Obsah
Artroskopie je minimálně invazivní chirurgická metoda používaná k diagnostice a léčbě onemocnění kloubů pomocí malé kamery zavedené do postižené oblasti, která nabízí jasný vnitřní obraz pro přesné vyšetření v nemocnicích a ortopedických klinikách.
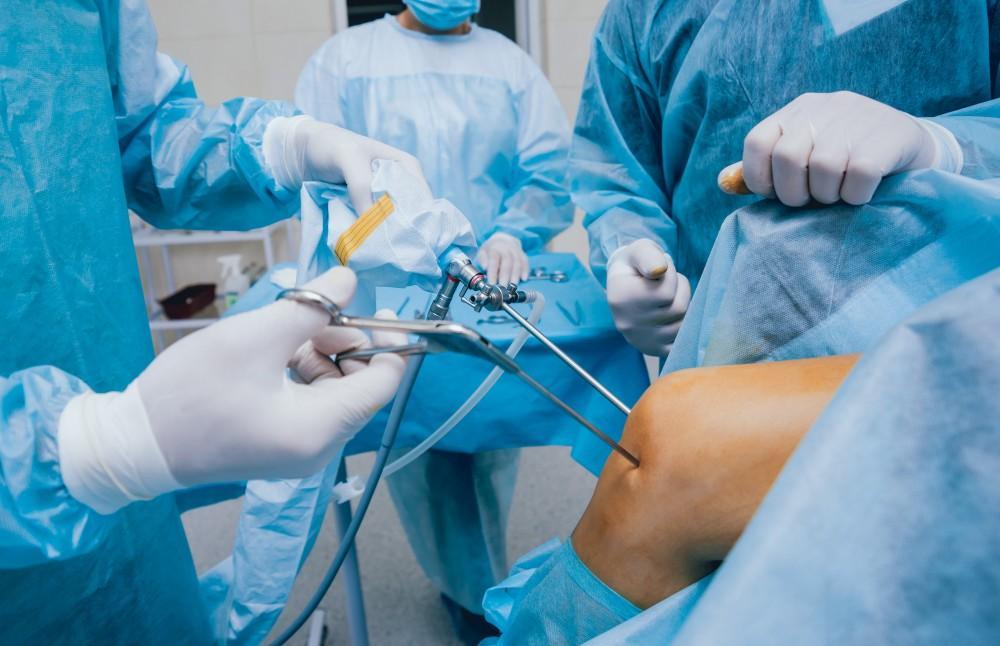
V moderní chirurgii se artroskopie vztahuje na použití tenkého, specializovaného optického přístroje známého jako artroskop. Toto zařízení se zavádí do kloubu malým řezem a jeho miniaturní kamera přenáší živé snímky s vysokým rozlišením na monitor v operačním sále.
Umožněním přímé vizualizace chrupavky, vazů a okolních tkání pomáhá artroskopie chirurgům provádět cílené zákroky s menším narušením zdravých struktur. Stala se nezbytným nástrojem ve sportovní medicíně, traumatologii a péči o degenerativní klouby.
Nástroje používané pro tyto operace se běžně vyrábějí v moderní artroskopické továrně, kde každý krok – od přesného obrábění až po optickou montáž – probíhá podle přísných norem pro zdravotnické prostředky. Renomovaní výrobci artroskopických pomůcek se zaměřují na ergonomický design, odolnost a integraci s chirurgickými zobrazovacími systémy, zatímco důvěryhodný dodavatel artroskopických pomůcek zajišťuje, aby nemocnice, distributoři a nákupní oddělení obdrželi vybavení včas a v optimálním stavu.
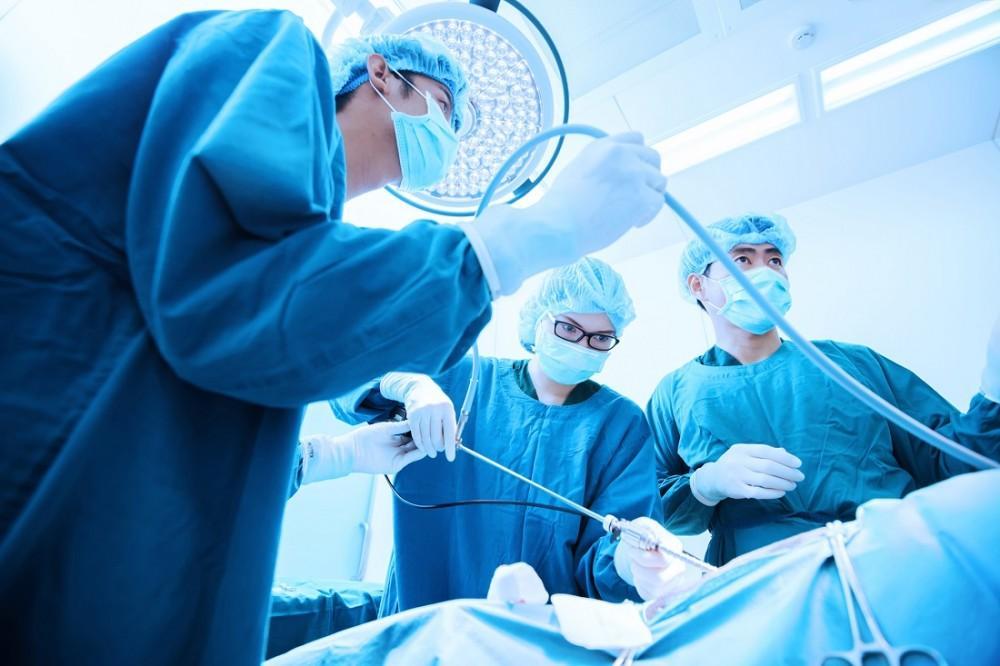
Primárním účelem artroskopie je poskytnout přesnou diagnózu a léčbu problémů s klouby bez nutnosti velkých řezů. Tato technika je obzvláště užitečná, když neinvazivní zobrazovací metody, jako je magnetická rezonance (MRI) nebo počítačová tomografie (CT), neposkytují dostatečnou jasnost obrazu.
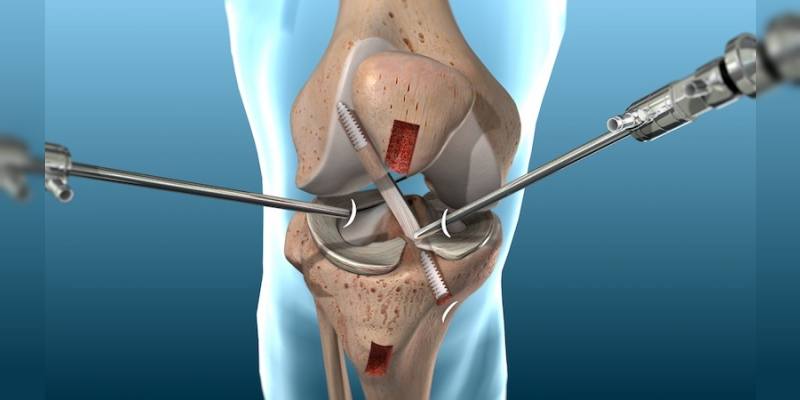
Během jediného zákroku mohou chirurgové prohlédnout vnitřek kloubu, odstranit poškozenou tkáň, opravit natržení a dokonce implantovat malé zařízení pro obnovení funkce. Tato metoda se široce používá u stavů, jako jsou poranění menisku v koleni, natržení rotátorové manžety v rameni, defekty chrupavky v kotníku a natržení labru v kyčli.
Aby nemocnice dosáhly těchto výsledků, spoléhají se na specializované vybavení od zkušeného dodavatele artroskopických zařízení. Tato zařízení se často vyrábějí ve specializovaných výrobních závodech, které používají vysoce kvalitní nerezovou ocel, lékařské polymery a pokročilé optické čočky pro zajištění přesnosti.
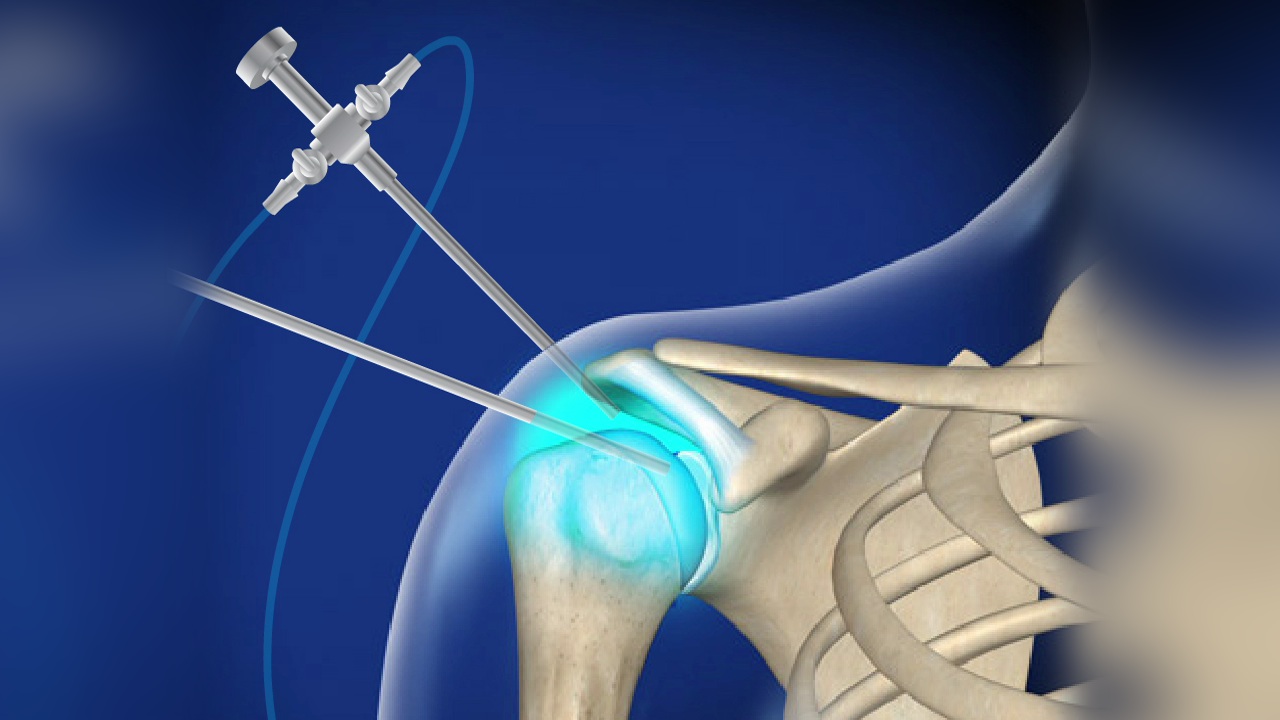
Artroskopie ramene je ve srovnání s otevřenými operacemi ramene považována za minimálně invazivní zákrok, přesto však vyžaduje odborné provedení a specializované nástroje. Během zákroku se provedou malé řezy kolem ramenního kloubu a dovnitř se zavede artroskop spolu s miniaturními chirurgickými nástroji k provedení oprav nebo odstranění poškozené tkáně.
Často se používá k řešení stavů, jako jsou poranění rotátorové manžety, kostní výrůstky, natržení labra a nestabilita ramene. Výhodou artroskopie je menší narušení okolních svalů a vazů, což může v mnoha případech vést k hladšímu pooperačnímu rekonvalescenci.
Nemocnice si vybírají vybavení od renomovaných výrobců artroskopie, protože zákroky na rameni vyžadují vizualizaci s vysokým rozlišením, systémy pro správu tekutin a přesné chirurgické nástroje. Dodavatelský řetězec řízený spolehlivou továrnou na artroskopii zajišťuje, že tyto kritické nástroje splňují mezinárodní standardy předtím, než se dostanou na operační sál.
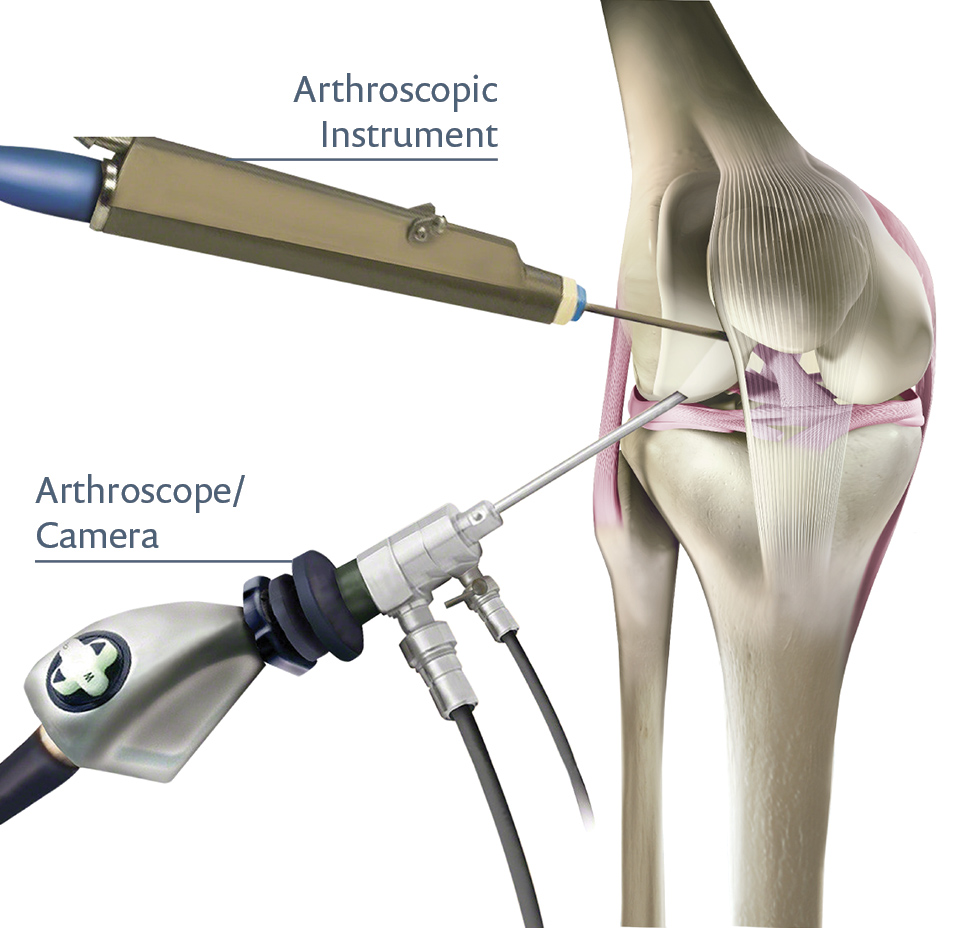
Týmy pro nákup v nemocnicích často spolupracují s přímými výrobci i se schválenými distributory, aby zajistily artroskopické systémy. Tyto systémy mohou zahrnovat kompletní věže s řídicími jednotkami kamer, světelnými zdroji, čerpadly kapalin a řadou ručních nástrojů.
Zavedený dodavatel artroskopických systémů koordinuje harmonogramy dodávek, dokumentaci k dodržování předpisů a školení chirurgických týmů v oblasti produktů. Na globálních trzích zdravotní péče se při rozhodování o zadávání veřejných zakázek zohledňují také faktory, jako je dostupnost servisní podpory, logistika náhradních dílů a kompatibilita se stávající infrastrukturou operačních sálů.
Továrny na artroskopii, které se specializují na OEM a ODM výrobu, mohou poskytovat konfigurace na míru pro nemocniční sítě, čímž zajišťují standardizaci napříč různými zařízeními a zároveň splňují regionální lékařské předpisy.
Přesné inženýrství je zásadní, protože artroskopie se spoléhá na miniaturní nástroje pracující v citlivém prostředí. I drobné vychýlení v sestavě čočky nebo výrobní vada v hrotu sondy může ovlivnit chirurgické výsledky.
Výrobci artroskopických pomůcek používají pro kovové součásti stroje s numerickým řízením (CNC), pro kalibraci čoček optické seřizovací stanice a pro montáž v čistých prostorách používají k udržení sterility. Kontroly kvality zahrnují testování odolnosti, posouzení čistoty obrazu a ověření těsnosti součástí pro manipulaci s tekutinami.
Spolehlivý dodavatel artroskopických pomůcek přidává další vrstvu jistoty prováděním kontrol před odesláním, ověřováním neporušenosti obalů a zajištěním doručení produktů bez kontaminace nebo fyzického poškození.
Pokroky v zobrazovacích technologiích proměnily artroskopii z diagnostického nástroje v komplexní chirurgické řešení. Kamery s vysokým rozlišením a 4K nyní umožňují bezprecedentní jasnost i těch nejmenších anatomických struktur. Některé systémy integrují algoritmy umělé inteligence, které chirurgům pomáhají identifikovat jemné abnormality tkání.
Moderní artroskopické továrny začleňují tyto prvky do svých zařízení, což nemocnicím umožňuje zavádět nejnovější techniky minimálně invazivní péče. Například osvětlení optickými vlákny zlepšuje viditelnost v kloubních prostorech se slabým osvětlením, zatímco úzkopásmové zobrazování může zlepšit diferenciaci tkání.
Výrobci artroskopických zařízení také zkoumají bezdrátový přenos videa pro flexibilnější uspořádání operačních sálů a dodavatelé zajišťují, aby tato zařízení splňovala bezpečnostní certifikace před distribucí do nemocnic a center pro lékařské zakázky po celém světě.
Kromě poskytování vybavení dodavatel artroskopického vybavení často slouží zdravotnickým zařízením jako strategický partner. To zahrnuje nabídku technického školení, koordinaci zkoušek produktů a poskytování podpory na místě během počátečního nasazení.
Pro velké nemocniční skupiny nebo národní zadávací agentury mohou dodavatelé také spravovat programy zásobování, čímž zajistí, aby byly základní artroskopické nástroje skladem a připraveny k plánovaným operacím. Tento proaktivní přístup minimalizuje zpoždění a optimalizuje alokaci zdrojů mezi zařízeními.
Shoda s předpisy začíná výběrem surovin – používají se pouze certifikované slitiny a polymery lékařské kvality. Výroba se řídí normami řízení kvality ISO 13485 a produkty často vyžadují další certifikaci, jako je označení CE pro Evropu nebo schválení FDA pro Spojené státy.
Každá šarže prochází před opuštěním zařízení funkčním testováním, vizuální kontrolou a ověřením sterility. Tento přísný proces zajišťuje, že každý artroskop, sonda a chirurgické příslušenství jsou bezpečné a spolehlivé. Nemocnice těží z této pozornosti k detailům, protože podporuje konzistentní chirurgický výkon a dlouhodobou životnost zařízení.
Oblast minimálně invazivní chirurgie se rychle vyvíjí a chirurgové hledají nástroje, které jsou menší, ergonomičtější a schopné integrace s jinými lékařskými systémy. Výrobci artroskopických pomůcek reagují na tyto potřeby investicemi do výzkumných a vývojových týmů, které úzce spolupracují se zdravotnickými pracovníky.
Mezi vylepšení může patřit návrh modulárních sad přístrojů pro vícekloubové aplikace, vývoj efektivnějších zavlažovacích systémů nebo vylepšení kamerových senzorů pro lepší výkon za slabého osvětlení. Inovace plynoucí z tohoto úsilí v konečném důsledku prospívají nemocnicím, klinikám i pacientům.
Hodnocení obvykle zahrnuje kontrolu technické dokumentace, provedení praktických zkoušek a shromažďování zpětné vazby od zkušených chirurgických týmů. Pracovníci zadávacího řízení si mohou od dodavatele artroskopie vyžádat živé ukázky, aby posoudili jasnost obrazu, pohodlí násadce a kompatibilitu se stávajícím vybavením operačního sálu.
Nemocnice začínají zkoumáním podrobné dokumentace k produktu, včetně hodnocení rozlišení, specifikací čoček, složení materiálu a kompatibility se sterilizací. Certifikace jako ISO 13485, označení CE a schválení FDA pomáhají ověřit, zda zařízení splňuje mezinárodní bezpečnostní a výkonnostní standardy.
Chirurgické týmy mohou požádat o zkušební použití artroskopických systémů v reálných postupech nebo simulačních laboratořích. Tyto zkoušky poskytují přímý vhled do toho, jak zařízení fungují v reálných podmínkách, a odhalují potenciální ergonomické nebo funkční výhody.
Biomedicínští inženýři vyhodnocují, jak snadno lze nástroje čistit, sterilizovat a udržovat. Zařízení navržená s modulárními komponenty a materiály odolnými proti korozi obvykle zkracují prostoje a prodlužují životnost.
Pracovníci zadávacího řízení často do rozhodovacího procesu zapojují ortopedické chirurgy, ošetřovatele a technický personál. Tím je zajištěno, že snadnost provozu, kvalita obrazu a pohodlí při manipulaci jsou zohledněny ze všech hledisek.
Některé nemocnice do výběrového procesu zapojují také biomedicínské inženýry, aby zajistily, že zařízení splňují požadavky na údržbu a sterilizaci. Dlouhodobá partnerství se spolehlivými dodavateli a renomovanými výrobci pomáhají udržovat konzistentní kvalitu napříč různými cykly zadávání zakázek.
Artroskopie změnila podobu ortopedické a sportovní medicíny tím, že umožnila přesné, minimálně invazivní operace kloubů. Tento pokrok je udržován společným úsilím zkušených výrobců artroskopických produktů, vysoce kvalitních továren na artroskopické produkty a spolehlivých dodavatelů artroskopických produktů, kteří slouží nemocnicím, distributorům a klientům v oblasti B2B nákupu po celém světě. Společnost XBX je i nadále odhodlána poskytovat pokročilá řešení, která podporují vyvíjející se potřeby globální lékařské komunity.
Nemocnice obvykle vyžadují, aby výrobci artroskopických nástrojů měli certifikát ISO 13485, označení CE a schválení FDA, aby bylo zajištěno, že chirurgické nástroje splňují bezpečnostní a kvalitativní standardy.
Ano, mnoho dodavatelů a výrobců artroskopických nástrojů podporuje úpravy OEM/ODM, což umožňuje nemocnicím požadovat řídicí jednotky kamer na míru, čerpadla tekutin nebo ergonomické ruční nástroje.
Spolehlivý výrobce artroskopických zařízení zajišťuje interoperabilitu integrací standardních chirurgických zobrazovacích protokolů, nastavení pro správu tekutin a architektury operačního sálu již během návrhu a testování.
Artroskopie je minimálně invazivní chirurgický zákrok, který umožňuje lékařům vyšetřovat klouby pomocí malé kamery a nástrojů. Nemocnice si jí cení, protože zkracuje dobu rekonvalescence a zlepšuje přesnost diagnostiky.
Nejčastěji se artroskopie provádí na koleni a rameni, ale artroskopie může být použita i na kyčli, kotníku, zápěstí a lokti k léčbě sportovních zranění nebo onemocnění kloubů.
Na rozdíl od otevřené operace vyžaduje artroskopie pouze malé řezy. To znamená menší poškození tkáně, nižší riziko infekce, rychlejší rehabilitaci a kratší dobu hospitalizace.
Moderní artroskopy nabízejí zvětšené a vysoce kvalitní zobrazení chrupavky, vazů a synoviální membrány, což chirurgům pomáhá odhalit drobná natržení nebo poškození, která se nemusí objevit na rentgenových snímcích nebo magnetické rezonanci.
Systémy obvykle obsahují světelné zdroje, irigační čerpadla, řídicí jednotky kamery a chirurgické nástroje určené pro opravu kloubů nebo odběr vzorků tkání.
Autorská práva © 2025.Geekvalue Všechna práva vyhrazena.Technická podpora: TiaoQingCMS