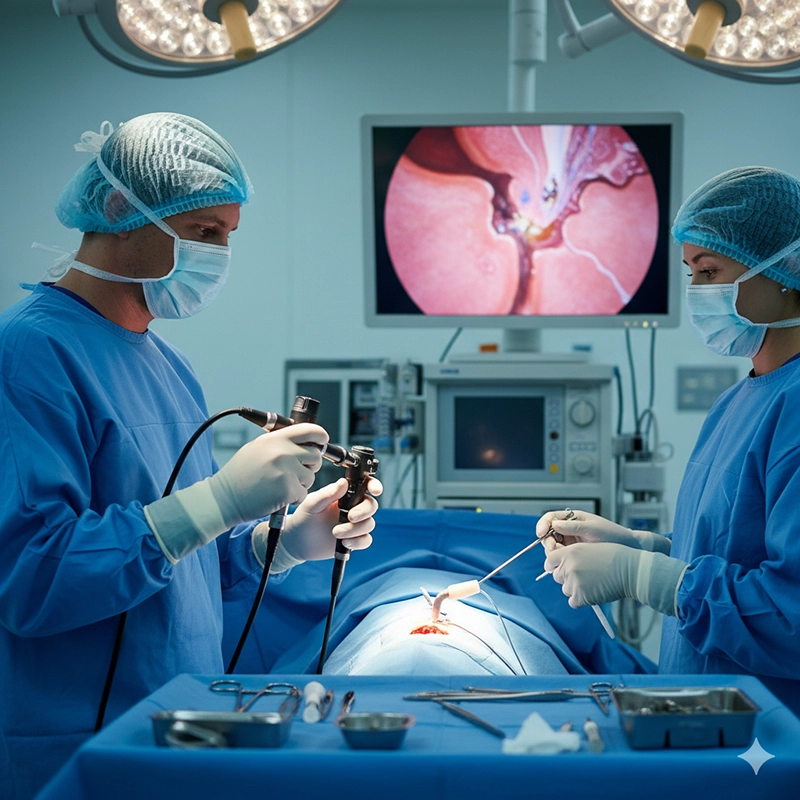
Høj optisk klarhed med flere linsesystemer, der leverer skarpe og detaljerede billeder.
Fiberoptisk belysning, der sender klart lys ind i næse- eller bihulehulen.
Størrelsesmuligheder i varierende diametre og længder for at imødekomme forskellige anatomiske områder.
Endoskopisk ØNH-kirurgi såsom funktionel endoskopisk sinuskirurgi, polypfjernelse og tumorbiopsi.
Træning og undervisning, hvor billeder i høj opløsning understøtter medicinsk uddannelse.
Robust og holdbar til mange års brug på hospitaler.
Nem sterilisering med standardautoklaver.
Relativt lavere startomkostninger sammenlignet med fleksible videosystemer.
Lavere patientkomfort ved ambulant diagnostisk brug.
Begrænset evne til at navigere i buede anatomiske strukturer.
Et fleksibelt ØNH-endoskop indeholder fiberoptik eller en digital sensor i spidsen, der gør det muligt for skaftet at bøje og navigere i kurver i næsehulen eller halsen. Dette design forbedrer patientkomforten og udvider diagnostiske muligheder.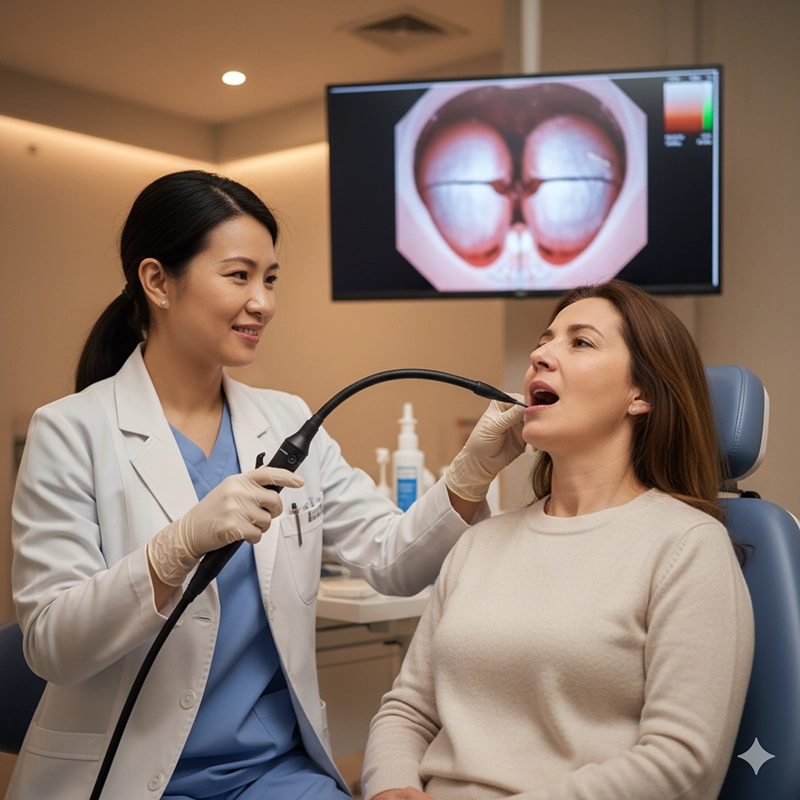
Bøjelig skaft styret af et håndtag for præcis bevægelse.
Billeddannelse via fiberbundter eller chip-on-tip sensorer til visualisering i realtid.
Bærbare formfaktorer, der er lette og kompakte.
Ambulant nasal endoskopi til vurdering af rhinitis, devieret septum og bihuledrænage.
Hals- og strubehovedundersøgelser, der muliggør evaluering af stemmebåndene under tale eller vejrtrækning.
Pædiatrisk ØNH-behandling, hvor en mindre invasiv tilgang foretrækkes.
Høj patienttolerance og reduceret ubehag.
Dynamisk evaluering af strukturer såsom stemmebånd i bevægelse.
Bærbar til brug i mindre klinikker eller sengeliggende faciliteter.
Større skrøbelighed, der kræver omhyggelig håndtering.
Potentielt lavere billedopløsning end stive kikkerter, afhængigt af optikken.
Højere vedligeholdelses- og reparationsomkostninger, især ved fiberbrud.
Den primære forskel ligger i design og anvendelse: stive endoskoper foretrækkes til kirurgi, der kræver høj præcision, mens fleksible modeller udmærker sig ved diagnostik og patientkomfort.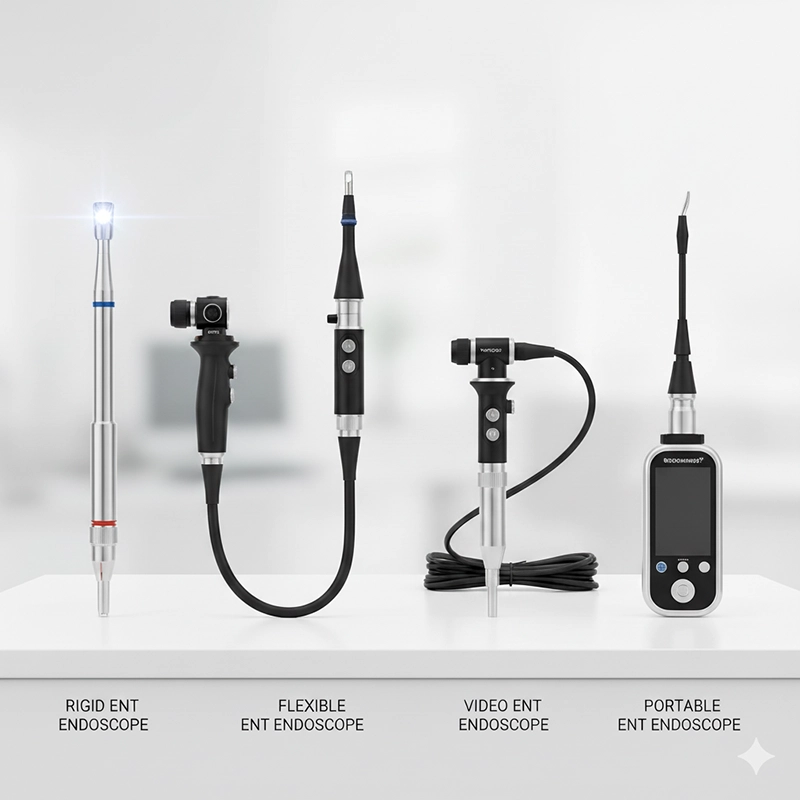
| Funktion | Stivt ØNH-endoskop | Fleksibelt ØNH-endoskop |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Lige skaft i rustfrit stål | Bøjelig, manøvrerbar skaft |
| Billedkvalitet | Høj opløsning, fremragende optisk klarhed | God klarhed; kan begrænses af fiberoptik |
| Patientkomfort | Lavere komfort, primært kirurgisk brug | Højere komfort, ideel til diagnostik |
| Sterilisering | Nem og robust | Skånsom rengøring og desinfektion kræves |
| Applikationer | Kirurgi, biopsi, træning | Næse- og halsundersøgelser, dynamiske luftvejstest |
| Prisinterval (USD) | $1,500–$3,000 | $2,500–$5,000+ |
Uanset om de er stive eller fleksible, fungerer ØNH-endoskoper inden for et bredere system af medicinsk udstyr og periferiudstyr.
ØNH-endoskopkamera til videooutput og undervisning.
Lyskilde såsom LED- eller fiberoptisk belysning.
Displayskærm til visning i realtid i klinikker og operationsstuer.
Optageudstyr til dokumentation og postoperativ analyse.
Bærbart ØNH-endoskopudstyr til opsøgende brug og mindre klinikker.
At sikre kompatibilitet mellem oscilloskoper, kameraer og lyskilder er et afgørende indkøbstrin for hospitaler.
Hospitaler afvejer prisen på ØNH-endoskoper mod funktionalitet og livscyklusomkostninger, når de planlægger indkøb.
Materialer og teknologi: Stive kikkerter bruger enklere og mere holdbare konstruktioner; fleksible kikkerter bruger avancerede fibre eller CMOS-sensorer.
Leverandørmodel: Direkte køb fra producenter kan reducere omkostningerne, mens distributører yder lokal service.
OEM- eller ODM-tilpasning: skræddersyede konfigurationer øger prisen, men forbedrer den langsigtede værdi.
Vedligeholdelse: Fleksible kikkerter kræver generelt hyppigere reparationer og omhyggelig håndtering.
Storindkøb: Hospitalnetværk kan forhandle rabatter gennem volumenkontrakter.
At tage hensyn til livscyklusomkostninger er med til at sikre, at det valgte system leverer klinisk ydeevne og værdi over tid.
Hospitalernes indkøbsteams bruger strukturerede evalueringsrammer, når de vælger ØNH-endoskopudstyr.
Hvis fokus er på endoskopisk ØNH-kirurgi, prioriteres stive ØNH-endoskoper.
For ambulante diagnostiske klinikker er fleksible ØNH-endoskoper ofte nødvendige.
Store hospitaler indkøber normalt begge dele for at sikre fuld dækning af procedurer.
Prisen på ØNH-endoskoper spiller en central rolle i indkøbsplanlægningen.
Indkøbschefer skal overveje de indledende købsomkostninger og den langsigtede vedligeholdelse.
Finansieringen kan også dække træning, forbrugsvarer og softwareintegration.
Hospitaler undersøger, om producenten af ØNH-endoskoper har certificeringer som ISO 13485, CE-mærkning eller FDA-godkendelse.
Omdømme og eftersalgsservice har betydelig indflydelse på de endelige beslutninger.
Leverandører, der tilbyder OEM/ODM-tilpasning, foretrækkes ofte af større institutioner.
Hospitaler kan udføre pilotforsøg med stive og fleksible ØNH-endoskoper for at sammenligne brugervenligheden.
Læger, sygeplejersker og biomedicinske ingeniører giver feedback om billedkvalitet, håndtering og rengøringsprocedurer.
Indkøbskontrakter inkluderer ofte serviceaftaler, garantiforlængelser og levering af reservedele.
Hospitaler søger partnerskaber frem for engangskøb for at sikre kontinuitet i servicen.

En patient med kronisk bihulebetændelse gennemgik funktionel endoskopisk bihulekirurgi (FESS). Et stift ØNH-endoskop blev valgt, fordi det gav billeder i høj opløsning, hvilket gjorde det muligt for kirurgen at identificere små polypper og fjerne dem med præcision. Det stive endoskops holdbarhed sikrede kompatibilitet med standard steriliseringsprocesser.
I et ambulant tilfælde blev en patient med tilbagevendende næseobstruktion undersøgt ved hjælp af et fleksibelt ØNH-endoskop. Det bøjelige skaft gjorde det muligt for lægen at evaluere næsepassagerne og stemmebåndene komfortabelt uden bedøvelse. Dette understregede fordelen ved fleksible endoskoper i rutinemæssig diagnostik.
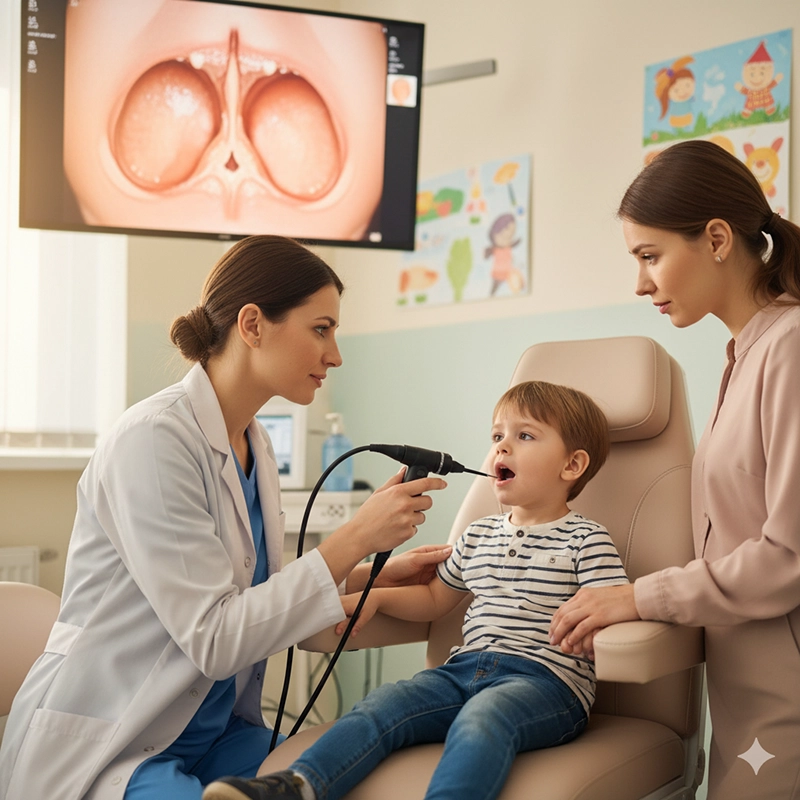
En pædiatrisk patient med mistanke om stemmebåndslammelse gennemgik fleksibel laryngoskopi. Det fleksible ØNH-endoskop muliggjorde dynamisk visualisering af stemmebåndsbevægelser, mens barnet talte, en opgave, der ville have været ubehagelig og upraktisk med et stift skop.
Disse cases illustrerer, hvordan forskellige ØNH-endoskopsystemer ikke er udskiftelige, men snarere komplementære i klinisk praksis.
HD-endoskopkameraer til øre-næse-hals-kirurgi er ved at blive standarden til både kirurgiske og diagnostiske anvendelser.
Videodokumentation understøtter medicinsk uddannelse, telemedicin og AI-assisteret diagnose.
Hospitaler i Sydøstasien, Afrika og Latinamerika investerer i ØNH-endoskopudstyr.
Lokale distributører spiller en større rolle i at levere overkommelige stive endoskoper.
Bekymringer om infektionskontrol har øget interessen for engangsskoper.
Hybridsystemer, der kombinerer stiv klarhed med fleksibel manøvredygtighed, er under udvikling.
AI-værktøjer testes for at hjælpe med at fortolke fund fra nasal endoskopi og sinusendoskopi.
Digitale sundhedsplatforme muliggør fjernkonsultation ved hjælp af ØNH-endoskopvideofeeds.
| Type | Prisinterval (USD) | Vigtigste fordele | Begrænsninger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stivt ØNH-endoskop | $1,500–$3,000 | Høj billedklarhed, holdbarhed, nem sterilisering | Mindre behagelig for patienter, begrænset navigation |
| Fleksibelt ØNH-endoskop | $2,500–$5,000+ | Manøvredygtig, høj patientkomfort, dynamisk evaluering | Skrøbelig, højere reparations- og vedligeholdelsesomkostninger |
| Video ØNH-endoskop | $5,000–$10,000+ | HD-billeddannelse, videooptagelse, avanceret undervisningsbrug | Højere initialinvestering |
| Bærbart ØNH-endoskop | $2,000–$4,000 | Letvægts, egnet til mobil brug | Begrænset billedopløsning vs. hospitalstårne |
Denne tabel fremhæver, hvordan stive modeller forbliver overkommelige, mens fleksible modeller og videomodeller er dyrere på grund af teknologisk kompleksitet.
AI-drevet diagnostik: Automatiseret genkendelse af næsepolypper, bihuleblokeringer eller unormal stemmebåndsbevægelse.
Mindre, mere bærbare enheder: For at nå klinikker i fjerntliggende områder.
Avancerede steriliseringsløsninger: Inklusive engangsskeder og fuldt engangsskoper.
Hybridsystemer: Kombinerer stiv optisk klarhed med fleksibel manøvredygtighed.
Bæredygtig produktion: Hospitaler foretrækker i stigende grad miljøvenlige leverandører.
I 2030 vil ØNH-endoskoper sandsynligvis være fuldt integreret med elektroniske patientjournaler, hvilket ikke blot vil give visualisering, men også datadrevet indsigt til præcisionsmedicin.
Købere skal inkludere oplysninger om akselfleksibilitet, billeddannelsestype (fiberoptisk eller digital), diameter, krav til arbejdskanaler og om et bærbart eller tårnbaseret ØNH-endoskopudstyrssystem foretrækkes.
Prisen for et ØNH-endoskop er angivet baseret på enhedsprisen, inkluderet tilbehør (ØNH-endoskopkamera, lyskilde, skærm), garantidækning og leveringsbetingelser. Store ordrer kan give rabat.
Ja, mange producenter af ØNH-endoskoper tilbyder OEM/ODM-tjenester. Hospitaler kan anmode om branding, tilpasset tilbehør eller integration med specifikke ØNH-endoskopkameraer og optagelsessystemer.
Typiske betingelser inkluderer levering inden for 30-60 dage, en garanti på et til tre år og valgfrie udvidede servicekontrakter. Fleksible ØNH-endoskoper kræver ofte detaljerede vedligeholdelsesaftaler på grund af højere reparationsbehov.
Ja, adskillelse af tilbud giver indkøbsteams mulighed for at sammenligne de samlede ejeromkostninger for stive og fleksible ØNH-endoskoper, inklusive tilbehør, træning og eftersalgsservice.
Ophavsret © 2025.Geekvalue Alle rettigheder forbeholdes.Teknisk support: TiaoQingCMS